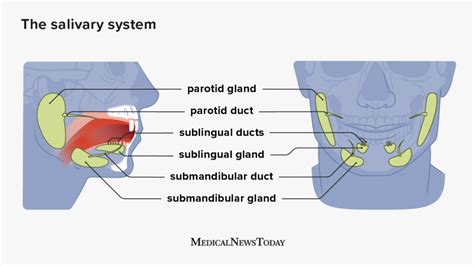
The parotid gland, one of the major salivary glands, plays a crucial role in the production of saliva, which aids in the digestion of food and maintains oral hygiene. However, like any other part of the body, the parotid gland is susceptible to infections, which can lead to a range of symptoms and complications. In this article, we will delve into the world of parotid gland infections, exploring the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
Understanding Parotid Gland Infections
Parotid gland infections, also known as parotitis, can be caused by a variety of factors, including bacterial, viral, and fungal pathogens. The most common cause of parotitis is the bacterial infection, which can be further divided into two categories: acute and chronic. Acute parotitis is typically caused by the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus, while chronic parotitis is often associated with the bacterium Streptococcus aureus.
Causes of Parotid Gland Infections
- Bacterial Infections: Bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Haemophilus influenzae can cause parotid gland infections.
- Viral Infections: Viruses such as the mumps virus, influenza virus, and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) can also lead to parotid gland infections.
- Fungal Infections: Fungal pathogens such as Aspergillus and Candida can cause parotid gland infections, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems.
- Blockage of the Parotid Duct: Blockage of the parotid duct, which carries saliva from the gland to the mouth, can lead to the accumulation of saliva and bacteria, resulting in infection.
- Reduced Saliva Production: Decreased saliva production, which can be caused by various factors such as dehydration, certain medications, or autoimmune disorders, can increase the risk of parotid gland infections.
Symptoms of Parotid Gland Infections
The symptoms of parotid gland infections can vary depending on the severity and type of infection. Common symptoms include:
- Swelling and Pain: Swelling and pain in the parotid gland area, which can radiate to the ear and jaw.
- Redness and Warmth: Redness and warmth of the skin over the parotid gland.
- Fever: Fever, which can range from mild to severe.
- Discharge: Purulent discharge from the parotid duct, which can be foul-smelling.
- Difficulty Swallowing: Difficulty swallowing due to pain and swelling.
- Loss of Appetite: Loss of appetite due to pain and discomfort.
Diagnosis of Parotid Gland Infections
Diagnosing parotid gland infections involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. The following tests may be used to diagnose parotid gland infections:
- Physical Examination: A physical examination of the parotid gland area to assess swelling, pain, and redness.
- Imaging Studies: Imaging studies such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) scan, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to visualize the parotid gland and detect any abnormalities.
- Laboratory Tests: Laboratory tests such as complete blood count (CBC), blood culture, and sensitivity testing to identify the causative pathogen.
- Fine-Needle Aspiration: Fine-needle aspiration of the parotid gland to collect a sample of fluid or tissue for examination.
Treatment Options for Parotid Gland Infections
The treatment of parotid gland infections depends on the severity and type of infection. The following treatment options may be used:
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics such as penicillin, amoxicillin, or clindamycin to treat bacterial infections.
- Pain Management: Pain management with over-the-counter or prescription pain medications.
- Warm Compresses: Warm compresses to reduce swelling and pain.
- Surgical Drainage: Surgical drainage of the parotid gland to remove accumulated pus and debris.
- Supportive Care: Supportive care such as hydration, rest, and a soft diet to manage symptoms and promote healing.
Prevention Strategies for Parotid Gland Infections
Preventing parotid gland infections involves maintaining good oral hygiene, staying hydrated, and managing underlying medical conditions. The following prevention strategies may be used:
- Good Oral Hygiene: Practicing good oral hygiene such as brushing and flossing teeth regularly to reduce the risk of bacterial infections.
- Staying Hydrated: Staying hydrated to maintain saliva production and prevent dehydration.
- Managing Underlying Medical Conditions: Managing underlying medical conditions such as diabetes, autoimmune disorders, and HIV to reduce the risk of parotid gland infections.
- Avoiding Trauma: Avoiding trauma to the parotid gland area to prevent injury and infection.
What are the common causes of parotid gland infections?
+Parotid gland infections can be caused by bacterial, viral, and fungal pathogens, as well as blockage of the parotid duct and reduced saliva production.
What are the symptoms of parotid gland infections?
+The symptoms of parotid gland infections include swelling and pain in the parotid gland area, redness and warmth of the skin, fever, discharge, difficulty swallowing, and loss of appetite.
How are parotid gland infections diagnosed?
+Parotid gland infections are diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests such as imaging studies, laboratory tests, and fine-needle aspiration.
What are the treatment options for parotid gland infections?
+The treatment options for parotid gland infections include antibiotics, pain management, warm compresses, surgical drainage, and supportive care.
How can parotid gland infections be prevented?
+Parotid gland infections can be prevented by maintaining good oral hygiene, staying hydrated, managing underlying medical conditions, and avoiding trauma to the parotid gland area.
In conclusion, parotid gland infections are a serious medical condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk of developing parotid gland infections and manage symptoms effectively. Remember, maintaining good oral hygiene, staying hydrated, and managing underlying medical conditions are key to preventing parotid gland infections and promoting overall health and well-being.