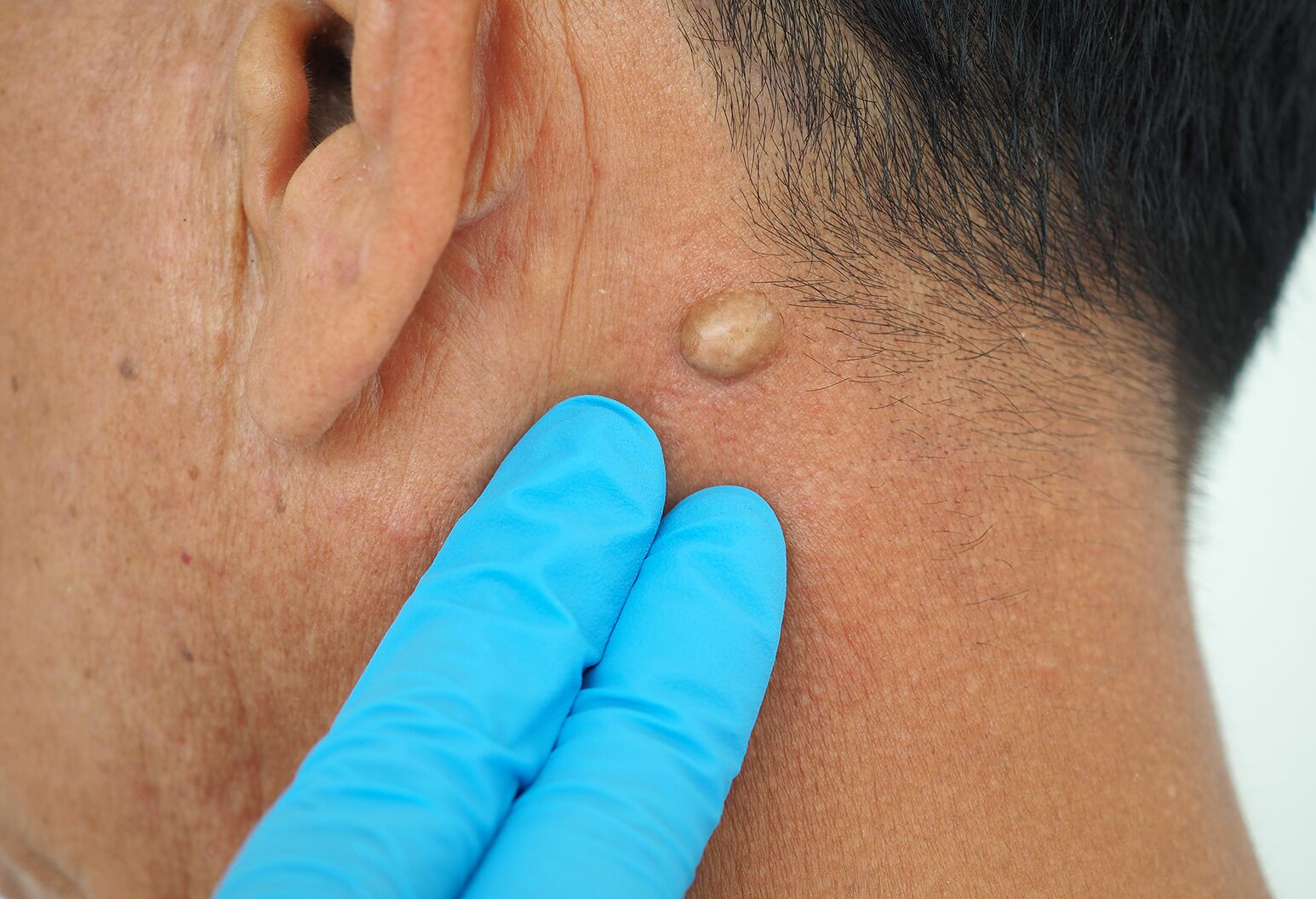
Infected Lymph Node
The lymphatic system, a complex network of vessels, organs, and tissues, plays a vital role in maintaining the body’s immune defense. One of the key components of this system is the lymph nodes, small, bean-shaped structures that filter lymph fluid, trapping pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses, and activating the immune response. However, when lymph nodes become infected, it can lead to a range of symptoms and complications. In this article, we will delve into the world of infected lymph nodes, exploring the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of this condition.
