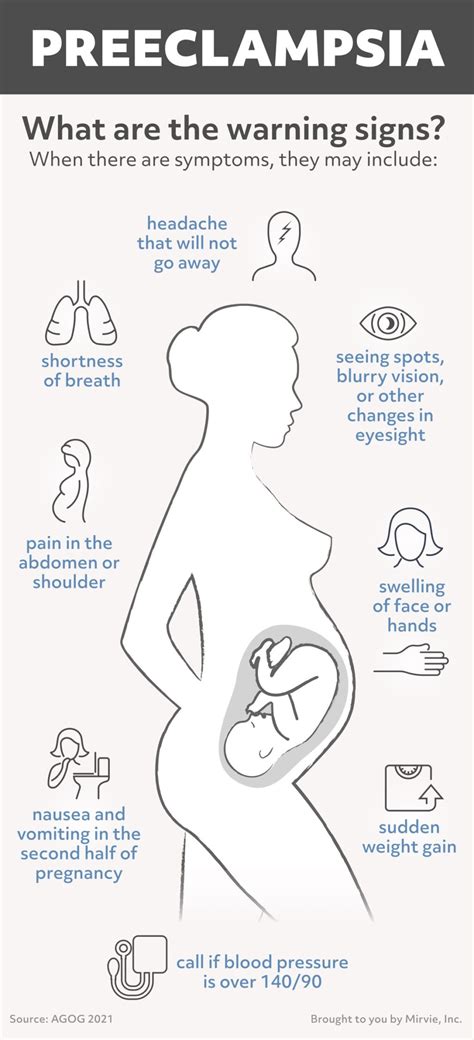
Glucose Level Normal
Understanding glucose levels and their impact on our health is crucial for maintaining overall wellbeing. Glucose, a simple sugar, is a primary source of energy for the body’s cells. It is derived from the food we eat, particularly from carbohydrates, and is regulated by the body to ensure that it remains within a narrow, healthy range. The management of glucose levels is fundamental in preventing and managing conditions such as diabetes, a disorder characterized by the body’s inability to adequately regulate blood glucose.
Normal Glucose Levels
Normal glucose levels vary throughout the day, influenced by factors like the timing and composition of meals, physical activity levels, and individual health conditions. Fasting glucose levels, measured after at least 8 hours without food or drink (except water), are generally considered normal if they are below 100 mg/dL. Postprandial glucose levels, measured 2 hours after eating, are considered normal if they are below 140 mg/dL. These values can slightly vary depending on the laboratory conducting the test and the specific guidelines being followed.
Factors Influencing Glucose Levels
Several factors can influence glucose levels. Diet plays a crucial role, with the consumption of high glycemic index foods leading to sharper spikes in blood glucose. Physical activity also impacts glucose levels; regular exercise can improve the body’s sensitivity to insulin, thereby lowering blood glucose. Stress levels, both physical and psychological, can cause the body to release stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can elevate blood glucose levels. Sleep and body weight are additional factors; poor sleep quality and excess body weight, particularly around the abdominal area, can lead to insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin.
Maintaining Healthy Glucose Levels
Maintaining healthy glucose levels is essential for preventing complications associated with diabetes and other metabolic disorders. Dietary adjustments, focusing on balanced meals with whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can help stabilize blood glucose levels. Regular physical activity, including aerobic exercises, strength training, and high-intensity interval training, can improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Stress management techniques, such as meditation, yoga, and mindfulness, can also contribute to better glucose control by reducing the impact of stress hormones.
Monitoring Glucose Levels
For individuals with diabetes or those at risk, monitoring glucose levels is a critical aspect of disease management. This can be achieved through various methods, including:
- Fingerstick glucose testing: Provides immediate feedback on blood glucose levels and is useful for making decisions about meals, exercise, and medication.
- Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs): Offer real-time glucose data and trends, allowing for more precise management of glucose levels.
- Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) tests: Measure average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months, providing a broader picture of glucose control.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing glucose levels is a multifaceted process that involves dietary choices, physical activity, stress management, and, when necessary, medical intervention. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits and monitoring glucose levels, individuals can better control their blood sugar and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications. It’s also essential to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment plans, especially for those with pre-existing conditions or concerns about their glucose levels.
What is the normal range for fasting glucose levels?
+Fasting glucose levels are considered normal if they are below 100 mg/dL. However, levels between 100 mg/dL and 125 mg/dL may indicate impaired fasting glucose, a condition that can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
How does diet affect glucose levels?
+Diet plays a significant role in managing glucose levels. Consuming foods with a low glycemic index, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, can help keep glucose levels stable. On the other hand, foods with a high glycemic index, like sweets and refined carbohydrates, can cause sharp spikes in blood glucose.
Can exercise lower glucose levels?
+Yes, regular physical activity can improve the body's sensitivity to insulin, thereby lowering blood glucose levels. Both aerobic exercises and strength training can be beneficial in managing glucose levels and improving overall health.
In conclusion, maintaining healthy glucose levels is a dynamic process that involves a comprehensive approach to health, including dietary management, regular physical activity, stress reduction, and, when necessary, medical intervention. By understanding the factors that influence glucose levels and adopting healthy lifestyle practices, individuals can better manage their glucose levels and reduce the risk of diabetes and other metabolic disorders.