How To Tell Your Dehydrated
Dehydration is a common condition that occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in, causing an imbalance in the body’s water and electrolyte levels. It can happen to anyone, regardless of age or health status, and can be caused by a variety of factors, including excessive sweating, diarrhea, vomiting, and certain medical conditions. But how do you know if you’re dehydrated?
Understanding the Signs and Symptoms of Dehydration
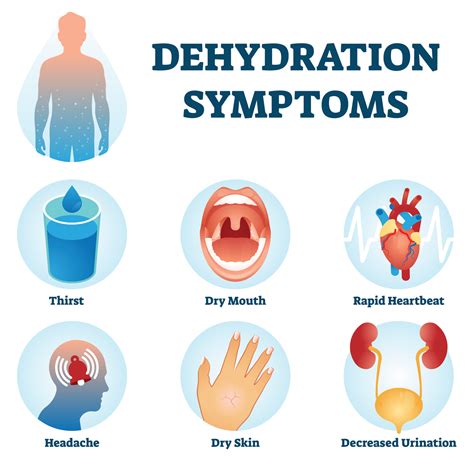
Dehydration can manifest itself in different ways, ranging from mild to severe. Here are some common signs and symptoms to look out for:
- Dry mouth and throat: One of the earliest signs of dehydration is a dry, sticky mouth and throat.
- Fatigue and weakness: Dehydration can cause feelings of fatigue, weakness, and a lack of energy.
- Headaches: Dehydration can lead to headaches, which can range from mild to severe.
- Dizziness and lightheadedness: Dehydration can cause dizziness and lightheadedness, especially when standing up or changing positions.
- Dark urine: If your urine is dark yellow or amber-colored, it may be a sign that you’re not drinking enough water.
- Decreased urine output: If you’re not urinating frequently enough, it can be a sign of dehydration.
- Rapid heartbeat: Dehydration can cause a rapid heartbeat, which can be a sign of severe dehydration.
Who is at Risk of Dehydration?
While anyone can become dehydrated, certain groups of people are more susceptible to dehydration than others. These include:
- Older adults: Older adults may be more prone to dehydration due to age-related changes in the body, such as decreased thirst sensation and changes in the body’s ability to regulate fluids.
- Young children: Young children are also at risk of dehydration, especially if they’re not drinking enough fluids or are experiencing diarrhea or vomiting.
- Athletes and individuals who engage in strenuous physical activity: Athletes and individuals who engage in strenuous physical activity may be at risk of dehydration due to excessive sweating.
- People with certain medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, kidney disease, and heart disease, can increase the risk of dehydration.
How to Treat Dehydration
If you’re experiencing symptoms of dehydration, it’s essential to treat it promptly to prevent complications. Here are some steps you can take:
- Drink plenty of fluids: Drink water, clear broths, or electrolyte-rich beverages, such as sports drinks.
- Rest: Rest and avoid strenuous activity to help your body recover.
- Eat hydrating foods: Eat foods that are high in water content, such as watermelon, cucumbers, and celery.
- Avoid caffeine and sugary drinks: Avoid consuming caffeine and sugary drinks, which can exacerbate dehydration.
Preventing Dehydration
Preventing dehydration is always better than treating it. Here are some tips to help you stay hydrated:
- Drink plenty of water: Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water a day.
- Monitor your urine output: If your urine is dark yellow or amber-colored, it may be a sign that you’re not drinking enough water.
- Eat hydrating foods: Eat foods that are high in water content, such as watermelon, cucumbers, and celery.
- Avoid excessive sweating: Avoid engaging in strenuous physical activity, especially in hot weather.
FAQs
What are the most common causes of dehydration?
+The most common causes of dehydration include excessive sweating, diarrhea, vomiting, and certain medical conditions, such as diabetes and kidney disease.
How can I tell if I'm dehydrated?
+You can tell if you're dehydrated by looking out for signs and symptoms, such as dry mouth and throat, fatigue and weakness, headaches, dizziness and lightheadedness, dark urine, and decreased urine output.
What are the best ways to treat dehydration?
+The best ways to treat dehydration include drinking plenty of fluids, resting, eating hydrating foods, and avoiding caffeine and sugary drinks.
How can I prevent dehydration?
+You can prevent dehydration by drinking plenty of water, monitoring your urine output, eating hydrating foods, and avoiding excessive sweating.
What are the complications of dehydration?
+The complications of dehydration include seizures, brain damage, and even death. It's essential to treat dehydration promptly to prevent these complications.
By understanding the signs and symptoms of dehydration, who is at risk, how to treat it, and how to prevent it, you can stay hydrated and healthy. Remember to always drink plenty of fluids, monitor your urine output, eat hydrating foods, and avoid excessive sweating to prevent dehydration. If you’re experiencing symptoms of dehydration, treat it promptly to prevent complications.