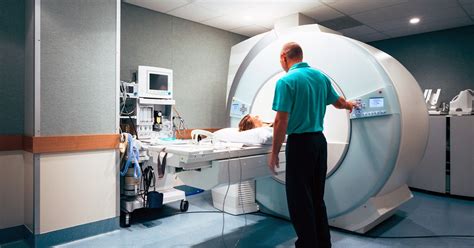
The duration of an MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scan can vary significantly depending on the type of scan, the body part being imaged, and the specific requirements of the diagnostic procedure. Generally, an MRI scan can last anywhere from 15 to 90 minutes, with some scans taking even longer.
Factors Influencing MRI Scan Duration
Type of Scan: Different types of MRI scans have varying durations. For example, a basic MRI scan of a joint might be quicker than a detailed scan of the brain or an MRI that requires contrast dye to be injected.
Body Part: The part of the body being scanned also affects the duration. Scans of smaller body parts, like the wrist or ankle, tend to be shorter than scans of larger areas, such as the spine or abdomen.
Claustrophobia and Comfort: Some patients might experience claustrophobia or discomfort during the scan, which could necessitate breaks or adjustments, potentially lengthening the overall procedure time.
Contrast Agents: If a contrast agent (dye) is used to enhance the images, this might add some time to the procedure for the injection and for the contrast to take effect.
Machine Capability: The specifications and capabilities of the MRI machine itself can influence how quickly scans are performed. Newer, high-field strength MRI machines tend to produce higher quality images in less time compared to older models.
Typical Durations for Common MRI Scans
- Brain MRI: 30-60 minutes
- Spine MRI: 30-90 minutes (can vary depending on the sections of the spine being imaged)
- Joint MRI (e.g., knee, shoulder): 15-30 minutes
- Abdomen or Pelvis MRI: 30-60 minutes
- Breast MRI: 30-60 minutes
- Full Body MRI: 60-90 minutes (used for comprehensive evaluations or in cancer staging)
Preparation and What to Expect
Before the scan, patients are usually asked to change into a gown and remove any metallic objects. The scan itself involves lying on a table that slides into the MRI machine. Patients are instructed to remain as still as possible during the scan, as movement can blur the images. Depending on the type of scan, patients might be given headphones to listen to music or instructions during the procedure, or they might be able to talk to the technician through an intercom system.
After the scan, the images are reviewed by a radiologist, who then reports the findings to the patient’s doctor. The results might be discussed immediately if the scan reveals critical information, or they might be communicated later, once the radiologist has had a chance to thoroughly review the images.
In summary, while the exact length of an MRI scan can vary, understanding the factors that influence scan duration and knowing what to expect can help prepare patients for their procedure.