How To Lower Sugar 500 Fast? Action Plan
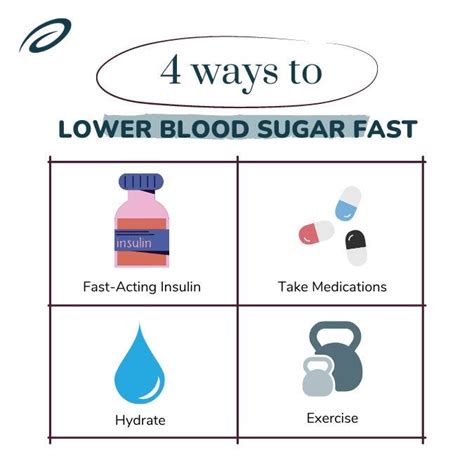
Lowering blood sugar levels quickly and safely requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, and, if necessary, medication adjustments under medical supervision. If your blood sugar level is 500 or higher, it’s considered a medical emergency, and you should seek immediate attention. However, for those looking to manage and lower their blood sugar levels effectively, here’s a structured action plan:
Understanding High Blood Sugar
Before diving into the action plan, it’s crucial to understand what high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) means. Blood sugar levels are considered high if they are above 180 mg/dL for people with diabetes, though this can vary based on the time of day, when you last ate, and other factors. Levels of 500 mg/dL or higher are dangerous and can lead to serious complications, including diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a potentially life-threatening condition.
Immediate Actions for Extremely High Blood Sugar (Above 500 mg/dL)
- Seek Medical Attention: If your blood sugar is this high, you need immediate medical care. Do not attempt to treat yourself without consulting a healthcare provider.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink water to help your body remove excess glucose through urine.
Action Plan for Managing High Blood Sugar
1. Dietary Changes
- Reduce Carbohydrate Intake: Focus on lowering carb intake, especially from simple sugars and refined grains. Choose complex carbohydrates like whole grains, vegetables, and fruits.
- Increase Fiber Intake: Fiber can help slow down glucose absorption. Include foods high in fiber like beans, lentils, and leafy greens.
- Choose Proteins and Healthy Fats: Proteins and fats can help regulate blood sugar levels. Include lean proteins, nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil in your diet.
2. Lifestyle Modifications
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity can lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. However, if you have extremely high blood sugar, consult your doctor before starting any new exercise regimen.
- Stress Management: Stress can raise blood sugar levels. Engage in stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Sleep Hygiene: Ensure you get adequate sleep, as poor sleep quality and duration can affect blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity.
3. Medication and Monitoring
- Follow Your Medication Plan: If you are on medication for diabetes, follow your prescription carefully. Do not adjust your medication without consulting your healthcare provider.
- Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: Regularly check your blood sugar levels as advised by your healthcare provider to understand how different foods and activities affect your levels.
4. Stay Hydrated
- Drink Plenty of Water: Aim for at least 8 cups (64 ounces) of water a day, and consider increasing this amount if you have high blood sugar levels.
Long-Term Management
- Consult a Dietitian: A professional can help you develop a personalized meal plan.
- Regular Check-Ups: Regular health check-ups can help monitor your condition and make necessary adjustments to your management plan.
- Consider Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): CGM devices can provide real-time feedback on your glucose levels, helping you make informed decisions.
FAQs
What should I do if my blood sugar is over 500 mg/dL?
+If your blood sugar level exceeds 500 mg/dL, it is a medical emergency. Stay hydrated by drinking water, and immediately seek medical attention.
How can diet help lower blood sugar levels?
+Focusing on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help manage blood sugar levels. Reducing carbohydrate intake, especially from simple sugars, is also beneficial.
Can exercise lower blood sugar immediately?
+Yes, exercise can help lower blood sugar levels. However, if your blood sugar is extremely high (above 500 mg/dL), consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regimen to avoid complications.
Remember, managing high blood sugar requires a long-term commitment to lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and, if prescribed, medication adherence. Always consult with a healthcare provider before making significant changes to your regimen.