Hmo Vs Ppo: Save Money On Healthcare Costs
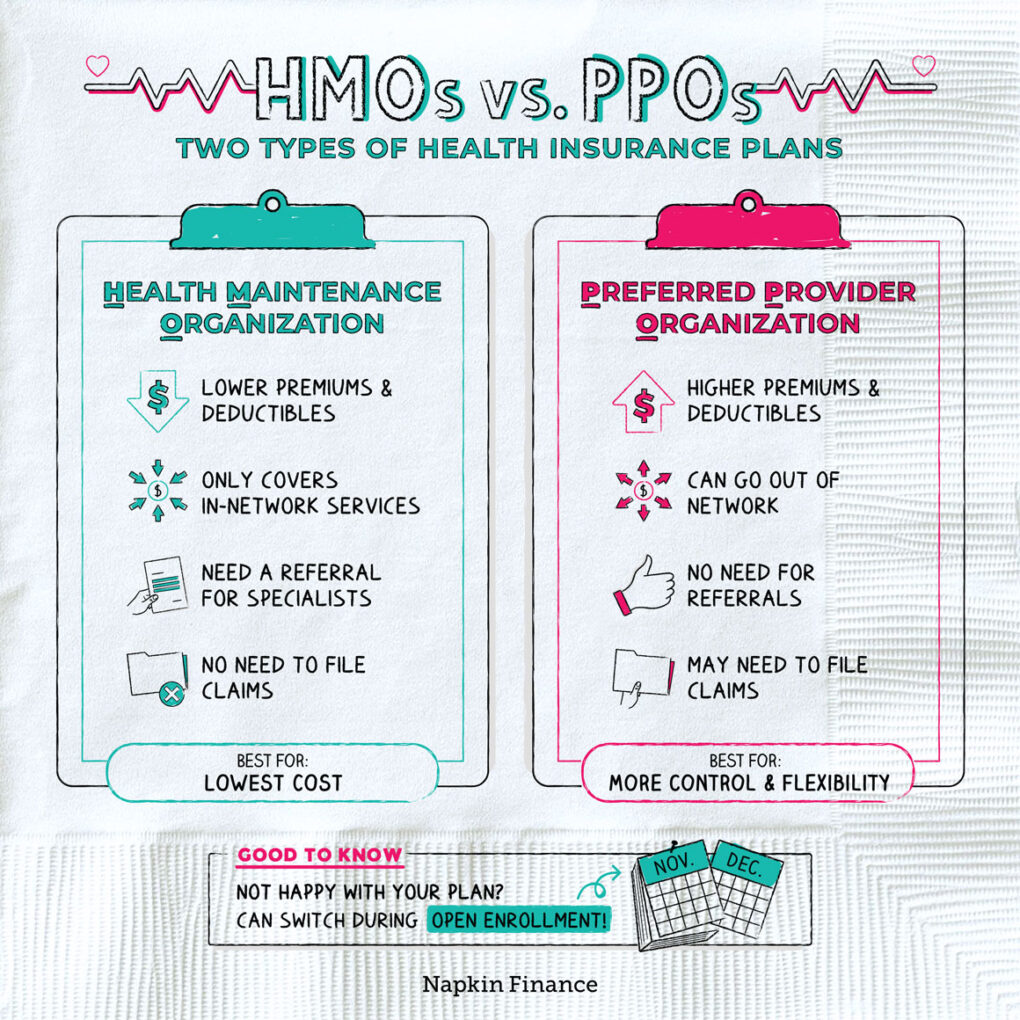
When it comes to healthcare, navigating the complexities of insurance plans can be overwhelming. Two of the most common types of health insurance plans are Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) and Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) plans. Understanding the differences between these two plans is crucial in making an informed decision about which one is best for your healthcare needs and budget. In this article, we will delve into the details of HMO and PPO plans, exploring their advantages and disadvantages, and provide guidance on how to choose the right plan for you.
Introduction to HMO Plans
HMO plans are a type of health insurance that requires you to receive medical care and services from a specific network of healthcare providers. These plans are designed to provide comprehensive healthcare services to their members at a lower cost. HMO plans often have lower premiums compared to PPO plans, but they may have more restrictions on which healthcare providers you can see.
