Glucose Control Guide: Normal Levels Explained
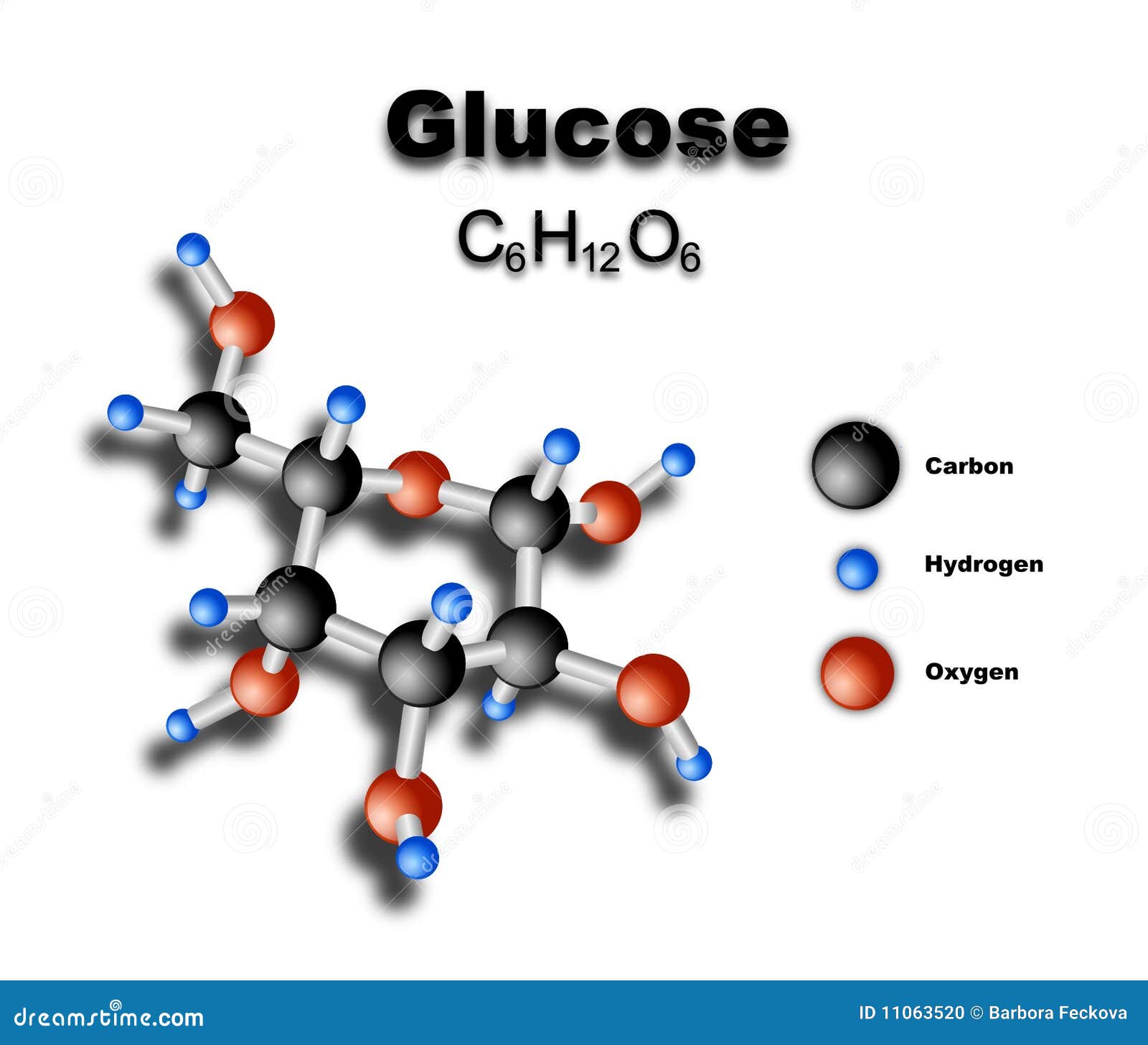
Maintaining normal glucose levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Glucose, a simple sugar, is the primary source of energy for the body’s cells. The body regulates blood glucose levels through a complex process involving the pancreas, liver, and insulin. Understanding normal glucose levels and how they are controlled can help individuals make informed decisions about their diet, lifestyle, and health.
What are Normal Glucose Levels?
