Hemoglobin A1c: Control Diabetes With Simple Tests
The impact of diabetes on global health is undeniable, with millions of people worldwide living with this condition. One of the most effective ways to manage diabetes is by monitoring blood sugar levels, and one crucial test for doing so is the Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test. This test provides a snapshot of a person’s average blood glucose levels over the past 2 to 3 months, making it an invaluable tool for both patients and healthcare providers.
Understanding Hemoglobin A1c
Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. When blood sugar levels are high, some of the sugar molecules bind to the hemoglobin, forming Hemoglobin A1c. The higher the blood sugar levels, the more hemoglobin gets bound with sugar, resulting in higher HbA1c levels. This process is irreversible and occurs over the lifespan of a red blood cell, which is approximately 120 days.
Why is HbA1c Important?
The HbA1c test is crucial for several reasons:
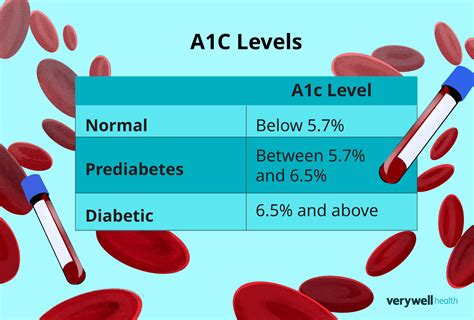
- Diagnosis: It helps in diagnosing diabetes and prediabetes. The American Diabetes Association recommends the following HbA1c values for diagnosis: less than 5.7% for normal, 5.7% to 6.4% for prediabetes, and 6.5% or higher for diabetes.
- Monitoring: For individuals already diagnosed with diabetes, the HbA1c test is a standard tool to monitor the effectiveness of their treatment plan. It provides insight into how well the diabetes is being controlled over time.
- Risk Assessment: High HbA1c levels are associated with an increased risk of complications from diabetes, such as heart disease, kidney failure, and nerve damage. Therefore, maintaining a target HbA1c level can significantly reduce these risks.
How to Interpret HbA1c Results
Interpreting HbA1c results involves understanding what the percentages mean and how they relate to average blood glucose levels. Here is a general guide:
- Less than 5.7%: Normal
- 5.7% to 6.4%: Prediabetes
- 6.5% or higher: Diabetes
For people with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association suggests an HbA1c goal of less than 7% for most adults. However, this target may vary based on individual factors such as age, other health conditions, duration of diabetes, life expectancy, resources, and support system.
Factors Influencing HbA1c Levels
While HbA1c is a reliable indicator of blood glucose control, there are factors that can influence its accuracy. These include:
- Hemolytic Anemia: Conditions that reduce red blood cell lifespan can lead to falsely low HbA1c readings.
- Kidney Disease: Individuals with chronic kidney disease may have altered red blood cell turnover, affecting HbA1c accuracy.
- Pregnancy: HbA1c levels can be lower in pregnancy due to increased red blood cell turnover.
Managing and Lowering HbA1c Levels
For individuals with diabetes, managing and potentially lowering HbA1c levels involves a comprehensive approach:
- Medication Adherence: Following the prescribed medication regimen as directed by a healthcare provider.
- Dietary Changes: Implementing a balanced diet that is low in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats, and high in fiber and nutrients.
- Physical Activity: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, to improve insulin sensitivity.
- Monitoring Blood Glucose: Regularly checking blood sugar levels to understand how different factors (like food and exercise) affect them.
Conclusion
The Hemoglobin A1c test is a powerful tool in the management of diabetes. By understanding what HbA1c is, how it’s used, and what factors can influence its results, individuals with diabetes can better navigate their condition. Through a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring, it’s possible to achieve and maintain target HbA1c levels, reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications and improving overall quality of life.
What is a good HbA1c level for someone with diabetes?
+A good HbA1c level for someone with diabetes is generally considered to be less than 7%. However, this target may be adjusted based on individual factors, such as age, other health conditions, and duration of diabetes.
How often should I get an HbA1c test if I have diabetes?
+The frequency of HbA1c testing for individuals with diabetes can vary. Generally, it's recommended to have the test done at least twice a year if your diabetes is well-controlled. If your diabetes is not well-controlled or if you've made recent changes to your treatment plan, your healthcare provider may recommend more frequent testing.
Can I lower my HbA1c levels through diet and exercise alone?
+Yes, it is possible to lower HbA1c levels through diet and exercise. A balanced diet low in sugar and unhealthy fats, combined with regular physical activity, can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels. However, for many people with diabetes, a combination of lifestyle changes and medication is necessary to achieve and maintain target HbA1c levels.
In conclusion, the Hemoglobin A1c test is a vital component of diabetes management, offering a clear picture of blood sugar control over time. By understanding its significance, how to interpret results, and factors that can influence these results, individuals can take proactive steps towards better health. Whether through medication, lifestyle adjustments, or a combination of both, achieving and maintaining target HbA1c levels is crucial for minimizing the risk of diabetes-related complications and ensuring a high quality of life.


