Fecal Blood Test Guide: Accurate Results
The presence of blood in stool can be a symptom of various gastrointestinal issues, ranging from minor to severe. A fecal blood test, also known as a fecal occult blood test (FOBT), is a diagnostic tool used to detect hidden blood in the stool. This test is crucial for identifying potential health problems early on, enabling timely intervention and treatment. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of fecal blood tests, exploring their significance, procedures, interpretation of results, and the importance of accurate testing.
Understanding Fecal Occult Blood Tests
A fecal occult blood test is designed to identify tiny amounts of blood in the stool that may not be visible to the naked eye. The presence of blood can indicate bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, which could be due to several factors, including ulcers, polyps, colon cancer, or inflammatory bowel disease. The test is often recommended as part of a routine check-up for individuals over the age of 50 or for those with a family history of colorectal cancer.
How FOBT Works
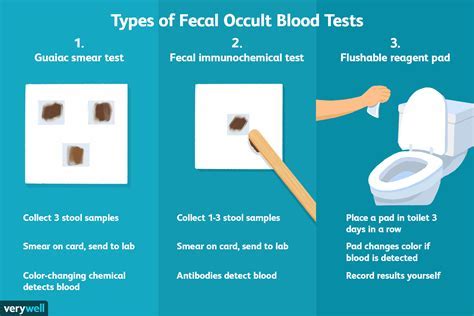
The fecal occult blood test works by detecting the peroxidase activity of hemoglobin in the stool sample. When blood is present, the hemoglobin reacts with a chemical substance added to the sample, leading to a color change that indicates a positive result. There are two main types of FOBT: the guaiac-based test and the immunochemical test. The guaiac-based test is the traditional method and detects the peroxidase activity of hemoglobin, while the immunochemical test uses antibodies to detect human hemoglobin specifically, making it more sensitive and specific.
Preparing for a Fecal Blood Test
Proper preparation is key to obtaining accurate results from a fecal blood test. Patients are usually advised to avoid certain foods and medications that could interfere with the test results. These include:
- Vitamin C: High doses of vitamin C can interfere with the test results, so it’s recommended to avoid taking vitamin C supplements for a few days before the test.
- Red Meat: Consuming red meat can lead to false-positive results due to the presence of hemoglobin in the meat. It’s advised to avoid red meat for a few days before collecting the stool sample.
- Certain Medications: Aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can cause bleeding in the stomach and lead to false-positive results. Consult with your healthcare provider about stopping these medications before the test.
Collecting the Stool Sample
The process of collecting a stool sample for a fecal blood test is straightforward but requires attention to detail to ensure accurate results. Here are the general steps:
- Obtain the Test Kit: Your healthcare provider will give you a test kit that includes a special card or device for collecting and testing the stool sample.
- Collect the Sample: You will need to collect a small sample of stool using the provided collection device. The kit will include instructions on how to do this hygienically.
- Apply the Sample to the Test Card: Follow the instructions to apply a small amount of the stool sample to the test card. This usually involves smearing a tiny amount onto a specific area of the card.
- Develop the Test: The card will then be treated with a chemical that will cause a color change if blood is present. The color change area will indicate the test result.
Interpreting Fecal Blood Test Results
Understanding the results of a fecal blood test can be straightforward. Here’s what the outcomes typically mean:
- Negative Result: A negative result means no blood was detected in the stool sample. However, it’s essential to remember that a negative result does not completely rule out the presence of gastrointestinal issues, as some conditions may not always cause bleeding.
- Positive Result: A positive result indicates that blood was detected in the stool sample. This does not necessarily mean you have colon cancer, but it does signal that further testing, such as a colonoscopy, is needed to determine the source of the bleeding.
The Importance of Accurate Testing
Accurate fecal blood testing is crucial for the early detection and management of gastrointestinal diseases. False-negative or false-positive results can lead to unnecessary anxiety, further testing, or delayed diagnosis. Factors that can affect the accuracy of the test include the type of test used, the quality of the stool sample, and adherence to pre-test preparation instructions.
Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
Beyond the fecal occult blood test, there are other diagnostic tools and techniques used to investigate gastrointestinal issues, including:
- Colonoscopy: A procedure where a flexible tube with a camera is used to visually examine the inside of the colon and rectum for polyps, cancer, or other abnormalities.
- Imaging Tests: Such as CT scans or MRI scans, which can provide detailed images of the abdominal organs and help diagnose conditions affecting the gastrointestinal tract.
- Biopsy: The removal of a small tissue sample for examination under a microscope to check for cancer cells or other abnormalities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a fecal blood test is a vital diagnostic tool for detecting hidden blood in the stool, which can be an early sign of gastrointestinal problems. Understanding the test, its preparation, and its results is essential for individuals and healthcare providers alike. By emphasizing the importance of accurate testing and further diagnostic techniques when necessary, we can work towards earlier intervention and better outcomes for those affected by gastrointestinal diseases.
What are the common causes of a positive fecal blood test result?
+A positive result can be due to several factors, including ulcers, polyps, colon cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, or even the consumption of certain foods or medications that cause bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.
How often should I undergo a fecal blood test?
+The frequency of fecal blood tests depends on several factors, including age, family history of colorectal cancer, and previous test results. Generally, adults over 50 are recommended to have regular screenings, with the specific interval determined by their healthcare provider based on individual risk factors.
Can a fecal blood test detect all types of gastrointestinal cancers?
+While a fecal blood test is primarily used to detect colon cancer, it may not detect all types of gastrointestinal cancers, especially those that do not bleed, such as early-stage stomach cancer. Comprehensive diagnostic approaches, including other screening tests and medical evaluations, are necessary for a thorough assessment.