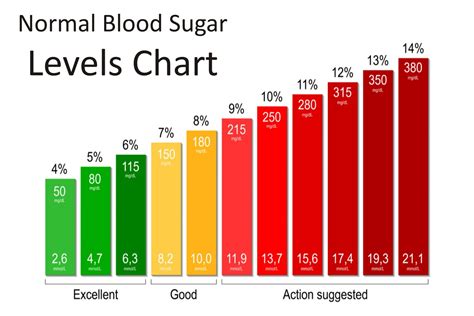
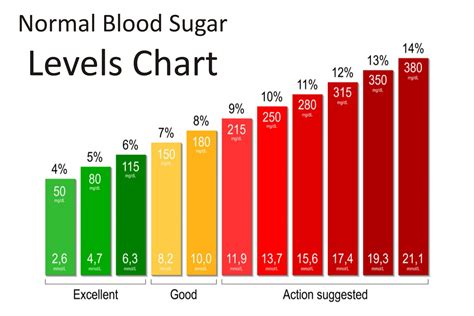
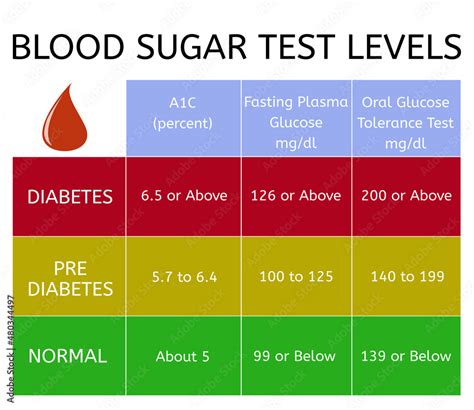
Normal glucose levels vary throughout the day, depending on factors such as diet, physical activity, and sleep patterns. Fasting glucose levels, which are measured after an overnight fast, should be between 70 and 99 mg/dL. Postprandial glucose levels, which are measured after eating, should be less than 140 mg/dL. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends the following glucose level targets: * Fasting glucose: 70-99 mg/dL * Postprandial glucose: less than 140 mg/dL * Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c): less than 5.7%
How is Glucose Controlled?
The body controls glucose levels through a negative feedback loop involving the pancreas, liver, and insulin. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of the process: 1. Glucose enters the bloodstream: After eating, glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream from the digestive tract. 2. Pancreas releases insulin: The pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream. 3. Insulin binds to cells: Insulin binds to insulin receptors on the surface of cells, triggering a signaling cascade that allows glucose to enter the cells. 4. Glucose enters cells: Glucose enters the cells, where it is used for energy production, growth, and repair. 5. Liver regulates glucose: The liver stores excess glucose as glycogen, which can be broken down and released into the bloodstream when glucose levels are low. 6. Glucagon is released: When glucose levels are low, the pancreas releases glucagon, a hormone that stimulates the liver to release stored glucose (glycogen) into the bloodstream.
Factors that Affect Glucose Levels
Several factors can affect glucose levels, including: * Diet: Consuming high-carbohydrate foods can cause a spike in glucose levels, while a balanced diet that includes protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates can help regulate glucose levels. * Physical activity: Regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity, helping to regulate glucose levels. * Sleep patterns: Poor sleep patterns can disrupt glucose regulation, leading to elevated glucose levels. * Stress: Chronic stress can raise glucose levels by stimulating the release of stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline.
Glucose Control Strategies
Here are some strategies to help maintain normal glucose levels: * Eat a balanced diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, including vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. * Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help regulate glucose levels. * Exercise regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week. * Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to help regulate glucose levels. * Manage stress: Engage in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
What are the symptoms of high glucose levels?
+High glucose levels can cause symptoms such as increased thirst and urination, blurred vision, fatigue, and slow healing of cuts and wounds.
How often should I check my glucose levels?
+The frequency of glucose monitoring depends on individual factors, such as diabetes diagnosis, medication, and lifestyle. Consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best monitoring schedule.
Can I still eat sweets if I have diabetes?
+While it's best to limit sweets and sugary foods, it's not necessary to completely eliminate them from your diet. Choose sweets that are low in added sugars and pair them with protein and healthy fats to help regulate glucose levels.
Conclusion
Maintaining normal glucose levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. By understanding how glucose levels are controlled and implementing strategies to regulate them, individuals can reduce their risk of developing diabetes and related complications. Remember to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best approach for individual glucose control needs.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), more than 34 million Americans have diabetes, and an additional 88 million have prediabetes. By making informed lifestyle choices and monitoring glucose levels, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent or manage diabetes.
In conclusion, glucose control is a critical aspect of overall health, and understanding normal glucose levels and how they are controlled can help individuals make informed decisions about their diet, lifestyle, and health. By implementing glucose control strategies and consulting with a healthcare provider, individuals can reduce their risk of developing diabetes and related complications.