How To Control Sugar Level Range? Daily Tips
Maintaining a healthy blood sugar level range is crucial for overall well-being, especially for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. The good news is that controlling sugar levels can be achieved through a combination of dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring. Here, we’ll delve into the daily tips to help you manage your sugar levels effectively.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
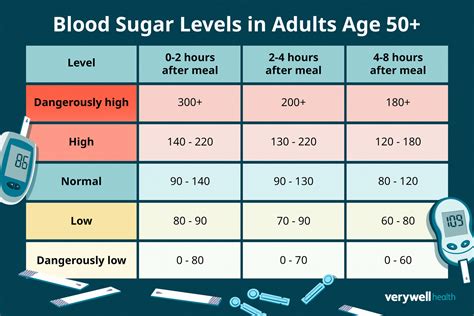
Before we dive into the tips, it’s essential to understand the importance of blood sugar levels and their ideal range. Blood sugar, or glucose, is the primary source of energy for your body’s cells. The ideal blood sugar level range varies throughout the day, but generally, it’s as follows: - Fasting blood sugar (before eating): 70 to 99 mg/dL for people without diabetes, and less than 130 mg/dL for those with diabetes. - After eating: Less than 140 mg/dL for people without diabetes, and less than 180 mg/dL for those with diabetes.
Dietary Changes
Your diet plays a significant role in managing blood sugar levels. Here are some dietary tips: 1. Choose Complex Carbohydrates: Foods rich in fiber like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are digested slowly, which helps in gradual increase in blood sugar levels. 2. Incorporate Protein and Healthy Fats: Protein and healthy fats can help slow down the digestion of carbohydrates, thereby reducing the spike in blood sugar levels. Include foods like lean meats, fish, eggs, avocados, and nuts in your diet. 3. Limit Sugary Drinks and Foods: Avoid consuming sugary drinks and foods high in added sugars, as they can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. 4. Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water can help keep your blood sugar levels within a healthy range. Sometimes, thirst can be mistaken for hunger or a craving for sweets.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to dietary changes, incorporating the following lifestyle modifications can help manage blood sugar levels: 1. Regular Physical Activity: Exercise, especially aerobic exercises like walking, can help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week. 2. Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can improve insulin sensitivity, which helps the body to more effectively use insulin, thereby lowering blood sugar levels. 3. Stress Management: Chronic stress can elevate blood sugar levels. Engage in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. 4. Get Enough Sleep: Lack of quality sleep can affect blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night.
Monitoring and Medication Adherence
For individuals with diabetes, regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and adherence to medication are crucial: 1. Use a Glucose Meter: Regularly check your blood sugar levels as recommended by your healthcare provider to understand how different factors affect your levels. 2. Adhere to Your Medication Plan: If you’re prescribed diabetes medications, take them as directed. Your medication plan may need adjustments over time based on your blood sugar level trends.
Additional Tips
- Keep a Food Diary: Tracking what you eat and how it affects your blood sugar levels can provide valuable insights for managing your diet more effectively.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol can affect blood sugar levels and interact with diabetes medications. If you choose to drink, do so in moderation.
- Stay Informed and Connected: Joining a diabetes support group or consulting with a diabetes educator can provide additional tips and support tailored to your specific needs.
In conclusion, controlling sugar levels is a multifaceted process that involves dietary adjustments, lifestyle changes, regular monitoring, and, if necessary, medication adherence. By incorporating these daily tips into your routine and staying committed, you can effectively manage your blood sugar levels and lead a healthier life.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking your blood sugar levels depends on the type of diabetes you have and your treatment plan. Generally, people with type 1 diabetes or those using insulin therapy need to check their levels more frequently, often before meals and before bedtime, and occasionally after meals. For those with type 2 diabetes not using insulin, checking levels once or twice a day may be sufficient, but this can vary based on your health provider's recommendations and your specific condition.
What foods can help lower blood sugar levels?
+Foods that are rich in fiber and protein can help lower blood sugar levels. Examples include leafy greens, broccoli, citrus fruits, avocados, nuts, and seeds. Additionally, foods with a low glycemic index (GI) like whole grains, sweet potatoes, and most vegetables can help manage blood sugar levels because they are digested more slowly, causing a gradual rise in blood sugar.
Can stress affect my blood sugar levels?
+Yes, stress can affect your blood sugar levels. When you're under stress, your body releases stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones can cause a increase in blood sugar levels by stimulating the release of glucose stored in the body's cells and also by making the body more resistant to insulin. Practicing stress-reducing techniques can help mitigate this effect.
How can I prevent spikes in blood sugar levels after eating?
+To prevent spikes in blood sugar levels after eating, consider the following strategies: Eat smaller, more frequent meals to avoid overloading on carbohydrates at one time. Choose foods that are low on the glycemic index, which cause a slower and more gradual increase in blood sugar. Incorporate protein and healthy fats into your meals, as they can help slow down the digestion of carbohydrates. Finally, consider a short walk after meals to improve insulin sensitivity.
Can I still eat sweets if I have diabetes?
+While it's generally recommended to limit sweets and foods high in added sugars, an occasional treat can be part of a healthy meal plan if done thoughtfully. Consider the following: Keep portion sizes very small, choose sweets that are low in added sugars and rich in fiber and protein, and balance your dessert with other food choices throughout the day to maintain overall blood sugar control. It's also a good idea to discuss your diet with a diabetes educator or a registered dietitian who can provide personalized advice.
Implementing these strategies and staying informed about managing blood sugar levels can significantly improve your ability to control them and lead a healthier, more balanced life. Remember, managing diabetes or prediabetes is a journey that requires patience, persistence, and the right support.



