Health Insurance Deductible Guide: Save Money
Understanding and navigating the complex world of health insurance can be daunting, especially when it comes to managing costs. One of the key components of health insurance plans that significantly affects how much you pay out of pocket is the deductible. A deductible is the amount you must pay each year before your health insurance plan starts to pay its share of costs. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the specifics of health insurance deductibles, how they work, the different types, and most importantly, strategies to save money on your health insurance deductible.
What is a Health Insurance Deductible?
A health insurance deductible is essentially an annual cost that you, as the policyholder, must meet before your insurance provider begins covering medical expenses. For example, if your deductible is 1,000, you will pay the first 1,000 of your medical bills out of pocket. After you meet this deductible amount, your insurance plan will start to cover a portion of your medical costs, depending on the specifics of your plan, such as copays, coinsurance, and maximum out-of-pocket expenses.
Types of Health Insurance Deductibles
Health insurance plans come with various types of deductibles, each serving a different purpose and applying to different aspects of healthcare.
- Individual Deductible: Applies to individual health insurance plans where each person covered by the plan has their own deductible to meet.
- Family Deductible: Applies to family health insurance plans, where the deductible must be met by the combined medical expenses of all family members covered under the plan before the insurance kicks in.
- Embedded Deductible: Found in family plans, an embedded deductible means there is both an individual deductible and a family deductible. If one family member meets the individual deductible, the insurance starts covering their expenses, while the family deductible is still being met by the combined expenses of all family members.
- Split Deductible: Some plans may have split deductibles, where different services (like prescriptions, doctor visits, and hospital stays) have separate deductibles.
How Do Health Insurance Deductibles Work?
To illustrate how deductibles work, let’s consider a simple example: Suppose you have a health insurance plan with a 1,500 deductible, and during the year, you incur 2,000 in medical expenses.
- First, you pay the deductible: You pay the first $1,500 out of pocket.
- Then, insurance coverage begins: After meeting the deductible, your insurance plan starts to cover its share of your medical expenses. If your plan has a 20% coinsurance, for the remaining 500 (2,000 total expenses - 1,500 deductible), you'll pay 100 (20% of 500), and your insurance will cover 400 (80% of $500).
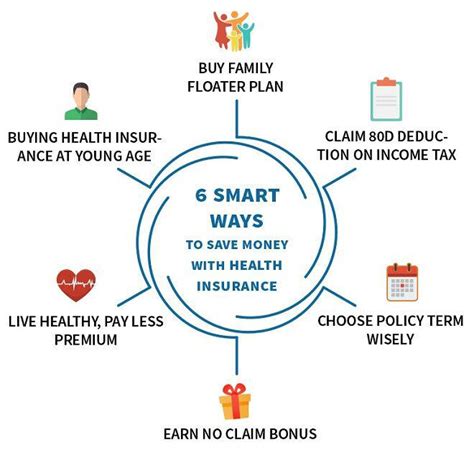
Strategies to Save Money on Your Health Insurance Deductible
Saving money on health insurance deductibles involves a combination of choosing the right plan, managing your healthcare expenses wisely, and taking advantage of available savings options. Here are some strategies:
- Select a Plan Carefully: Consider your typical annual medical expenses and the potential for any large medical bills when choosing between plans with different deductibles. A higher deductible plan might be cheaper upfront but could cost more in the long run if you need extensive medical care.
- Health Savings Accounts (HSAs): If you have a High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP), you may be eligible for an HSA. Contributions to an HSA are tax-deductible, and the money can be used tax-free for qualified medical expenses, helping you save for your deductible and other healthcare costs.
- Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs): Similar to HSAs but available with other types of health plans, FSAs allow you to set aside pre-tax dollars for medical expenses, which can help cover deductibles and other out-of-pocket costs.
- Negotiate Medical Bills: Sometimes, you can negotiate the cost of medical services, especially if you’re paying out of pocket. This can significantly reduce the amount you need to pay towards your deductible.
- Preventive Care: Utilize preventive care services that are often covered without needing to meet your deductible. Regular check-ups and screenings can prevent more severe conditions that would increase your medical expenses.
Future Trends in Health Insurance Deductibles
The healthcare landscape is constantly evolving, with changes in policy, technology, and consumer expectations influencing the design of health insurance plans, including deductibles.
- Increased Transparency: There’s a growing demand for more transparent and understandable billing practices, which could lead to reforms in how deductibles and other cost-sharing mechanisms are structured and communicated to policyholders.
- Personalized Insurance Plans: With advancements in data analysis and AI, there’s potential for more personalized health insurance plans that take into account an individual’s health status, genetic predispositions, and lifestyle, potentially leading to more tailored and cost-effective deductible structures.
- Digital Health Technologies: The integration of digital health technologies, such as telemedicine and health apps, could change how healthcare is delivered, potentially reducing costs and the impact of deductibles on policyholders.
Expert Perspective: Health Insurance Deductibles and Policyholder Behavior
According to health insurance experts, policyholders often underestimate the impact of deductibles on their healthcare decisions. “Higher deductibles can deter people from seeking necessary care due to the upfront cost, which can have long-term health implications. Therefore, it’s crucial for individuals to understand their deductible, plan accordingly, and explore options like HSAs and FSAs to mitigate these costs,” notes a leading insurance analyst.
Conclusion
Health insurance deductibles are a critical component of managing healthcare expenses, and understanding how they work can significantly impact your financial planning and healthcare decisions. By choosing the right health insurance plan, leveraging savings vehicles like HSAs and FSAs, and being proactive about your healthcare expenses, you can navigate the complexities of deductibles more effectively and save money in the process. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, staying informed about changes in health insurance deductibles and exploring innovative strategies to manage them will be essential for making the most of your health insurance coverage.
FAQ Section
What is the difference between a deductible and copay in health insurance?
+A deductible is the amount you pay each year before your health plan starts to pay its share of costs, while a copay (or copayment) is a fixed amount you pay for a healthcare service after you’ve met your deductible. For example, you might pay a $30 copay for each doctor’s visit after meeting your deductible.
Can I change my health insurance deductible during the year?
+Typically, you cannot change your deductible outside of the annual open enrollment period or a special enrollment period triggered by a qualifying life event. However, some employers may offer a flexible benefits plan that allows changes during the year, or you might be able to make adjustments if you experience a significant life change, such as marriage, divorce, or the birth of a child.
What happens if I don’t meet my deductible by the end of the year?
+If you don’t meet your deductible by the end of the year, you won’t be able to carry over any unused portion to the next year. Each year, you start fresh with your deductible. However, if you’ve enrolled in a plan with an HSA, you can keep contributing to and using your HSA funds year after year, which can help with future deductibles and medical expenses.
Can I use my HSA funds for anything besides medical expenses?
+While HSA funds are intended for qualified medical expenses, you can use them for non-medical expenses, but you’ll have to pay income tax on those withdrawals, and you may also face a penalty, depending on your age and the circumstances. After age 65, you can use HSA funds for any purpose without penalty, though you’ll still pay income tax on non-medical withdrawals.
How can I find the most cost-effective health insurance plan with a deductible that fits my needs?
+Start by assessing your typical annual medical expenses and consider any potential large medical bills. Use online health insurance marketplaces or consult with a licensed insurance agent to compare plans. Don’t focus solely on the deductible; also consider copays, coinsurance, the maximum out-of-pocket costs, and the network of providers. Sometimes, a plan with a higher deductible but lower premiums and better coverage might be more cost-effective for you.