Gfr Calculation: Know Your Kidney Health
The glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is a crucial metric in assessing kidney function and overall health. It measures the rate at which the kidneys filter waste and excess fluids from the blood. A decreased GFR indicates impaired kidney function, which can lead to serious health complications if left unchecked. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of GFR calculation, its significance, and how it relates to kidney health.
Understanding GFR
GFR is calculated based on several factors, including age, sex, race, and serum creatinine levels. Serum creatinine is a waste product that comes from the normal wear and tear on muscles of the body, and the kidneys are responsible for filtering it out of the blood. When kidney function is impaired, creatinine levels rise, indicating a decrease in GFR. The most common formula used to estimate GFR is the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) study equation, which takes into account the Serum creatinine level, age, gender, and race.
Factors Affecting GFR
Several factors can influence GFR, including:
- Age: GFR naturally decreases with age, even in healthy individuals.
- Sex: Females typically have a lower GFR than males due to differences in muscle mass.
- Race: African Americans have a higher serum creatinine level than Caucasians, which affects GFR calculations.
- Body Size: Muscle mass can impact serum creatinine levels; hence, GFR calculations need to consider body size.
- Diet: A high-protein diet can increase serum creatinine levels temporarily.
Calculating GFR
The MDRD study equation for estimating GFR is as follows:
GFR (mL/min/1.73 m²) = 175 × (Serum Creatinine)^-1.154 × (Age)^-0.203 × (0.742 if female) × (1.212 if African American)
However, this formula has its limitations, especially in individuals with normal or near-normal kidney function. The Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation is another formula that is considered more accurate for a broader range of GFR values.
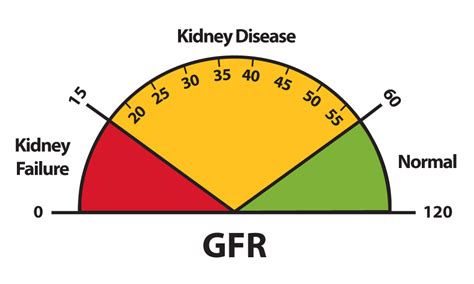
Stages of Kidney Disease Based on GFR
Kidney disease is categorized into five stages based on the GFR level, with Stage 1 being the least severe and Stage 5 indicating kidney failure.
- Stage 1: Kidney damage with normal or increased GFR (> 90 mL/min/1.73 m²)
- Stage 2: Mild kidney damage with a GFR between 60-89 mL/min/1.73 m²
- Stage 3: Moderate kidney damage, further divided into 3A (45-59 mL/min/1.73 m²) and 3B (30-44 mL/min/1.73 m²)
- Stage 4: Severe kidney damage with a GFR between 15-29 mL/min/1.73 m²
- Stage 5: Kidney failure, with a GFR less than 15 mL/min/1.73 m² or the need for renal replacement therapy
Importance of Monitoring GFR
Monitoring GFR is essential for the early detection and management of kidney disease. Regular checks can help identify individuals at risk, allowing for timely intervention to slow disease progression. Lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and managing blood pressure and blood sugar levels, can significantly impact kidney health.
Practical Steps for Improving Kidney Health
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water helps the kidneys function properly.
- Maintain a Healthy Blood Pressure: High blood pressure is a leading cause of kidney disease.
- Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: Diabetes is a significant risk factor for kidney disease.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity helps maintain healthy blood pressure and improves overall health.
- Don’t Smoke: Smoking can reduce blood flow to the kidneys and worsen kidney function.
Conclusion
GFR calculation is a vital tool in assessing kidney health and diagnosing kidney disease. Understanding the factors that affect GFR and the different stages of kidney disease based on GFR levels can empower individuals to take proactive steps towards maintaining their kidney health. Regular monitoring and lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of kidney disease and its progression. As kidney health is intricately linked with overall well-being, prioritizing it is essential for a healthy and fulfilling life.
What does a low GFR indicate?
+A low GFR indicates that the kidneys are not functioning as well as they should, which can be a sign of kidney disease or other health issues. The severity of the decrease in GFR correlates with the stage of kidney disease, with lower GFR values indicating more severe kidney impairment.
How can I improve my GFR naturally?
+Natural ways to improve or maintain GFR include staying hydrated, reducing protein intake, exercising regularly, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy weight. Additionally, controlling blood pressure and blood sugar levels through diet and exercise can help prevent kidney damage and slow the progression of kidney disease.
Can kidney function be restored?
+While some kidney function may be restored with proper treatment and lifestyle changes, especially in the early stages of kidney disease, advanced kidney damage is often irreversible. Early detection and intervention are critical to preserving kidney function and preventing the progression to more severe stages of kidney disease.