How Does Silver Sulfadiazine Cream Work? Wound Healing Guide
Silver sulfadiazine cream is a topical antibiotic cream used primarily to prevent or treat infections on areas of burned skin. It belongs to a class of medications known as sulfonylureas and works by releasing silver ions, which have antimicrobial properties. These ions disrupt the microbial cell wall, ultimately leading to the death of the microorganisms. The sulfadiazine component of the cream also contributes to its antibacterial effects by inhibiting the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms.
When applied to a wound, silver sulfadiazine cream forms a protective barrier on the wound’s surface. This barrier not only prevents bacteria from entering the wound but also promotes an environment conducive to healing. The presence of silver ions can help reduce the risk of infection in second- and third-degree burns by minimizing bacterial colonization on the wound surface. This is crucial because burns can severely compromise the skin’s natural barrier function, making the affected area highly susceptible to infection.
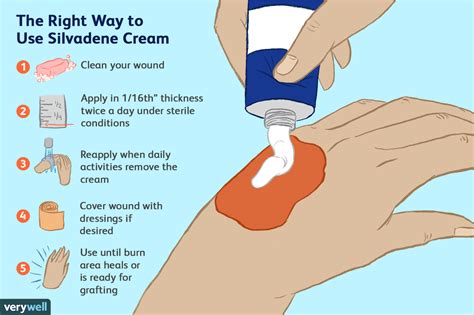
The application of silver sulfadiazine cream is relatively straightforward. It is typically applied to the affected area once or twice daily, depending on the severity of the burn and the physician’s recommendations. Before applying the cream, the wound should be cleaned with saline solution to remove any debris or dead tissue that could interfere with the healing process. A thick layer of the cream (about 1⁄16 inch) is then applied uniformly over the wound, ensuring that all areas are covered. The cream should be reapplied as directed by a healthcare professional, usually after wound dressing changes.
One of the benefits of using silver sulfadiazine cream is its broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, which includes effectiveness against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a common pathogen in burn wounds. Additionally, silver sulfadiazine has been shown to have some activity against fungi and viruses, making it a versatile agent in the management of burn wounds. However, it is essential to use the cream under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as improper use can lead to adverse effects or reduce its effectiveness.
Despite its benefits, silver sulfadiazine cream can have potential side effects. These may include skin discoloration (due to the silver content), itchiness, redness, or rash at the application site. In rare cases, more severe reactions such as leukopenia (a decrease in white blood cell count) have been reported, especially with prolonged use. It is crucial for patients to monitor their condition and report any unusual symptoms to their healthcare provider.
The role of silver sulfadiazine cream in wound healing is multifaceted. Not only does it prevent infection, but it also supports the healing process by maintaining a moist environment that encourages tissue repair. The antimicrobial properties of the cream reduce the bacterial load, which can otherwise prolong the inflammatory phase of wound healing and delay the progression to the proliferative phase, where new tissue growth occurs.
In the broader context of wound care, silver sulfadiazine cream is just one component of a comprehensive treatment plan. Other critical aspects include proper wound cleaning and debridement, use of appropriate dressings, management of pain, and nutritional support to optimize the body’s healing capabilities. Additionally, regular monitoring of the wound for signs of infection or other complications is essential to adjust the treatment plan as needed.
For individuals with burns or other wounds, understanding how silver sulfadiazine cream works and its role in wound healing can provide reassurance and promote compliance with treatment recommendations. By combining the use of this cream with other evidence-based wound care practices, patients can improve their outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
In conclusion, silver sulfadiazine cream plays a vital role in the management of burns and other wounds by providing antimicrobial coverage and promoting a conducive environment for healing. Its effectiveness against a broad spectrum of pathogens makes it a valuable tool in preventing infections, which are a significant risk for individuals with compromised skin integrity.
What is silver sulfadiazine cream used for?
+Silver sulfadiazine cream is used primarily to prevent or treat infections on areas of burned skin. It has antimicrobial properties that help reduce the risk of infection in second- and third-degree burns.
How does silver sulfadiazine cream work?
+Silver sulfadiazine cream works by releasing silver ions, which disrupt microbial cell walls, leading to the death of microorganisms. The sulfadiazine component also inhibits bacterial growth, contributing to its antibacterial effects.
What are the benefits of using silver sulfadiazine cream?
+The benefits of using silver sulfadiazine cream include its broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, effectiveness against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, and its role in promoting a moist environment conducive to wound healing.
What are the potential side effects of silver sulfadiazine cream?
+Potential side effects of silver sulfadiazine cream include skin discoloration, itchiness, redness, or rash at the application site. Rarely, more severe reactions such as leukopenia have been reported, especially with prolonged use.
How should silver sulfadiazine cream be applied?
+Silver sulfadiazine cream should be applied to the affected area once or twice daily, depending on the severity of the burn and the physician's recommendations. A thick layer of the cream should be applied uniformly over the wound after it has been cleaned with saline solution.
What role does silver sulfadiazine cream play in wound healing?
+Silver sulfadiazine cream plays a multifaceted role in wound healing by preventing infection, reducing the bacterial load, and maintaining a moist environment that encourages tissue repair, thereby supporting the progression of wound healing through its various phases.
In the context of wound care, it is essential to recognize that while silver sulfadiazine cream is a valuable tool, it is part of a broader treatment strategy. Proper wound management, including regular monitoring, appropriate dressing changes, and nutritional support, is critical to optimizing wound healing outcomes. As with any medication, it is crucial to follow the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure safe and effective use.
Expert Insight: The use of silver sulfadiazine cream in wound care highlights the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to managing burns and other complex wounds. By combining antimicrobial therapy with other evidence-based practices, healthcare providers can significantly improve patient outcomes and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
In conclusion, silver sulfadiazine cream is a vital component of wound care, offering broad-spectrum antimicrobial protection and supporting the healing process. Its application, as part of a comprehensive wound management plan, can significantly impact the recovery of individuals with burns or other wounds, underscoring the need for careful consideration of all aspects of wound care to achieve optimal healing outcomes.