Hmo Versus Ppo

When it comes to choosing a health insurance plan, two of the most popular options are Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) and Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs). While both types of plans have their advantages and disadvantages, they differ significantly in terms of their approach to healthcare delivery, costs, and flexibility. In this article, we’ll delve into the details of HMOs and PPOs, exploring their characteristics, benefits, and drawbacks to help you make an informed decision about which type of plan is best for you.
What is an HMO?
A Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) is a type of health insurance plan that provides coverage for a fixed monthly fee. HMOs are designed to emphasize preventive care and early intervention, with the goal of reducing healthcare costs in the long run. In an HMO, you typically choose a primary care physician (PCP) from a network of participating providers, who will coordinate your care and refer you to specialists as needed. HMOs often have a narrower network of providers compared to PPOs, which means you may have fewer options for choosing your doctors and hospitals.
How does an HMO work?
Here’s an example of how an HMO might work:
- You choose a PCP from the HMO’s network of providers.
- Your PCP provides routine care and refers you to specialists within the network if needed.
- You pay a fixed copayment for each office visit, and the HMO covers the remaining costs.
- If you need to see a specialist, your PCP will provide a referral, and the HMO will cover the costs of the specialist’s care.
What is a PPO?
A Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) is a type of health insurance plan that offers a broader network of providers compared to an HMO. In a PPO, you can see any healthcare provider, both in-network and out-of-network, without needing a referral from a PCP. PPOs typically have higher premiums compared to HMOs, but they offer more flexibility in terms of choosing your healthcare providers.
How does a PPO work?
Here’s an example of how a PPO might work:
- You can see any healthcare provider, both in-network and out-of-network, without needing a referral.
- You pay a higher premium for the PPO plan compared to an HMO.
- You pay a deductible, copayment, or coinsurance for each office visit, depending on the provider’s network status.
- If you see an out-of-network provider, you may pay a higher percentage of the costs or a higher deductible.
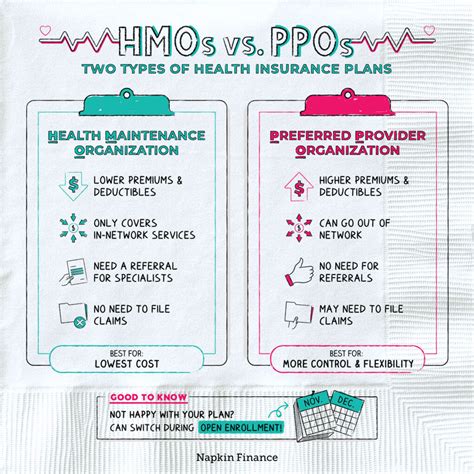
Key differences between HMOs and PPOs
Here are the main differences between HMOs and PPOs:
- Network size and flexibility: PPOs have a larger network of providers and offer more flexibility in terms of choosing your healthcare providers. HMOs have a narrower network and require referrals from a PCP to see specialists.
- Costs: HMOs typically have lower premiums compared to PPOs, but you may pay more for out-of-network care. PPOs have higher premiums, but you may pay less for out-of-network care.
- Referrals: HMOs require referrals from a PCP to see specialists, while PPOs do not.
- Preventive care: HMOs emphasize preventive care and early intervention, while PPOs may not have the same level of emphasis on preventive care.
When choosing between an HMO and a PPO, it's essential to consider your individual healthcare needs and preferences. If you prioritize preventive care and don't mind seeing a PCP for referrals, an HMO might be a good choice. However, if you prefer more flexibility in terms of choosing your healthcare providers and don't mind paying higher premiums, a PPO might be a better fit.
Comparison of HMOs and PPOs
Here’s a comparison of HMOs and PPOs in terms of their characteristics, benefits, and drawbacks:
| Characteristics | HMO | PPO |
|---|---|---|
| Network size | Narrower network | Larger network |
| Referrals | Required from PCP | Not required |
| Costs | Lower premiums, higher out-of-network costs | Higher premiums, lower out-of-network costs |
| Preventive care | Emphasized | Not emphasized as much |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | More flexible |
Case study: Choosing between an HMO and a PPO
Let’s say you’re a 35-year-old individual with a family history of chronic illnesses. You prioritize preventive care and want to ensure that you have access to a wide range of healthcare providers. In this case, a PPO might be a better choice for you, as it offers a larger network of providers and more flexibility in terms of choosing your healthcare providers. However, if you’re a healthy individual who doesn’t anticipate needing specialty care, an HMO might be a more cost-effective option.
Step-by-step guide to choosing between an HMO and a PPO
- Assess your individual healthcare needs and preferences.
- Consider the size and flexibility of the network.
- Evaluate the costs, including premiums, deductibles, and copayments.
- Think about the importance of preventive care and early intervention.
- Choose a plan that aligns with your priorities and budget.
Future trends in HMOs and PPOs
The healthcare landscape is constantly evolving, and HMOs and PPOs are no exception. In the future, we can expect to see more emphasis on value-based care, which prioritizes quality and outcomes over volume and fees. HMOs and PPOs will need to adapt to these changes by incorporating more innovative care delivery models, such as telehealth and population health management.
Pros and cons of HMOs and PPOs
Pros of HMOs:
- Lower premiums
- Emphasis on preventive care
- Coordinate care through PCP
Cons of HMOs:
- Narrower network
- Referrals required
- Higher out-of-network costs
Pros of PPOs:
- Larger network
- No referrals required
- More flexibility
Cons of PPOs:
- Higher premiums
- Higher out-of-network costs
- Less emphasis on preventive care
FAQs
What is the main difference between an HMO and a PPO?
+The main difference between an HMO and a PPO is the size and flexibility of the network. HMOs have a narrower network and require referrals from a PCP, while PPOs have a larger network and do not require referrals.
Which type of plan is better for individuals with chronic illnesses?
+A PPO might be a better choice for individuals with chronic illnesses, as it offers a larger network of providers and more flexibility in terms of choosing healthcare providers. However, the best plan for an individual with a chronic illness will depend on their specific needs and preferences.
Can I switch from an HMO to a PPO or vice versa?
+Yes, you can switch from an HMO to a PPO or vice versa, but you may need to wait until the next open enrollment period or experience a qualifying life event, such as a change in employment or marriage.
In conclusion, HMOs and PPOs are two different types of health insurance plans that offer distinct advantages and disadvantages. While HMOs emphasize preventive care and early intervention, PPOs offer more flexibility in terms of choosing healthcare providers. When choosing between an HMO and a PPO, it’s essential to consider your individual healthcare needs and preferences, as well as the size and flexibility of the network, costs, and emphasis on preventive care. By understanding the differences between HMOs and PPOs, you can make an informed decision about which type of plan is best for you.