Hmo Vs Ppo: Compare Plans Easily
When it comes to choosing a health insurance plan, two of the most popular options are HMO (Health Maintenance Organization) and PPO (Preferred Provider Organization). Both types of plans have their own set of benefits and drawbacks, and understanding the differences between them is crucial to making an informed decision. In this article, we’ll delve into the details of HMO and PPO plans, exploring their characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages, to help you compare them easily and make the best choice for your healthcare needs.
Introduction to HMO Plans
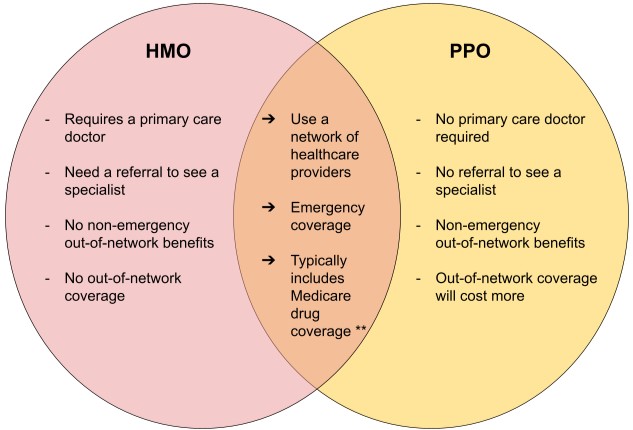
HMO plans are a type of health insurance that requires you to receive medical care from a specific network of providers, except in emergency situations. These plans are designed to provide comprehensive care at a lower cost, with an emphasis on preventive care. HMOs often have a primary care physician (PCP) who coordinates your care and refers you to specialists within the network if needed.
Key Characteristics of HMO Plans:
- Network Restrictions: You must use providers within the HMO’s network, except in emergencies.
- Primary Care Physician (PCP): You often need to choose a PCP who manages your care and refers you to specialists.
- Referrals: To see a specialist, you usually need a referral from your PCP.
- Cost: Generally, HMOs are more cost-effective, with lower premiums, deductibles, and copays.
- Preventive Care: HMOs often emphasize preventive care, covering services like annual physicals, vaccinations, and health screenings.
Introduction to PPO Plans
PPO plans, on the other hand, offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers. You can see any healthcare provider you wish, both in and out of the PPO’s network, without needing a referral from a primary care physician. While this flexibility is beneficial, it comes at a higher cost compared to HMO plans.
Key Characteristics of PPO Plans:
- Network Flexibility: You can use providers both in and out of the network, but costs vary.
- No Primary Care Physician Requirement: You don’t need to choose a PCP, and you can see any specialist without a referral.
- Out-of-Network Coverage: PPOs cover out-of-network care, but at a higher cost to you.
- Higher Costs: PPOs typically have higher premiums, deductibles, and copays compared to HMOs.
- Greater Provider Choice: The flexibility to see any healthcare provider is a significant advantage for those who value choice and do not mind the higher costs.
Comparative Analysis: HMO vs. PPO
Choosing between an HMO and a PPO plan depends on your personal preferences, healthcare needs, and budget. Here’s a summary comparison to help you decide:
| Features | HMO | PPO |
|---|---|---|
| Network | Limited to network providers (except emergencies) | Can use in-network and out-of-network providers |
| Primary Care Physician | Required to choose a PCP | Not required |
| Referrals | Needed for specialists | Not needed |
| Cost | Generally lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs | Higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | More flexible |
| Preventive Care | Emphasizes preventive care | Offers preventive care, but may vary |

Decision Framework
To make an informed decision between HMO and PPO plans, consider the following factors:
- Healthcare Needs: If you have ongoing health issues that require seeing specialists frequently, a PPO might be more suitable due to its flexibility.
- Budget: If cost is a significant concern, HMOs might be more appealing due to their generally lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
- Provider Preference: If you have a preferred doctor or hospital that is out of network, a PPO would allow you to continue seeing them, albeit at a higher cost.
- Administrative Burden: If you prefer less administrative hassle, such as not needing referrals for specialists, a PPO could be the better choice.
Future Trends in Healthcare Plans
The healthcare landscape is constantly evolving, with technological advancements and policy changes affecting the insurance market. Trends such as personalized medicine, telehealth services, and value-based care models are likely to influence the future of HMO and PPO plans. Insurers may incorporate more flexible network arrangements, expanded preventive care services, and incentives for healthy behaviors.
Conclusion
HMO and PPO plans cater to different needs and preferences, making it essential to weigh their characteristics against your personal situation. Whether you prioritize cost savings, provider flexibility, or comprehensive preventive care, understanding the nuances of these plans will help you make an informed decision. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, being aware of future trends and how they might impact insurance options will be crucial for navigating the complex world of health insurance.
What is the main difference between HMO and PPO health insurance plans?
+The main difference lies in their network restrictions and flexibility. HMO plans require you to use providers within the network (except in emergencies) and often need a referral to see a specialist, whereas PPO plans offer more flexibility, allowing you to see any healthcare provider, both in and out of network, without needing a referral.
Which type of plan is generally more cost-effective?
+HMO plans are generally more cost-effective, with lower premiums, deductibles, and copays, making them a more affordable option for those who are willing to stay within the network for their healthcare needs.
Do PPO plans cover out-of-network care?
+Yes, PPO plans cover out-of-network care, but at a higher cost to the patient. This means you will pay more out of pocket for services received from providers outside the plan’s network compared to services received from in-network providers.