Epididymal Cyst Treatment
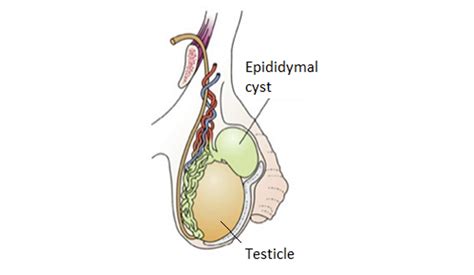
Epididymal cysts, also known as spermatocele, are fluid-filled growths that develop in the epididymis, a tube at the back of the testicle that stores and carries sperm. These cysts are usually harmless and may not cause any symptoms, but in some cases, they can become large enough to cause discomfort or pain. In this article, we will delve into the treatment options for epididymal cysts, exploring both conservative and surgical approaches.
Understanding Epididymal Cysts
Before discussing treatment, it’s essential to understand the nature of epididymal cysts. They are typically filled with a clear fluid and can grow to varying sizes, from small, pea-sized cysts to larger ones that may be several centimeters in diameter. The exact cause of epididymal cysts is often unclear, but they may be related to blockages or injuries in the epididymal tubes, which can lead to fluid accumulation.
Conservative Management
For small, asymptomatic epididymal cysts, a wait-and-see approach may be recommended. This involves regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor the cyst’s size and ensure it does not cause any issues. In some cases, the cyst may resolve on its own without the need for intervention. For larger cysts or those causing discomfort, conservative management may include:
- Pain management: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help alleviate any discomfort or pain associated with the cyst.
- Scrotal support: Wearing supportive underwear or a jockstrap can help reduce discomfort and prevent further irritation.
- Warm bath therapy: Soaking in a warm bath may help reduce swelling and alleviate pain.
Surgical Options
In cases where the cyst is large, symptomatic, or causing significant discomfort, surgical intervention may be necessary. The primary goal of surgery is to remove the cyst while preserving the epididymis and testicle. Surgical options include:
- Surgical excision: This involves removing the cyst through a small incision in the scrotum. The procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia, and the patient can usually return home the same day.
- Spermatocele marsupialization: This procedure involves creating a small incision in the scrotum and removing the fluid from the cyst. The cyst is then sewn to the scrotal skin, allowing it to drain and reducing the risk of recurrence.
Potential Complications and Risks
While surgical treatment for epididymal cysts is generally safe, there are potential complications and risks to consider. These may include:
- Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection. Antibiotics may be prescribed to minimize this risk.
- Scarring: Surgical excision may result in scarring, although this is typically minimal.
- Recurrence: In some cases, the cyst may recur after surgical treatment. Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider can help monitor for any signs of recurrence.
Pros and Cons of Surgical Treatment
- Pros:
- Relief from symptoms and discomfort
- Reduced risk of recurrence
- Minimally invasive procedure
- Cons:
- Risk of infection or scarring
- Potential for recurrence
- Requires surgical intervention
Post-Surgical Care and Recovery
Following surgical treatment for an epididymal cyst, it’s essential to follow post-operative instructions carefully to ensure a smooth recovery. This may include:
- Rest and relaxation: Avoiding strenuous activities, such as heavy lifting or exercise, for several days after surgery.
- Pain management: Taking prescribed pain medication as directed to manage discomfort.
- Follow-up appointments: Scheduling follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider to monitor healing and remove any sutures.
Post-Surgical Care and Recovery: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Rest and relax for several days after surgery
- Take prescribed pain medication as directed
- Attend follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider
- Avoid strenuous activities for several weeks
- Monitor for signs of infection or recurrence
Conclusion
Epididymal cysts can be a source of discomfort and anxiety, but with proper treatment, individuals can find relief. Whether through conservative management or surgical intervention, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment. By understanding the nature of epididymal cysts and exploring treatment options, individuals can make informed decisions about their care and take the first step towards a symptom-free life.
What are the symptoms of an epididymal cyst?
+Symptoms of an epididymal cyst may include a palpable mass or swelling in the scrotum, discomfort or pain, and occasionally, a sensation of heaviness or dragging in the testicle.
How are epididymal cysts diagnosed?
+Epididymal cysts are typically diagnosed through a physical examination and ultrasound imaging. A healthcare provider may also perform a transillumination test, where a bright light is shone through the scrotum to determine if the cyst is filled with fluid.
Can epididymal cysts be prevented?
+While the exact cause of epididymal cysts is often unclear, maintaining good genital hygiene, avoiding injury to the testicles, and seeking medical attention for any symptoms or concerns may help reduce the risk of developing an epididymal cyst.



