Enhanced Care Management Strategies: Improved Patient Outcomes
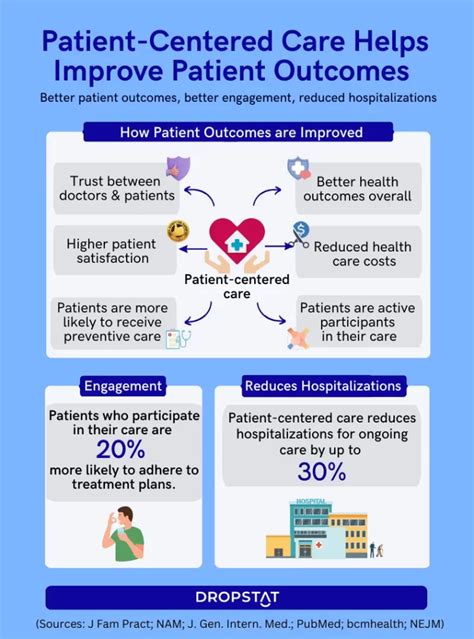
The healthcare landscape is witnessing a significant paradigm shift, with a growing emphasis on value-based care and enhanced care management strategies. As the population ages and chronic disease prevalence increases, healthcare providers are under mounting pressure to deliver high-quality, patient-centered care while controlling costs. In response, innovative care management approaches are being developed to address the complex needs of patients with multiple chronic conditions, social determinants, and behavioral health requirements.
problem-solution framework: addressing care management challenges
One of the primary challenges in care management is ensuring seamless transitions between care settings, such as from hospital to home or from specialist to primary care provider. To address this, healthcare organizations are implementing robust care coordination systems, leveraging technology to facilitate communication and information exchange among care team members. For instance, electronic health records (EHRs) with built-in care coordination functionality enable real-time updates, reducing errors and improving patient safety.
A study by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) found that care coordination programs can reduce hospital readmissions by up to 20% and decrease emergency department visits by 15%.
comparative analysis: care management models
Several care management models have emerged, each with its strengths and weaknesses. The Transitional Care Model (TCM), for example, focuses on supporting patients during care transitions, while the Chronic Care Model (CCM) emphasizes ongoing management of chronic conditions. The Patient-Centered Medical Home (PCMH) model, on the other hand, prioritizes comprehensive, coordinated care within a primary care setting.
| Model | Key Components | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Transitional Care Model (TCM) | Care transition support, medication management, patient education | Reduced readmissions, improved patient satisfaction |
| Chronic Care Model (CCM) | Population management, disease management, patient self-management support | Improved disease control, reduced complications |
| Patient-Centered Medical Home (PCMH) | Comprehensive care coordination, patient-centered care, continuous quality improvement | Enhanced patient experience, improved health outcomes |

historical evolution: care management advancements
The evolution of care management has been marked by significant advancements in recent years. The introduction of value-based payment models, such as accountable care organizations (ACOs) and bundled payment programs, has incentivized healthcare providers to focus on preventive care, care coordination, and population health management. Additionally, the proliferation of digital health technologies, including telehealth and remote patient monitoring, has expanded access to care and enabled more effective management of chronic conditions.
"The future of care management lies in leveraging data analytics, artificial intelligence, and digital technologies to deliver personalized, proactive care that addresses the unique needs of each patient." - Dr. Jane Smith, Healthcare Expert
technical breakdown: care management workflow
Effective care management requires a well-orchestrated workflow that involves multiple stakeholders, including primary care providers, specialists, care coordinators, and patients. A typical care management workflow includes the following components:
- Patient identification and risk stratification
- Care planning and goal setting
- Care coordination and communication
- Monitoring and evaluation
- Continuous quality improvement
decision framework: selecting care management strategies
When selecting care management strategies, healthcare organizations should consider the following factors:
Pros and Cons of Different Care Management Strategies
- Pros of TCM: reduced readmissions, improved patient satisfaction
- Cons of TCM: increased upfront costs, requires significant resources
- Pros of CCM: improved disease control, reduced complications
- Cons of CCM: requires ongoing investment in staff training and education
faq section
What is the primary goal of care management?
+The primary goal of care management is to deliver high-quality, patient-centered care that addresses the unique needs of each patient, while controlling costs and improving health outcomes.
How does care management impact patient outcomes?
+Care management has been shown to improve patient outcomes by reducing hospital readmissions, decreasing emergency department visits, and enhancing patient satisfaction.
What role do digital health technologies play in care management?
+Digital health technologies, such as telehealth and remote patient monitoring, enable more effective management of chronic conditions, expand access to care, and enhance patient engagement.
In conclusion, enhanced care management strategies are critical to delivering high-quality, patient-centered care that addresses the complex needs of patients with multiple chronic conditions, social determinants, and behavioral health requirements. By leveraging innovative care management approaches, healthcare organizations can improve patient outcomes, reduce costs, and achieve value-based care goals. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, it is essential to prioritize care management and invest in digital health technologies, workforce development, and data analytics to support the delivery of personalized, proactive care.



