Hmo And Ppo: Choose Best Coverage
Understanding the nuances of health insurance can be a daunting task, especially when it comes to choosing between an HMO (Health Maintenance Organization) and a PPO (Preferred Provider Organization). Both types of plans have their own set of benefits and drawbacks, and selecting the right one depends on various factors, including your health needs, budget, and personal preferences. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the details of HMOs and PPOs, exploring their differences, advantages, and disadvantages, to help you make an informed decision about which type of coverage is best for you.
Introduction to HMOs

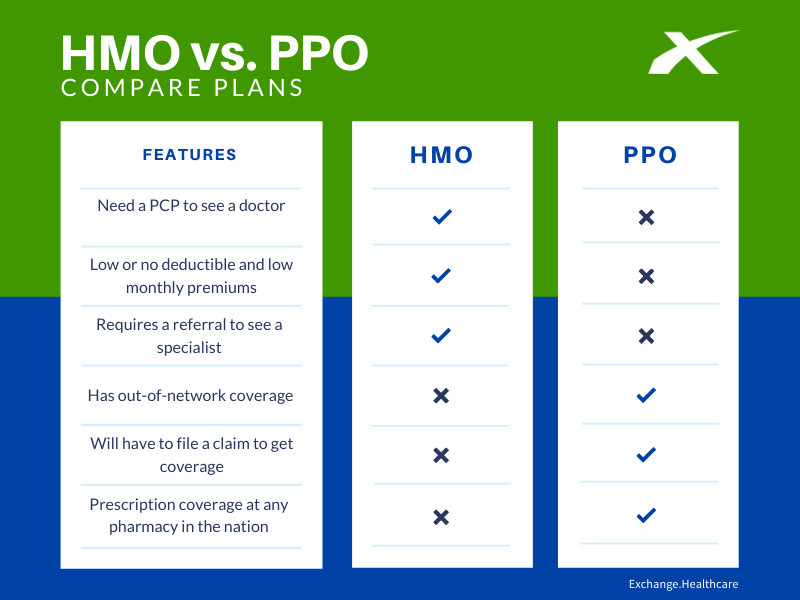
HMOs are a type of health insurance plan that provides coverage for medical services in exchange for a monthly premium. They typically have a network of participating healthcare providers, including primary care physicians, specialists, and hospitals. One of the key characteristics of HMOs is that they require you to receive medical care from providers within their network, except in emergency situations. This narrow network approach allows HMOs to negotiate lower rates with providers, which can result in lower premiums for members.
How HMOs Work
When you enroll in an HMO, you are usually required to choose a primary care physician (PCP) from the network. Your PCP serves as your main point of contact for medical care and coordinates your treatment, including referrals to specialists if needed. HMOs often have a more structured approach to healthcare, emphasizing preventive care and early intervention to manage health issues before they become severe.
Advantages of HMOs
- Lower Premiums: HMOs tend to have lower monthly premiums compared to PPOs, making them a more affordable option for many individuals and families.
- Preventive Care Focus: HMOs place a strong emphasis on preventive care, which can lead to better health outcomes and lower healthcare costs in the long run.
- Structured Care Coordination: The requirement to use a PCP and the structured referral process can lead to more coordinated and comprehensive care.
Disadvantages of HMOs
- Limited Provider Network: HMOs have a narrower network of providers, which may limit your choices and require you to switch doctors if your current physician is not part of the network.
- Out-of-Network Care Restrictions: Receiving care from providers outside the network, except in emergencies, can result in significant out-of-pocket costs or even denied claims.
- Referral Requirements: The need for a referral from your PCP to see a specialist can sometimes delay care and add an extra layer of bureaucracy.
Introduction to PPOs

PPOs are another type of health insurance plan that offers a balance between flexibility and cost savings. Unlike HMOs, PPOs have a larger network of participating providers and do not require you to choose a PCP or obtain referrals to see specialists. This flexibility comes at a cost, as PPO premiums are generally higher than those of HMOs.
How PPOs Work
PPOs allow you to receive care from any healthcare provider, both in and out of the network. When you use providers within the network, you typically pay lower copays and coinsurance rates. Out-of-network care is covered, but at a higher cost to you, reflecting the higher rates charged by non-participating providers.
Advantages of PPOs
- Greater Flexibility: PPOs offer more freedom in choosing healthcare providers, allowing you to see any doctor or visit any hospital without needing a referral.
- Larger Provider Network: The network of participating providers in a PPO is often larger than in an HMO, giving you more options for care.
- Out-of-Network Coverage: While more expensive, PPOs do cover out-of-network care, providing a safety net in case you need to see a specialist or receive care outside the network.
Disadvantages of PPOs
- Higher Premiums: The flexibility and larger network of PPOs come at a cost, with premiums typically being higher than those of HMOs.
- Higher Out-of-Pocket Costs: Even with in-network care, copays and coinsurance rates can be higher in PPOs compared to HMOs, and out-of-network care costs can be significantly higher.
- More Complex: With more options and higher costs for out-of-network care, PPOs can be more complex to navigate, especially for those unfamiliar with health insurance terminology and rules.
Choosing Between HMO and PPO: Consider Your Needs
When deciding between an HMO and a PPO, it’s crucial to consider your specific health needs, financial situation, and personal preferences. Here are some factors to consider:
- Health Needs: If you have chronic conditions or see specialists regularly, a PPO might offer more flexibility and fewer restrictions on care.
- Budget: If cost is a primary concern, an HMO might be more appealing due to lower premiums, despite its more restrictive network.
- Provider Preferences: If you have a preferred doctor or hospital that is not part of an HMO’s network, a PPO could be a better option.
- Travel: If you travel frequently, a PPO’s out-of-network coverage might provide better peace of mind.
Conclusion
Both HMOs and PPOs have their strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice for you depends on a careful evaluation of your health needs, budget, and preferences. Understanding the differences and implications of each type of plan can help you make an informed decision, ensuring you have the right coverage to meet your healthcare needs without breaking the bank. Remember, health insurance is a personal decision, and what works best for someone else may not be the ideal choice for you.
Frequently Asked Questions

What is the main difference between an HMO and a PPO?
+The main difference lies in the flexibility and network size. HMOs have a narrower network of providers and require a primary care physician referral for specialist care, while PPOs have a larger network and do not require referrals, offering more flexibility at a higher cost.
Which is more cost-effective, an HMO or a PPO?
+HMOs are generally more cost-effective due to lower premiums. However, the total cost of care can vary depending on your health needs and usage of out-of-network services in a PPO.
Can I switch from an HMO to a PPO or vice versa?
+Yes, you can switch during open enrollment periods or under certain qualifying life events. It's essential to evaluate your needs and the plan details before making a switch to ensure the new plan aligns with your current health and financial situation.
How do I choose the best health insurance plan for my family?
+Consider factors such as the health needs of family members, budget, preferred providers, and the level of flexibility needed. It might be helpful to consult with a health insurance broker or advisor who can provide personalized guidance based on your family's specific situation.
Are there any other types of health insurance plans besides HMOs and PPOs?
+Yes, there are other types, including EPOs (Exclusive Provider Organizations), POS (Point of Service) plans, and indemnity plans, among others. Each has its unique features, advantages, and disadvantages. Researching and understanding these options can help you find the best fit for your health insurance needs.
In conclusion, the decision between an HMO and a PPO should be based on a thorough analysis of your individual circumstances, considering factors such as health needs, budget constraints, and personal preferences regarding healthcare providers and flexibility. By understanding the differences and implications of each plan type, you can make an informed decision that ensures you have the right health insurance coverage to meet your needs effectively.



