How To Check Blood Sugar
Checking blood sugar levels is a crucial aspect of managing diabetes, a condition characterized by the body’s inability to regulate blood glucose levels properly. Diabetes affects millions of people worldwide, and monitoring blood sugar is essential for controlling the disease and preventing its complications. In this article, we will delve into the process of checking blood sugar levels, the tools required, and the factors that can influence blood glucose readings.
Understanding Blood Sugar
Blood sugar, or glucose, is the primary source of energy for the body’s cells. It is derived from the food we eat, particularly from carbohydrates. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps to regulate blood sugar levels by facilitating the entry of glucose into the cells. In people with diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces (Type 2 diabetes), leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Why Check Blood Sugar?
Checking blood sugar levels is vital for several reasons: - Management of Diabetes: Regular monitoring helps individuals with diabetes understand how different factors, such as food, physical activity, and medication, affect their blood sugar levels. This insight allows for better management of the condition. - Prevention of Complications: High blood sugar levels over a prolonged period can lead to serious health complications, including heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems. Regular monitoring can help prevent these complications by ensuring blood sugar levels remain within a target range. - Adjusting Treatment Plans: Blood sugar readings provide valuable information for healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans, including diet, exercise, and medication.
Tools for Checking Blood Sugar
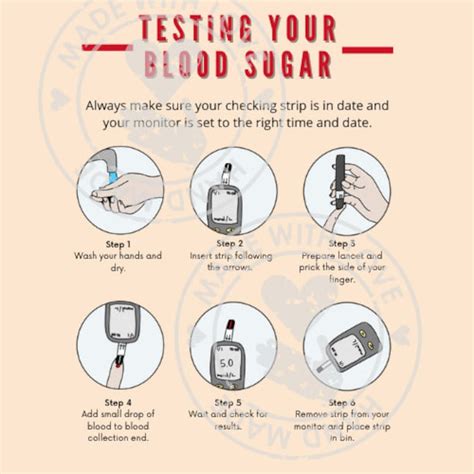
The primary tool for checking blood sugar levels at home is a glucose meter, also known as a glucometer. A glucose meter measures the amount of glucose in a small sample of blood, usually obtained from a fingertip. The process involves: 1. Preparing the Meter: Ensure the glucose meter is turned on and ready for use. Some meters may require a code to be entered from the test strip vial. 2. Obtaining a Blood Sample: Use a lancet to prick the side of your fingertip to obtain a small drop of blood. The side of the fingertip is recommended because it is less sensitive than the pads. 3. Applying the Blood Sample: Place the drop of blood onto the test strip, which is then inserted into the glucose meter. 4. Reading the Result: The meter will display the blood sugar level after a few seconds.
Factors Influencing Blood Glucose Readings
Several factors can influence blood glucose readings, including: - Food and Drink: Consuming food and drinks high in sugar and carbohydrates can raise blood sugar levels. - Physical Activity: Exercise can lower blood sugar levels by increasing the body’s sensitivity to insulin. - Stress and Emotions: Stress can cause the body to release hormones that increase blood sugar levels. - Medications: Certain medications, including steroids and some psychiatric drugs, can affect blood sugar levels. - Illness: Being sick can increase blood sugar levels due to the body’s stress response.
Target Blood Sugar Levels
The target blood sugar levels can vary depending on the individual, their diabetes type, and the timing relative to meals. Generally, the American Diabetes Association recommends the following targets: - Before Meals: 80 to 130 mg/dL - After Meals: Less than 180 mg/dL
Additional Monitoring Techniques
Besides using a glucose meter, there are other methods for monitoring blood sugar levels, including: - Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems: These devices provide real-time glucose readings throughout the day and night, offering a more detailed picture of glucose trends. - Urine Tests: While not as common for daily monitoring, urine tests can detect the presence of ketones, which are substances produced when the body breaks down fat for energy instead of glucose, a situation that can occur in people with diabetes.
Conclusion
Checking blood sugar levels is a fundamental aspect of diabetes management. By understanding how to use a glucose meter, being aware of the factors that influence blood glucose readings, and maintaining target blood sugar levels, individuals with diabetes can better control their condition and reduce the risk of complications. Regular monitoring, combined with a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and adherence to medication regimens, is key to living a healthy life with diabetes.
What are the target blood sugar levels for someone with diabetes?
+The target blood sugar levels can vary, but generally, before meals, the target is 80 to 130 mg/dL, and after meals, it’s less than 180 mg/dL. However, these targets may be adjusted based on individual factors and should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on the type of diabetes, the treatment plan, and the individual’s lifestyle. For example, someone with Type 1 diabetes may need to check their blood sugar levels more frequently than someone with Type 2 diabetes. It’s best to follow the advice of a healthcare provider on how often to check blood sugar levels.
Can I use urine tests to monitor my blood sugar levels?
+While urine tests can detect ketones, which are substances produced when the body breaks down fat for energy, they are not typically used for daily monitoring of blood sugar levels. Blood glucose meters or continuous glucose monitoring systems are more accurate and commonly used methods for monitoring blood sugar levels.



