Dupuytren's Surgery: Effective Treatment For Contracture Relief
Dupuytren’s contracture is a debilitating condition that affects the palmar fascia, a layer of tissue beneath the skin of the palm. It causes one or more fingers to bend into the palm, leading to significant restrictions in hand function and daily activities. While mild cases may be managed with conservative treatments, severe contractures often require surgical intervention to restore finger mobility and alleviate symptoms. Dupuytren’s surgery has emerged as a highly effective treatment option for contracture relief, offering individuals suffering from this condition a chance to regain control over their hands and improve their quality of life.
Understanding Dupuytren’s Contracture
Before delving into the specifics of Dupuytren’s surgery, it’s essential to understand the condition itself. Dupuytren’s contracture is characterized by the formation of nodules and thickened cords within the palmar fascia, which gradually tighten and pull the fingers toward the palm. This process can occur over several years, causing increasing disability. The exact cause of Dupuytren’s contracture remains unknown, but it is associated with genetic predisposition, age, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes and alcoholism.
Surgical Options for Dupuytren’s Contracture
Several surgical techniques are available for treating Dupuytren’s contracture, each with its indications, advantages, and potential complications. The choice of surgery depends on the severity of the contracture, the affected fingers, and the patient’s overall health. The primary surgical options include:
Fasciectomy: This is the most common surgical procedure for Dupuytren’s contracture, involving the removal of the affected palmar fascia. It can be partial (removing only the diseased tissue) or total (removing the entire palmar fascia). Fasciectomy is highly effective in correcting the contracture but carries a risk of recurrence.
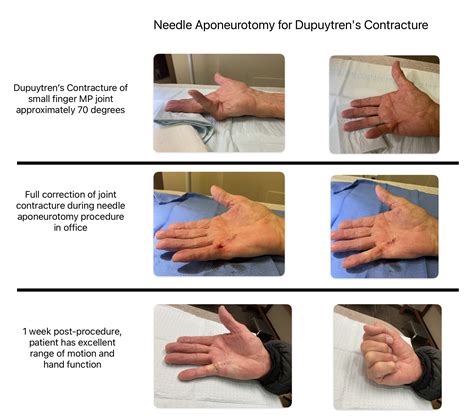
Needle Aponeurotomy (NA): NA is a less invasive procedure where a needle is used to puncture and cut the thickened cords. It’s often preferred for patients with milder contractures or those seeking a quicker recovery. However, NA may not be as long-lasting as fasciectomy and can be associated with a higher risk of recurrence.
Collagenase Injections: This involves injecting collagenase, an enzyme that breaks down collagen, directly into the cord. After injection, the patient returns in 1-3 days for manipulation of the treated finger to break the cord. Collagenase injection is a minimally invasive option with a relatively quick recovery but may require multiple injections and has specific indications.
Preparing for Dupuytren’s Surgery
Preparation is crucial for a successful surgical outcome. Patients should:
- Attend Pre-Surgical Consultations: Detailed discussions with the surgeon about the procedure, including its benefits, risks, and what to expect post-operatively.
- Undergo Pre-Surgical Tests: As required by the surgeon or anesthesiologist to ensure the patient is fit for surgery.
- Plan for Recovery: Understand the recovery process, including necessary exercises, follow-up appointments, and any modifications needed at home to facilitate healing.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
The recovery period for Dupuytren’s surgery varies depending on the surgical technique and the individual’s health. Generally, patients can expect:
- Immediate Post-Surgery: Pain, swelling, and bandaging of the hand. Pain management and wound care instructions are provided by the healthcare team.
- Early Rehabilitation: Gentle exercises to maintain finger mobility, starting as early as a few days post-surgery.
- Wound Healing: Typically takes a few weeks, during which time the patient must keep the wound clean and dry.
- Full Recovery: Can take several months, with a gradual return to normal activities. It’s crucial to follow the rehabilitation program to achieve the best possible outcomes and minimize the risk of complications.
Potential Complications and Considerations
While Dupuytren’s surgery is effective, it’s not without risks. Potential complications include infection, nerve or blood vessel damage, and recurrence of the contracture. The risk of complications can be minimized by choosing an experienced surgeon and strictly adhering to post-operative instructions.
Conclusion
Dupuytren’s surgery offers a viable solution for individuals suffering from severe contractures, providing significant relief and improvement in hand function. By understanding the condition, the available surgical options, and what to expect from the treatment process, patients can make informed decisions about their care. It’s essential to approach Dupuytren’s contracture treatment with a comprehensive understanding of the potential benefits and risks, ensuring the best possible outcome for those affected by this condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary causes of Dupuytren’s contracture?
+Dupuytren’s contracture is associated with genetic predisposition, age, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes and alcoholism. The exact cause remains unknown, but these factors increase the risk of developing the condition.
How long does it take to recover from Dupuytren’s surgery?
+Recovery from Dupuytren’s surgery can vary but generally takes several months. Immediate post-surgery care involves managing pain and wound care, followed by a rehabilitation program to regain hand function and mobility.
Can Dupuytren’s contracture recur after surgery?
+Yes, recurrence is a potential complication of Dupuytren’s surgery. The risk varies depending on the surgical technique and individual factors. Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider can help monitor for signs of recurrence.
What are the non-surgical treatments for Dupuytren’s contracture?
+Non-surgical treatments include observation for mild cases, physical therapy to maintain finger mobility, and injections such as collagenase or steroids to help break down the cord. These treatments are typically considered for patients with early-stage or mild contractures.
How do I choose the best surgical option for my Dupuytren’s contracture?
+Choosing the best surgical option involves consulting with a experienced surgeon who can evaluate the severity of your contracture, discuss your overall health and preferences, and recommend the most appropriate procedure based on your individual needs.