Key Characteristics of HMO Plans:
- Lower premiums
- Lower out-of-pocket costs
- Required to choose a primary care physician (PCP) from the HMO’s network
- Referrals from your PCP are often necessary to see a specialist
- Limited or no coverage for out-of-network care
Introduction to PPO Plans
PPO plans, on the other hand, offer more flexibility in terms of healthcare providers. With a PPO plan, you have the option to see any healthcare provider, both in and out of the network, without needing a referral from a primary care physician. While PPO plans offer greater flexibility, they often come with higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
Key Characteristics of PPO Plans:
- Higher premiums
- Higher out-of-pocket costs
- No requirement to choose a primary care physician
- No need for referrals to see specialists
- Coverage for both in-network and out-of-network care, although out-of-network care may be more expensive
HMO vs PPO: Which Plan is Right for You?
When deciding between an HMO and a PPO plan, there are several factors to consider. If you prioritize lower premiums and are willing to work within a specific network of healthcare providers, an HMO plan might be the better choice. However, if flexibility and the ability to see any healthcare provider without referrals are more important to you, a PPO plan could be the better option.
Consider the Following:
- Healthcare Needs: If you have a chronic condition or see specialists frequently, a PPO plan might offer more benefits due to its flexibility.
- Cost: If budget is a significant concern, HMO plans generally have lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
- Network: Check if your current healthcare providers are part of the plan’s network. If they are not, you might want to consider a PPO plan for more flexibility.
- Travel: If you travel frequently, a PPO plan could provide better coverage for emergency care outside of your network area.
Maximizing Savings with Your Choice
Regardless of whether you choose an HMO or PPO plan, there are several strategies to maximize your savings on healthcare costs:
- Preventive Care: Take advantage of preventive care services, which are often covered at no additional cost. Regular check-ups, vaccinations, and screenings can help prevent more severe health issues down the line.
- In-Network Care: If you have an HMO plan, ensure that you receive care from in-network providers to minimize costs. For PPO plans, while you have the flexibility to go out-of-network, staying in-network can save you money.
- Generic Medications: When possible, opt for generic medications over brand-name drugs. Generic medications are equivalent in quality and effectiveness but at a lower cost.
- Health Savings Account (HSA): If your plan is eligible, consider opening an HSA. Contributions to an HSA are tax-deductible, and the funds can be used to pay for qualified medical expenses.
Conclusion
Choosing between an HMO and a PPO plan depends on your individual healthcare needs, budget, and preferences. By understanding the characteristics of each plan and considering your specific situation, you can make an informed decision that saves you money on healthcare costs while ensuring you have the coverage you need. Always review the plan’s details carefully, including the provider network, coverage, and out-of-pocket costs, to make the best choice for your health and financial well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between HMO and PPO plans?
+The main difference between HMO (Health Maintenance Organization) and PPO (Preferred Provider Organization) plans is the flexibility in choosing healthcare providers. HMO plans require you to receive care from a specific network of providers and often need referrals for specialists, while PPO plans allow you to see any healthcare provider, both in and out of the network, without needing a referral.
Which plan typically has lower premiums?
+HMO plans typically have lower premiums compared to PPO plans. This is because HMOs limit the network of providers and often require referrals, which can help control costs.
Can I see any doctor with a PPO plan?
+Yes, with a PPO plan, you have the flexibility to see any healthcare provider, both in and out of the network. However, seeing out-of-network providers usually results in higher out-of-pocket costs compared to staying within the network.
How can I save money on healthcare costs with my insurance plan?
+To save money on healthcare costs, take advantage of preventive care services, which are often covered at no additional cost. Also, choosing in-network care can save you money, especially with PPO plans. Opting for generic medications instead of brand-name drugs can also reduce your expenses. If eligible, contributing to a Health Savings Account (HSA) can provide tax benefits and help pay for qualified medical expenses.
By considering these factors and strategies, you can navigate the world of HMO and PPO plans more effectively, ensuring that you find the right balance between coverage and cost that suits your healthcare needs and budget.



