How Much Mcg To Iu Vitamin D? Get Accurate Answers
Understanding the conversion between micrograms (mcg) and International Units (IU) for vitamin D is crucial for ensuring you’re getting the right amount of this essential nutrient. Vitamin D is vital for bone health, immune function, and overall well-being. The conversion factor is key to navigating different product labels and medical recommendations.
Conversion Factor
1 microgram (mcg) of vitamin D is equivalent to 40 International Units (IU). This conversion applies to both vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol), although D3 is more commonly recommended due to its higher bioavailability and effectiveness in raising vitamin D levels in the body.
Applying the Conversion
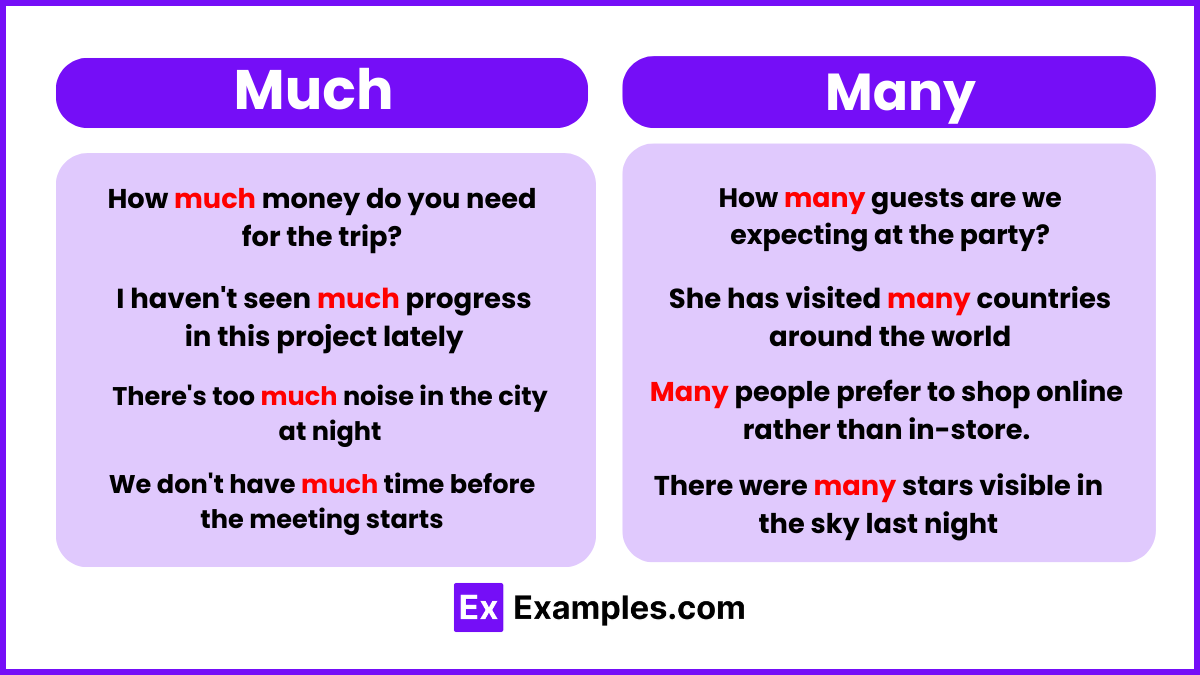
- To convert mcg to IU: Multiply the number of micrograms by 40. For example, 0.025 mcg * 40 = 1 IU.
- To convert IU to mcg: Divide the number of International Units by 40. For example, 1000 IU / 40 = 0.025 mcg or 25 mcg.
Importance of Vitamin D
Vitamin D plays a critical role in: - Bone Health: It helps the body absorb calcium, which is crucial for the normal mineralization of bone. - Immune System: Vitamin D has been shown to have immunomodulatory effects, helping to regulate immune cell activity. - Mood and Brain Health: There’s evidence suggesting vitamin D deficiency may be linked to depression, seasonal affective disorder, and other mood disorders.
Recommended Daily Intake
The recommended daily intake of vitamin D varies by age and other factors: - Infants 0-12 months: 400-1,000 IU (10-25 mcg) - Children and adolescents 1-18 years: 600-1,000 IU (15-25 mcg) - Adults 19-50 years: 600-800 IU (15-20 mcg) - Adults 51-70 years: 800-1,000 IU (20-25 mcg) - Adults over 70 years: 800-1,200 IU (20-30 mcg)
Sources of Vitamin D
- Sunlight: Exposure to sunlight triggers the synthesis of vitamin D in the skin, making it an essential source.
- Diet: Fatty fish (like salmon and mackerel), fortified dairy products, and some mushrooms are natural sources.
- Supplements: For those with deficiency or insufficiency, supplements can be an effective way to boost levels.
Conclusion
Understanding the conversion between mcg and IU for vitamin D is a fundamental step in managing and optimizing your intake of this vital nutrient. Whether through sunlight, diet, or supplementation, ensuring adequate vitamin D levels is critical for maintaining strong bones, a healthy immune system, and overall health.
How do I know if I have a vitamin D deficiency?
+A deficiency in vitamin D can be determined through a blood test that measures the level of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in your blood. Symptoms may include bone pain, fatigue, and mood changes, but often, individuals with deficiency are asymptomatic, making blood tests crucial for diagnosis.
Can I get too much vitamin D?
+Yes, it's possible to get too much vitamin D, a condition known as vitamin D toxicity or hypervitaminosis D. This can lead to elevated calcium levels in the blood, causing symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and weakness. It's essential to follow recommended intake guidelines and consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplements.
Are there different types of vitamin D supplements?
+Yes, the two main types are vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol). Vitamin D3 is generally considered more effective at raising vitamin D levels and is the type that's produced in the skin in response to sunlight. Always consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best type and dosage for your specific needs.
Incorporating vitamin D into your daily routine, whether through natural sources, supplements, or a combination of both, is a proactive step towards maintaining optimal health. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best approach tailored to your individual needs and health status.