Effusion Shoulder Joint: Relieve Pain Now
The shoulder joint, a complex and multifaceted system, is susceptible to various afflictions, one of which is the effusion shoulder joint. This condition, characterized by the accumulation of excess fluid within the shoulder joint, can lead to significant discomfort, pain, and limited mobility. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for effusion shoulder joint is crucial for individuals seeking to alleviate their suffering and restore optimal function to their shoulders.
Causes of Effusion Shoulder Joint
The effusion shoulder joint can result from a variety of factors, including injuries, inflammatory conditions, and infections. Trauma to the shoulder, such as fractures or dislocations, can cause inflammation and lead to fluid accumulation. Similarly, conditions like arthritis, bursitis, and tendinitis, which affect the tendons and joints, can also contribute to the development of an effusion shoulder joint. Infections, though less common, can also lead to this condition by causing inflammation and fluid buildup as the body attempts to fight off the infectious agent.
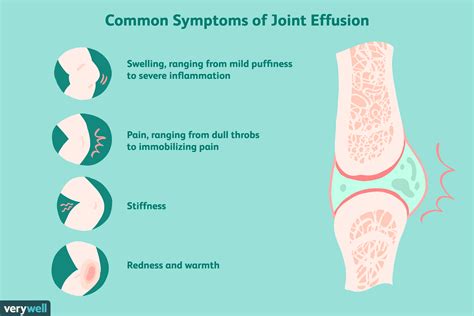
Symptoms of Effusion Shoulder Joint
Recognizing the symptoms of an effusion shoulder joint is essential for prompt diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include pain, which can range from mild to severe and is typically exacerbated by movement or pressure on the joint. Swelling and redness around the shoulder area are also indicative of an effusion, as they signify inflammation. Reduced mobility and stiffness in the shoulder are additional symptoms, as the excess fluid can cause the joint to feel tight and less flexible. In some cases, individuals may experience a sensation of warmth or heat around the affected area due to increased blood flow associated with inflammation.
Diagnostic Approaches
Diagnosing an effusion shoulder joint involves a combination of physical examination, medical history review, and imaging studies. A healthcare provider will typically begin by assessing the patient’s symptoms and performing a physical examination to evaluate shoulder mobility and check for signs of swelling or redness. Imaging tests, such as X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), may be ordered to confirm the presence of excess fluid and to rule out other potential causes of symptoms, such as fractures or tears in the tendons or ligaments.
Treatment Options
The treatment of an effusion shoulder joint is tailored to the underlying cause and severity of the condition. For mild cases, conservative management may suffice, including rest, ice application to reduce swelling, compression with a bandage to help reduce fluid accumulation, and elevation of the affected arm to reduce swelling. Over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications can also be recommended to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
In cases where conservative measures are insufficient or the condition is more severe, further interventions may be necessary. Aspiration of the fluid under sterile conditions can provide relief and help in diagnosing the cause through fluid analysis. Physical therapy is another crucial component, aimed at maintaining or improving joint mobility and strength. For chronic or recurrent cases, particularly those resulting from conditions like arthritis, management of the underlying condition is paramount, which may involve more specific medications or, in some instances, surgical intervention to address structural issues contributing to the effusion.
Preventive Measures
Preventing the occurrence or recurrence of an effusion shoulder joint involves maintaining overall shoulder health. Engaging in regular exercises that strengthen the muscles around the shoulder can help stabilize the joint and reduce the risk of injury. Proper warm-up and cool-down routines during physical activities, avoiding repetitive strain on the shoulder, and maintaining good posture can also mitigate risks. For individuals with pre-existing conditions like arthritis, adhering to the treatment plan and making lifestyle adjustments as recommended by healthcare providers can help manage symptoms and prevent complications like effusion.
Conclusion
The effusion shoulder joint, while potentially debilitating, can be effectively managed with appropriate diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and pursuing medical evaluation are critical steps towards alleviating pain and restoring function. By combining medical interventions with preventive strategies, individuals can work towards maintaining healthy shoulders and reducing the risk of future complications.
What are the primary causes of an effusion shoulder joint?
+The primary causes of an effusion shoulder joint include injuries such as fractures or dislocations, inflammatory conditions like arthritis or bursitis, and infections. These conditions lead to inflammation and fluid buildup within the shoulder joint.
How is an effusion shoulder joint diagnosed?
+Diagnosis involves a physical examination, review of medical history, and imaging studies such as X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI to confirm the presence of excess fluid and rule out other causes of symptoms.
What are the treatment options for an effusion shoulder joint?
+Treatment options range from conservative management with rest, ice, compression, elevation, and pain relievers, to more invasive procedures like fluid aspiration and physical therapy. In chronic cases, managing the underlying condition and considering surgical intervention may be necessary.
In conclusion, addressing an effusion shoulder joint requires a comprehensive approach that includes understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and pursuing appropriate medical interventions. By adopting preventive strategies and adhering to treatment plans, individuals can mitigate the discomfort and dysfunction associated with this condition, ultimately working towards healthier, more resilient shoulders.



