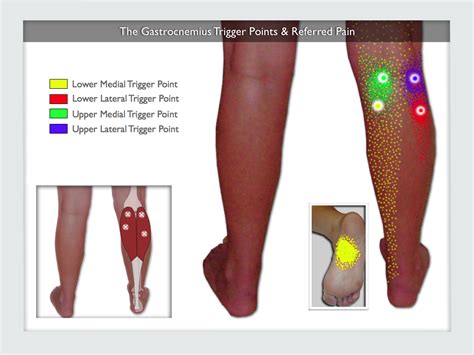
The gastrocnemius muscle, located in the lower leg, plays a crucial role in movement and stability. However, it is also prone to pain and injury, which can significantly impact daily activities and overall quality of life. Gastrocnemius muscle pain can arise from various factors, including overuse, trauma, and underlying medical conditions. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this type of pain is essential for effective management and recovery.
Anatomy and Function of the Gastrocnemius Muscle
To comprehend the nature of gastrocnemius muscle pain, it’s vital to first understand the anatomy and function of this muscle. The gastrocnemius is a two-joint muscle, meaning it crosses two joints (the knee and ankle), and it is one of the most superficial muscles in the calf. It originates from the medial and lateral condyles of the femur (thigh bone) and inserts into the calcaneus (heel bone) via the Achilles tendon. The primary function of the gastrocnemius muscle is plantarflexion of the foot (pointing the foot downward) and flexion of the knee. This muscle is crucial for everyday movements such as walking, running, and climbing stairs.
Causes of Gastrocnemius Muscle Pain
Gastrocnemius muscle pain can result from a variety of causes. Overuse injuries are common, particularly in individuals who engage in sports that involve running or repetitive jumping. Direct blows to the muscle, such as from a fall or being hit by an object, can also cause pain. Additionally, conditions like tendonitis (inflammation of the tendons) and compartment syndrome (increased pressure within the muscle compartments) can lead to gastrocnemius pain. In some cases, pain in the gastrocnemius muscle can be referred from other areas, such as the lower back, due to nerve compression or irritation.
Symptoms of Gastrocnemius Muscle Pain
The symptoms of gastrocnemius muscle pain can vary depending on the underlying cause but typically include pain in the calf area, which may worsen with activity and improve with rest. Swelling, redness, and warmth over the affected area can also occur, especially in cases of inflammation or infection. Patients might experience stiffness in the calf, particularly after periods of inactivity, and a decreased range of motion in the ankle and knee. In severe cases, the pain can be debilitating, affecting the ability to walk or perform daily tasks.
Diagnosis of Gastrocnemius Muscle Pain
Diagnosing gastrocnemius muscle pain involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and sometimes imaging studies. A healthcare provider will typically perform a thorough examination to assess pain locations, muscle strength, and range of motion. Questions about recent activities, previous injuries, and symptoms are crucial for identifying potential causes. Imaging tests like X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI scans may be ordered to rule out other conditions, such as fractures or ligament sprains, and to assess the extent of muscle or tendon damage.
Treatment Options for Gastrocnemius Muscle Pain
Treatment for gastrocnemius muscle pain aims to alleviate symptoms, promote healing, and prevent future injuries. Initial management often involves the RICE principle: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. Over-the-counter pain relievers can help reduce pain and inflammation. Physical therapy is beneficial for improving strength, flexibility, and range of motion. In cases where overuse is the culprit, modifying activities or incorporating stretching and strengthening exercises into one’s routine can be preventative. For more severe injuries or conditions, such as tendon tears or compartment syndrome, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing gastrocnemius muscle pain involves a proactive approach. Engaging in regular stretching and strengthening exercises, particularly those targeting the calf muscles, can reduce the risk of injury. Wearing appropriate footwear and using orthotics when necessary can also help by reducing strain on the muscles and tendons. Gradually increasing the intensity and duration of physical activities can prevent overuse injuries. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the strain on the muscles and joints of the lower extremities.
Complications and Long-Term Outlook
If left untreated or poorly managed, gastrocnemius muscle pain can lead to chronic conditions, such as tendonitis, which can significantly impact quality of life. In rare cases, severe injuries like muscle ruptures or compartment syndrome can have long-term consequences, including permanent muscle or nerve damage, if not promptly and appropriately treated. Early recognition and treatment of gastrocnemius muscle pain are critical for preventing such complications and ensuring a favorable long-term outlook.
Conclusion
Gastrocnemius muscle pain is a common condition that can result from various factors, including overuse, trauma, and underlying medical conditions. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking appropriate treatment are essential for managing this type of pain and preventing long-term complications. By adopting preventative strategies and maintaining a proactive approach to muscle health, individuals can reduce their risk of experiencing gastrocnemius muscle pain and ensure optimal lower limb function.
Gastrocnemius muscle pain highlights the importance of lower limb care and the need for prompt medical evaluation when symptoms persist or worsen over time. Adopting a holistic approach to health, including regular exercise, balanced diet, and stress management, can also contribute to the overall well-being of the muscles and tendons, reducing the risk of injuries and conditions that lead to pain.
What are the common causes of gastrocnemius muscle pain?
+Common causes include overuse injuries, direct trauma to the muscle, and conditions like tendonitis and compartment syndrome. Referred pain from the lower back due to nerve compression is also a possibility.
How is gastrocnemius muscle pain diagnosed?
+Diagnosis involves a physical examination, review of medical history, and sometimes imaging tests like X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI scans to assess the extent of muscle or tendon damage and rule out other conditions.
What are the treatment options for gastrocnemius muscle pain?
+Treatment options include the RICE principle (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation), over-the-counter pain relievers, physical therapy, and in severe cases, surgical intervention. Preventative measures such as regular stretching, appropriate footwear, and gradual increase in physical activity intensity can also help.
In conclusion, while gastrocnemius muscle pain can be debilitating, understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and implementing appropriate treatment and preventative strategies can lead to effective management and recovery. It’s essential for individuals experiencing persistent or severe pain to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and care.