How To Manage Blood Sugar Glucose Range? Easy Tips
Maintaining a healthy blood sugar glucose range is crucial for overall well-being, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Blood sugar levels fluctuate throughout the day in response to various factors, including diet, physical activity, and stress. Understanding how to manage these fluctuations is essential for preventing complications and ensuring optimal health.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
Before diving into the management strategies, it’s vital to understand what blood sugar levels are and how they are measured. Blood sugar, or glucose, is a type of sugar that serves as the primary source of energy for the body’s cells. The levels of glucose in the blood are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL).
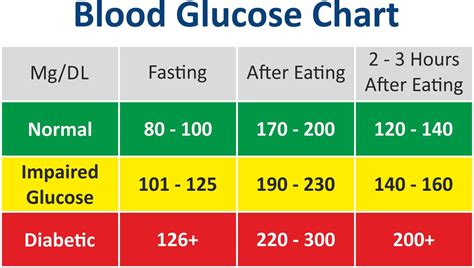
- Normal Blood Sugar Levels: For individuals without diabetes, normal blood sugar levels are typically between 70 mg/dL and 140 mg/dL after eating. Before eating (fasting), levels should be below 100 mg/dL.
- Diabetic Blood Sugar Levels: For people with diabetes, the goal is to keep blood sugar levels as close to the normal range as possible. The American Diabetes Association suggests targets of less than 130 mg/dL before meals and less than 180 mg/dL after eating.
Easy Tips for Managing Blood Sugar Glucose Range
Managing blood sugar levels effectively requires a combination of lifestyle adjustments and, for some, medication. Here are several easy-to-implement tips that can help:
1. Dietary Changes
- Balanced Diet: Focus on consuming a balanced diet that includes plenty of vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and whole grains. These foods are rich in nutrients and fiber, which can help slow down the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream.
- Portion Control: Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid consuming too many carbohydrates at once, which can spike blood sugar levels.
- Glycemic Index: Choose foods with a low glycemic index (GI), as they are digested and absorbed more slowly, causing a gradual and lower peak in blood sugar.
2. Regular Physical Activity
- Exercise Routine: Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, for at least 150 minutes per week. Exercise helps improve the body’s sensitivity to insulin, which can lower blood sugar levels.
- Resistance Training: Incorporate resistance training into your exercise routine to build muscle. Muscle tissue burns more glucose than fat tissue, even at rest.
3. Stress Management
- Mindfulness and Relaxation: Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises. Stress can raise blood sugar levels and worsen diabetes symptoms.
4. Hydration
- Drink Plenty of Water: Staying hydrated can help the body regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
5. Sleep
- Adequate Sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night. Poor sleep quality and duration can negatively affect blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity.
6. Monitoring and Medication
- Regular Monitoring: For individuals with diabetes, regularly checking blood sugar levels can help identify patterns and make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication.
- Adherence to Medication: If prescribed medication to manage blood sugar levels, it’s crucial to take it as directed by your healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Managing blood sugar glucose range is a multifaceted process that involves dietary adjustments, regular physical activity, stress management, proper hydration, adequate sleep, and, for some, medication. By incorporating these easy tips into daily life, individuals can better control their blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications and improving overall health and well-being.
FAQ Section
What is the ideal blood sugar level after eating?
+The ideal blood sugar level after eating should be less than 180 mg/dL for individuals with diabetes, according to the American Diabetes Association. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate target for your specific situation.
Can exercise lower blood sugar levels immediately?
+Yes, exercise can lower blood sugar levels immediately by increasing the body’s sensitivity to insulin and facilitating the uptake of glucose by muscles. This effect can last for several hours after exercise.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on the type of diabetes, treatment plan, and individual factors. Generally, individuals with type 1 diabetes and those using insulin may need to check their levels more frequently than those with type 2 diabetes or who are managing their condition through diet and exercise. Consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best monitoring schedule for your specific needs.