How To Use Gi Chart? Lower Blood Sugar Tips
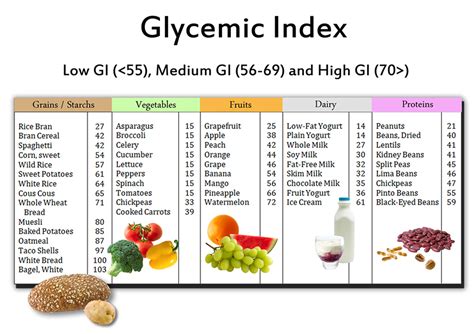
Understanding and utilizing the glycemic index (GI) chart is a powerful tool for managing blood sugar levels, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those looking to maintain a healthier diet. The GI chart ranks foods on a scale from 0 to 100 based on how much they raise blood sugar levels after eating. Foods are categorized into three main groups: low GI (0-55), medium GI (56-69), and high GI (70 and above). The concept is simple: choose foods with a lower GI to help keep blood sugar levels more stable.
What is the Glycemic Index?
The glycemic index is a measure that ranks foods on a scale from 0 to 100 based on how much they raise blood sugar levels after eating. Pure glucose is used as the reference point and is set at 100. The GI of a food can vary depending on several factors, including the type of carbohydrate it contains, its ripeness, cooking method, and the portion size. Generally, foods with a lower GI value are digested more slowly, causing a slower and smaller rise in blood sugar levels.
How to Use the GI Chart for Lowering Blood Sugar
Identify Low GI Foods: Look for foods with a GI value of 55 or less. These include most fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. Incorporating these foods into your diet can help regulate blood sugar levels.
Combine Foods for a Balanced Meal: Mixing low GI foods with moderate to high GI foods can help balance out the meal’s overall GI. For example, eating whole grain bread (lower GI) with avocado (low GI) and eggs can provide a meal that is satisfying and less likely to cause a spike in blood sugar.
Portion Control: Even with low GI foods, overeating can lead to an excessive intake of carbohydrates, which can affect blood sugar levels. Paying attention to serving sizes is crucial.
Be Mindful of Processing and Preparation: The more processed a food is, the higher its GI tends to be. Choosing whole, unprocessed foods as much as possible can help manage blood sugar levels. Additionally, how a food is prepared can affect its GI. For example, mashed potatoes have a higher GI than boiled potatoes because they are broken down more quickly during digestion.
Educate Yourself: Continuously learn about the GI of different foods. There are many resources available, including books, websites, and mobile apps, that provide detailed GI charts and dietary advice.
Practical Tips for Lowering Blood Sugar
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve overall health.
- Increase Physical Activity: Regular exercise can help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Monitor Your Carbohydrate Intake: Being mindful of the amount and type of carbohydrates consumed can significantly impact blood sugar management.
- Get Enough Sleep: Lack of sleep can disrupt hormones that regulate hunger and fullness, leading to overeating and poor food choices.
- Reduce Stress: Chronic stress can affect blood sugar levels. Engaging in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help.
Implementing GI in Daily Meals
For a practical approach, consider the following meal ideas that incorporate low GI foods: - Breakfast: Oatmeal with fruit and nuts, or whole-grain toast with avocado and eggs. - Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with mixed greens, cherry tomatoes, and a vinaigrette dressing, or a whole-grain pita stuffed with roasted vegetables and hummus. - Dinner: Grilled salmon with roasted sweet potatoes and steamed broccoli, or lentil soup with whole-grain bread.
Conclusion
The glycemic index is a valuable tool for anyone looking to manage their blood sugar levels more effectively. By understanding how different foods affect blood sugar and making informed choices, individuals can better control their diet and improve their overall health. Remember, the key to successful blood sugar management is balance, portion control, and a variety of whole, nutrient-dense foods.
What is the primary benefit of using the GI chart for diet planning?
+The primary benefit of using the GI chart is to help manage blood sugar levels by choosing foods that cause a slower and smaller rise in blood sugar, thereby reducing the risk of diabetes and other health issues.
How does the ripeness of fruit affect its GI?
+The ripeness of fruit can increase its GI because as fruit ripens, its starches convert to sugars, making them easier to digest and thus potentially causing a quicker rise in blood sugar levels.
Can the GI of a meal be reduced by combining foods?
+Yes, combining foods with different GIs can help balance out the overall GI of a meal. For example, pairing high GI foods with low GI foods can reduce the overall impact on blood sugar levels.



