Difference In Hmo And Ppo
Navigating the complex landscape of health insurance plans can be daunting, especially when faced with the myriad of acronyms and terminology that define different types of coverage. Two of the most common types of health insurance plans are Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) and Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) plans. Understanding the differences between HMO and PPO plans is crucial for choosing the health insurance coverage that best suits your needs and budget.
Introduction to HMO Plans
HMO plans are designed to provide healthcare services to members at a lower cost than traditional insurance plans. The core principle behind HMOs is to emphasize preventive care and early intervention to reduce the need for costly medical procedures. HMOs achieve this by creating a network of healthcare providers who agree to offer their services at discounted rates to plan members. In exchange, these providers receive a steady stream of patients and are often paid a fixed fee per patient, regardless of the actual number or nature of services provided.
One of the defining characteristics of HMO plans is the requirement for members to receive medical care and services from providers within the specified network, except in emergency situations. Members typically choose a primary care physician (PCP) from within the network, who acts as a gateway to other medical services. Referrals from the PCP are often necessary to see specialists within the network.
Introduction to PPO Plans
PPO plans offer more flexibility than HMO plans, allowing members to receive care from any healthcare provider, both in and out of the network. This flexibility comes at a cost, as members typically pay more for services received from out-of-network providers. Like HMOs, PPOs negotiate discounted rates with a network of healthcare providers. However, members are not required to choose a PCP or obtain referrals to see specialists.
The freedom to choose any healthcare provider is a significant advantage of PPO plans, especially for those who value the ability to consult with specialists without needing a referral. Additionally, PPO plans often provide some level of coverage for out-of-network care, although at a higher cost to the member.
Key Differences
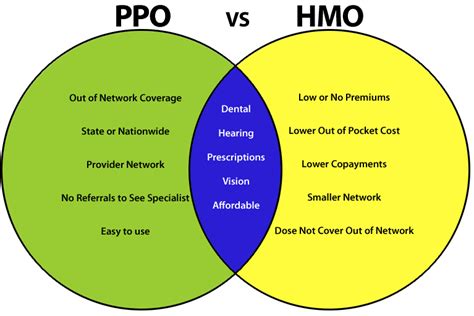
- Network Restrictions: HMO plans are more restrictive, requiring members to use providers within the network for non-emergency care, while PPO plans offer the flexibility to see any provider, in or out of network, albeit often at different costs.
- Primary Care Physician (PCP) and Referrals: HMO members typically need to select a PCP and may require referrals to see specialists, whereas PPO members do not need a PCP or referrals to access specialist care.
- Cost: HMO plans are often less expensive than PPO plans, both in terms of premiums and out-of-pocket costs, due to the network restrictions and emphasis on preventive care.
- Out-of-Network Coverage: PPO plans usually offer some coverage for out-of-network care, although at a higher cost to the member, while HMO plans generally do not cover out-of-network care except in emergencies.
- Flexibility and Choice: PPO plans provide more flexibility and choice in terms of healthcare providers, which can be valuable for individuals who have established relationships with healthcare providers outside of a particular network.
Choosing Between HMO and PPO Plans
The choice between an HMO and a PPO plan depends on several factors, including your personal preferences regarding healthcare, your budget, and your health needs. If cost is a significant concern and you are willing to work within a network of providers, an HMO might be the more economical choice. On the other hand, if flexibility and the ability to see any healthcare provider without restrictions are more important, a PPO plan might be preferable, despite potentially higher costs.
Ultimately, understanding the nuances of HMO and PPO plans can help you make an informed decision that aligns with your healthcare needs and financial situation. Whether you prioritize cost savings, flexibility, or comprehensive coverage, there is a health insurance plan designed to meet your requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between HMO and PPO health insurance plans?
+The main difference lies in the flexibility to choose healthcare providers. HMO plans require members to receive care from providers within the network, except in emergencies, while PPO plans allow members to see any healthcare provider, with more comprehensive coverage for in-network care.
Do HMO plans cover out-of-network care?
+Generally, HMO plans do not cover out-of-network care except in emergency situations. This is a key distinction from PPO plans, which offer some level of coverage for out-of-network care, although typically at a higher cost to the member.
Which type of plan is usually more cost-effective?
+HMO plans are often more cost-effective, offering lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs compared to PPO plans. This is due to the negotiated rates with in-network providers and the emphasis on preventive care.
Can I see a specialist without a referral in a PPO plan?
+Yes, one of the advantages of PPO plans is the ability to see specialists without needing a referral from a primary care physician. This flexibility is not typically available in HMO plans.
How do I choose between an HMO and a PPO plan?
+The choice between an HMO and a PPO plan should be based on your personal healthcare needs, budget, and preferences regarding provider flexibility. Consider factors such as cost, the need for specialist care, and your willingness to work within a provider network.
In conclusion, while both HMO and PPO plans have their advantages and disadvantages, the right choice for you will depend on your individual circumstances, including your health needs, financial situation, and personal preferences regarding healthcare flexibility. By understanding the differences and considering your unique situation, you can make an informed decision that ensures you have the right health insurance coverage for your well-being.