Giant Cell Arteritis Treatment
Giant cell arteritis, also known as temporal arteritis, is a condition characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels, particularly those in the head. This inflammation can lead to a range of symptoms, including headaches, scalp tenderness, jaw pain, and vision problems. If left untreated, giant cell arteritis can cause serious complications, such as blindness or stroke. Therefore, prompt and effective treatment is essential to manage the condition and prevent long-term damage.
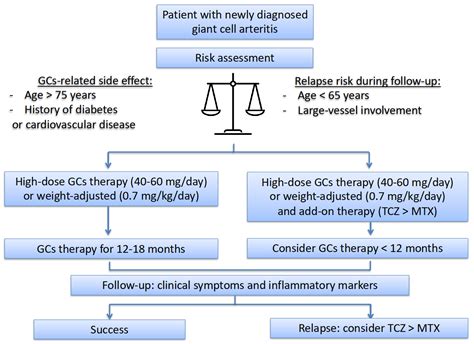
One of the primary goals of treatment is to reduce inflammation and prevent further damage to the blood vessels. Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are the most commonly used medications for treating giant cell arteritis. These medications work by suppressing the immune system and reducing inflammation. The dosage and duration of corticosteroid treatment vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s response to treatment.
In addition to corticosteroids, other medications may be used to treat giant cell arteritis. For example, methotrexate, a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD), may be prescribed to help reduce inflammation and prevent relapses. Aspirin or other antiplatelet medications may also be recommended to reduce the risk of blood clots and stroke.
Lifestyle modifications can also play a crucial role in managing giant cell arteritis. For example, maintaining a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and managing stress can help reduce inflammation and promote overall well-being. Additionally, avoiding certain activities that may exacerbate the condition, such as heavy lifting or bending, can help prevent further damage to the blood vessels.
In some cases, giant cell arteritis may require more aggressive treatment, such as surgery or other interventions. For example, if the condition has caused significant damage to the blood vessels or other tissues, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace the damaged areas.
As with any medical condition, it’s essential to weigh the pros and cons of different treatment options and work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan. By taking a comprehensive and proactive approach to treatment, individuals with giant cell arteritis can effectively manage their symptoms, prevent long-term damage, and improve their overall quality of life.
What are the most common symptoms of giant cell arteritis?
+The most common symptoms of giant cell arteritis include headaches, scalp tenderness, jaw pain, and vision problems. In some cases, individuals may also experience fever, fatigue, and weight loss.
How is giant cell arteritis diagnosed?
+Giant cell arteritis is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as blood work and imaging studies. A temporal artery biopsy may also be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
What are the potential complications of giant cell arteritis?
+If left untreated, giant cell arteritis can cause serious complications, such as blindness, stroke, and aortic aneurysm. Prompt and effective treatment can help prevent these complications and improve overall outcomes.
Can giant cell arteritis be cured?
+While there is no cure for giant cell arteritis, prompt and effective treatment can help manage symptoms, prevent long-term damage, and improve overall quality of life. In some cases, individuals may experience remission, but it's essential to continue working with a healthcare provider to monitor the condition and adjust treatment as needed.
How can I prevent giant cell arteritis?
+While there is no guaranteed way to prevent giant cell arteritis, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help reduce inflammation and promote overall well-being. Additionally, working with a healthcare provider to manage underlying medical conditions and monitor for potential symptoms can help identify and treat giant cell arteritis early on.
In conclusion, giant cell arteritis is a serious condition that requires prompt and effective treatment to manage symptoms and prevent long-term damage. By working closely with a healthcare provider and developing a personalized treatment plan, individuals can effectively manage their condition and improve their overall quality of life. It’s essential to be aware of the potential complications of giant cell arteritis and take proactive steps to prevent them. With the right treatment and lifestyle modifications, individuals can reduce their risk of complications and achieve optimal outcomes.


