Fecal Transplant Success: Restore Balance
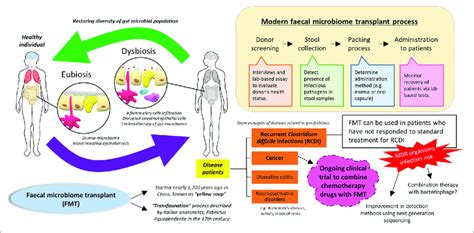
The human gut microbiome is a complex ecosystem composed of trillions of microorganisms, playing a crucial role in our overall health and well-being. An imbalance of the gut microbiome, also known as dysbiosis, has been linked to various diseases and conditions, including inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, and mental health disorders. One innovative approach to restoring balance to the gut microbiome is through fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), a procedure that involves transferring fecal matter from a healthy donor into the gut of a patient with dysbiosis.
Understanding the Science Behind FMT
FMT works by introducing beneficial microorganisms from the donor’s fecal matter into the patient’s gut, where they can colonize and establish a balanced ecosystem. The procedure typically involves several steps, including screening and selecting a healthy donor, preparing the donor’s fecal matter, and administering the transplant via colonoscopy, endoscopy, or oral capsules. The goal of FMT is to repopulate the patient’s gut with a diverse range of beneficial microorganisms, which can help to crowd out pathogenic bacteria and restore balance to the gut ecosystem.
Success Stories and Clinical Evidence
Numerous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of FMT in treating various conditions, including Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) infections, ulcerative colitis, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). For example, a 2019 systematic review published in the journal Gastroenterology found that FMT resulted in significant improvements in symptoms and quality of life for patients with IBS. Another study published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2013 found that FMT was highly effective in treating recurrent C. diff infections, with a success rate of 81% after a single treatment.
Key Benefits and Advantages
FMT offers several benefits and advantages over traditional treatments, including:
- High success rates: FMT has been shown to be highly effective in treating various conditions, with success rates ranging from 70% to 90%.
- Low risk of side effects: FMT is generally considered safe, with few reported side effects, such as mild abdominal discomfort or diarrhea.
- Restoration of balance: FMT helps to restore balance to the gut microbiome, which can have a positive impact on overall health and well-being.
- Holistic approach: FMT treats the underlying cause of dysbiosis, rather than just managing symptoms.
Overcoming Challenges and Limitations
While FMT has shown promising results, there are still several challenges and limitations to its widespread adoption. These include:
- Donor screening and selection: Finding suitable donors and screening for potential pathogens can be time-consuming and costly.
- Regulatory frameworks: FMT is still a relatively new field, and regulatory frameworks are evolving to ensure safety and efficacy.
- Standardization and scalability: There is a need for standardized protocols and large-scale production of FMT products to make the treatment more accessible.
Future Directions and Emerging Trends
As research continues to uncover the complexities of the gut microbiome, FMT is likely to play an increasingly important role in the treatment of various diseases and conditions. Emerging trends and areas of research include:
- Personalized FMT: Using advanced sequencing techniques to tailor FMT treatments to individual patients’ needs.
- FMT for mental health: Exploring the potential of FMT to treat mental health disorders, such as depression and anxiety.
- Combination therapies: Combining FMT with other treatments, such as diet and lifestyle modifications, to enhance efficacy.
What is the success rate of FMT for treating C. diff infections?
+Studies have shown that FMT can achieve success rates of up to 90% for treating recurrent C. diff infections.
Are there any risks or side effects associated with FMT?
+FMT is generally considered safe, with few reported side effects, such as mild abdominal discomfort or diarrhea.
Can FMT be used to treat conditions other than C. diff infections?
+Yes, FMT has been used to treat a range of conditions, including ulcerative colitis, IBS, and mental health disorders.
In conclusion, FMT has emerged as a promising treatment for restoring balance to the gut microbiome and addressing various diseases and conditions. While there are still challenges and limitations to its widespread adoption, the success stories and clinical evidence demonstrate the potential of FMT to revolutionize the field of gastroenterology and beyond. As research continues to uncover the complexities of the gut microbiome, FMT is likely to play an increasingly important role in the treatment of various diseases and conditions, offering new hope for patients and healthcare providers alike.