Ear Pe Tube Guide: Insertion To Recovery
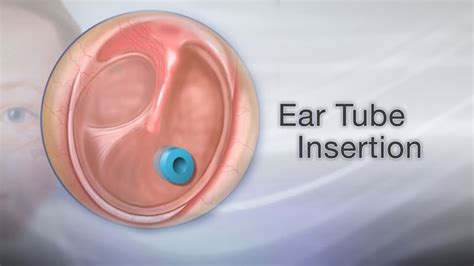
The insertion of ear tubes, also known as tympanostomy tubes, is a common surgical procedure used to treat recurring ear infections, persistent fluid buildup in the middle ear, and hearing loss due to these conditions. This guide will walk you through the process, from preparation to recovery, highlighting key aspects of the procedure, its benefits, and what to expect post-surgery.
Understanding Ear Tubes
Ear tubes are small, cylindrical devices made of metal or plastic that are surgically inserted into the eardrum to drain fluid from the middle ear. They come in different types, including short-term tubes that fall out on their own after 6-18 months and long-term tubes that may need to be removed by a doctor. The primary goal of ear tubes is to alleviate the pressure caused by fluid accumulation, reduce the risk of infection, and restore normal hearing.
Preparation for Ear Tube Insertion
Preparation for the procedure is crucial for a smooth and successful surgery. Here are some key steps:
- Pre-operative Consultation: Before the surgery, a consultation with an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist or an otolaryngologist is essential. This visit allows the doctor to examine the ears, discuss the procedure, and answer any questions you or your child may have.
- Medical History and Current Medications: It’s vital to share your or your child’s complete medical history, including any allergies, previous surgeries, and current medications. Some medications, such as blood thinners, may need to be paused before surgery.
- Day of Surgery Instructions: Typically, you’ll be asked not to eat or drink anything for a certain period before the surgery. This is to ensure your stomach is empty, reducing the risk of complications during anesthesia.
The Procedure
The insertion of ear tubes is usually performed under general anesthesia to ensure comfort and safety, especially in young children. The procedure is relatively quick:
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is administered, and once it takes effect, the procedure begins.
- Incision: A small incision is made in the eardrum, and any fluid is suctioned out.
- Tube Insertion: The ear tube is then carefully inserted through the incision into the middle ear.
- Verification: The doctor may perform a tympanometry test to verify the tube’s position and that the eardrum is functioning properly.
- Recovery: After the procedure, you’ll be taken to a recovery room where the anesthesia will wear off. This process usually takes about 30 minutes to an hour.
Post-Surgery Care and Recovery
Proper care after ear tube insertion is essential for a smooth recovery and to minimize the risk of complications:
- Pain Management: Mild pain or discomfort is common but can usually be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers as directed by your doctor.
- Follow-Up Appointment: A follow-up visit with your ENT specialist is crucial to check on the healing progress and the function of the ear tubes.
- Ear Drops: Your doctor may prescribe antibiotic ear drops to prevent infection.
- Avoidance of Water: It’s often recommended to avoid submerging the head in water (such as swimming or bathing) for a period to prevent water from entering the ear canal. However, showering is usually acceptable.
- Monitoring for Infection: Keep an eye out for signs of infection, such as fever, discharge, or increased pain, and contact your doctor if you notice any of these symptoms.
Benefits of Ear Tubes
The benefits of ear tubes are numerous, especially for children who suffer from recurring ear infections or persistent middle ear fluid:
- Reduced Infection Risk: By draining fluid from the middle ear, ear tubes significantly reduce the risk of further infections.
- Improved Hearing: Fluid buildup can cause hearing loss. Ear tubes help restore normal hearing by allowing the eardrum to move freely.
- Decreased Pressure: The accumulation of fluid can cause discomfort and pressure. Ear tubes alleviate this pressure, providing relief.
Potential Complications
While ear tube insertion is generally a safe procedure, there are potential complications to be aware of:
- Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there’s a risk of infection. This can usually be treated with antibiotics.
- Scarring: There may be minimal scarring on the eardrum, but this rarely affects hearing.
- Tube Blockage or Displacement: Sometimes, ear tubes can become clogged or fall out prematurely. In such cases, additional surgery may be needed.
Conclusion
The insertion of ear tubes is a straightforward and effective way to treat common ear problems, offering significant benefits in terms of reducing infections, improving hearing, and alleviating discomfort. By understanding the procedure, its benefits, and the necessary post-operative care, you can navigate this process with confidence, ensuring the best possible outcome for yourself or your child.
How long does the ear tube insertion procedure take?
+The procedure itself is relatively quick, typically lasting about 15-30 minutes. However, preparation and recovery time can add another couple of hours to the overall process.
Can adults get ear tubes?
+Yes, while ear tube insertion is more common in children, adults can also benefit from the procedure, especially if they suffer from recurring ear infections or persistent fluid buildup in the middle ear.
How do I know if my child needs ear tubes?
+Your child may need ear tubes if they experience recurring ear infections (more than 3 in 6 months or 4 in a year), persistent fluid buildup in the middle ear that doesn’t clear up after 3 months, or significant hearing loss due to these conditions. Consult with an ENT specialist for an accurate diagnosis and recommendation.