Understanding Lymph Nodes
Before we dive into the specifics of infected lymph nodes, it’s essential to understand the role of these tiny organs in the body. Lymph nodes are located throughout the body, with clusters found in the neck, armpits, groin, and abdomen. They act as filters, trapping harmful substances and microorganisms that enter the body through cuts, scrapes, or other means. When a lymph node detects the presence of a foreign invader, it springs into action, activating the immune system to fight the infection.
Causes of Infected Lymph Nodes
Infected lymph nodes, also known as lymphadenitis, can be caused by a range of factors, including:
- Bacterial infections: Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, and Escherichia coli are common culprits behind infected lymph nodes.
- Viral infections: Viruses such as HIV, herpes simplex, and cytomegalovirus can also lead to lymph node infections.
- Fungal infections: Fungi like Histoplasma capsulatum and Cryptococcus neoformans can infect lymph nodes, particularly in people with weakened immune systems.
- Parasitic infections: Certain parasites, such as Toxoplasma gondii, can also infect lymph nodes.
Symptoms of Infected Lymph Nodes
The symptoms of infected lymph nodes can vary depending on the location and severity of the infection. Common symptoms include:
- Swollen lymph nodes: Enlarged lymph nodes can be felt as tender, swollen lumps under the skin.
- Pain: Infected lymph nodes can be painful, especially when touched or moved.
- Redness and warmth: The skin over the infected lymph node may become red, warm, and inflamed.
- Fever: A low-grade fever can accompany infected lymph nodes, especially if the infection is caused by a bacterial or viral pathogen.
- Fatigue: Infected lymph nodes can cause fatigue, lethargy, and a general feeling of being unwell.
Diagnosis of Infected Lymph Nodes
Diagnosing infected lymph nodes typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. Your doctor may:
- Perform a physical examination: To check for swollen or tender lymph nodes.
- Take a medical history: To determine if you have recently been exposed to any infectious agents.
- Order laboratory tests: Such as blood tests, imaging studies (e.g., ultrasound, CT scan), or lymph node biopsies to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment of Infected Lymph Nodes
The treatment of infected lymph nodes depends on the underlying cause of the infection. Your doctor may prescribe:
- Antibiotics: To treat bacterial infections.
- Antiviral medications: To treat viral infections.
- Antifungal medications: To treat fungal infections.
- Supportive care: To manage symptoms, such as pain and fever, and prevent complications.
Prevention of Infected Lymph Nodes
While it’s not always possible to prevent infected lymph nodes, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk:
- Practice good hygiene: Wash your hands regularly, especially after coming into contact with someone who is sick.
- Get vaccinated: Stay up-to-date on recommended vaccinations to prevent infectious diseases.
- Avoid close contact: With people who have infectious diseases, such as tuberculosis or influenza.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and get enough sleep to keep your immune system strong.
Complications of Infected Lymph Nodes
If left untreated, infected lymph nodes can lead to complications, such as:
- Abscess formation: A pocket of pus can form within the infected lymph node, which may need to be drained surgically.
- Sepsis: A life-threatening condition that occurs when the infection spreads to the bloodstream.
- Lymphoma: A type of cancer that affects the lymphatic system.
Conclusion
Infected lymph nodes are a common condition that can be caused by a range of factors, including bacterial, viral, fungal, and parasitic infections. While symptoms can be uncomfortable and even painful, prompt treatment can help alleviate them and prevent complications. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of infected lymph nodes, you can take steps to protect your health and maintain a strong immune system.
What are the most common symptoms of infected lymph nodes?
+The most common symptoms of infected lymph nodes include swollen lymph nodes, pain, redness and warmth, fever, and fatigue.
How are infected lymph nodes diagnosed?
+Diagnosing infected lymph nodes typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as blood tests, imaging studies, or lymph node biopsies.
Can infected lymph nodes be prevented?
+While it's not always possible to prevent infected lymph nodes, practicing good hygiene, getting vaccinated, avoiding close contact with people who have infectious diseases, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can reduce your risk.
In conclusion, infected lymph nodes are a common condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of infected lymph nodes, you can take steps to protect your health and maintain a strong immune system. Remember to practice good hygiene, get vaccinated, and avoid close contact with people who have infectious diseases to reduce your risk of developing infected lymph nodes.