Face Chemical Burn
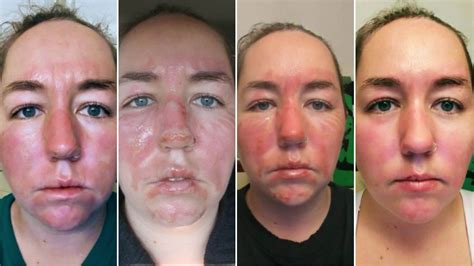
Chemical burns, also known as caustic burns, can occur when the skin comes into contact with a corrosive substance, causing damage to the skin and potentially underlying tissues. When a chemical burn occurs on the face, it can be particularly distressing due to the sensitive nature of the area and the potential for long-term cosmetic and functional damage. It’s crucial to understand the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures to manage and mitigate the effects of a chemical burn on the face.
Causes of Chemical Burns on the Face
Chemical burns on the face can result from a variety of sources, including but not limited to:
- Household Cleaning Products: Many cleaning solutions contain harsh chemicals like bleach, ammonia, or acid, which can cause severe burns upon contact with the skin.
- Industrial Chemicals: Workplace exposure to industrial chemicals without proper protective gear can lead to chemical burns.
- Skin Care Products: Certain skin care products, especially those with high concentrations of alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs), beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs), or other exfoliating agents, can cause chemical burns if used improperly or in excessive amounts.
- Battery Acid: Accidental splashing of battery acid can lead to severe chemical burns.
Symptoms of Chemical Burns on the Face
The symptoms of a chemical burn on the face can vary depending on the severity of the burn and the type of chemical involved. Common symptoms include:
- Pain: The burn area may be painful, and the intensity of the pain can increase with time if not treated.
- Redness and Swelling: The affected area may become red, swollen, and inflamed.
- Blistering: Blisters may form on the surface of the burn, which can rupture and become infected if not properly cared for.
- Discoloration: The skin may become discolored, turning white, black, or leathery.
- Breathing Difficulty: If the burn affects the nose or mouth, it can lead to breathing difficulties.
Treatment for Chemical Burns on the Face
The treatment of chemical burns on the face is critical and should be initiated immediately after the exposure. Here are the steps to follow:
- Flush the Area: Gently flush the affected area with cool or lukewarm water for at least 20 minutes to remove any residual chemical. Avoid using hot water, as it can activate certain chemicals and worsen the burn.
- Remove Contaminated Clothing: Take off any clothing or jewelry that may have come into contact with the chemical to prevent further skin contact.
- Neutralize the Chemical (If Applicable): For certain chemicals, a specific neutralizing agent may be recommended. However, this should only be done under the guidance of a medical professional or based on the advice of a poison control center.
- Apply Topical Creams: After flushing, apply a topical antibiotic ointment to prevent infection and cover the burn with a non-stick, sterile bandage.
- Seek Medical Attention: For all but the mildest burns, it’s crucial to seek medical attention. A healthcare provider can assess the burn’s severity and provide appropriate treatment, which may include further cleansing, topical treatments, and in some cases, surgical intervention.
Preventive Measures
Prevention is key when it comes to chemical burns. Here are some steps you can take to reduce the risk:
- Use Protective Gear: Wear protective gloves, masks, and eyewear when handling chemicals.
- Follow Instructions: Always read and follow the instructions on the label of any chemical product.
- Keep Chemicals Out of Reach: Ensure that chemicals are stored in a safe place, out of the reach of children and pets.
- Be Aware of Your Surroundings: When working with chemicals, be mindful of your surroundings to avoid accidental splashes or spills.
Long-Term Care and Potential Complications
The long-term care of a chemical burn on the face involves promoting healing, minimizing scarring, and addressing any potential complications. This may include ongoing medical treatment, such as topical creams or ointments, and in some cases, surgical procedures to repair damaged tissue or reduce scarring.
Potential complications can include infection, scarring, discoloration, and in severe cases, damage to the eyes or respiratory system. It’s essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to monitor the healing process and address any concerns or complications that may arise.
Conclusion
Chemical burns on the face require immediate and careful treatment to prevent long-term damage. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and knowing the appropriate treatment and preventive measures are crucial for managing and mitigating the effects of such burns. If you or someone you know has suffered a chemical burn, seeking medical attention promptly is the first step towards recovery and minimizing potential complications.
FAQ Section
What should I do immediately if I get a chemical burn on my face?
+Flush the area with cool or lukewarm water for at least 20 minutes, remove any contaminated clothing, and seek medical attention as soon as possible.
How can I prevent chemical burns on my face?
+Prevention involves using protective gear when handling chemicals, following instructions on chemical products, keeping chemicals out of reach of children and pets, and being mindful of your surroundings.
What are the potential long-term complications of a chemical burn on the face?
+Potential complications include infection, scarring, discoloration, and in severe cases, damage to the eyes or respiratory system. Proper medical care and follow-up are essential to minimize these risks.
When should I seek medical attention for a chemical burn on my face?
+Seek medical attention for all but the mildest chemical burns. If you’re unsure about the severity of the burn or if you experience symptoms like difficulty breathing, severe pain, or significant swelling, seek help immediately.
Can chemical burns on the face lead to permanent scarring?
+Yes, chemical burns can lead to permanent scarring. The risk and severity of scarring depend on the depth and extent of the burn, as well as the effectiveness of the treatment. Early and proper medical care can help minimize scarring.



