Inhalers For Copd
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung condition characterized by long-term breathing problems and poor airflow. The disease is often associated with a combination of emphysema and chronic bronchitis, and its symptoms can range from mild to severe. Managing COPD typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and the use of inhalers to help control symptoms and improve quality of life.
Understanding COPD Inhalers
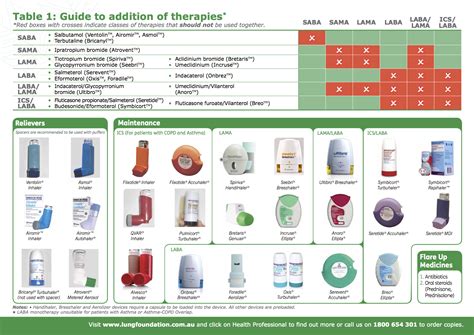
Inhalers for COPD are devices that deliver medication directly to the lungs, where it can help to open up the airways, reduce inflammation, and improve breathing. There are several types of inhalers available, including metered-dose inhalers (MDIs), dry powder inhalers (DPIs), and soft mist inhalers (SMIs). Each type of inhaler has its own unique characteristics and may be better suited for certain individuals or situations.
Types of Medications for COPD
There are several types of medications that can be used in inhalers to treat COPD, including:
- Bronchodilators: These medications help to relax the muscles around the airways, making it easier to breathe. There are two main types of bronchodilators: beta-agonists (such as salbutamol) and anticholinergics (such as tiotropium).
- Corticosteroids: These medications help to reduce inflammation in the airways, which can help to improve breathing and reduce symptoms. Examples of corticosteroids include fluticasone and budesonide.
- Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors: These medications help to reduce inflammation and improve lung function. An example of a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor is roflumilast.
Combination Inhalers for COPD
In some cases, a combination of medications may be used in a single inhaler to treat COPD. These combination inhalers can be convenient and may help to improve adherence to treatment. Examples of combination inhalers for COPD include:
- Fluticasone-salmeterol: This combination inhaler contains a corticosteroid (fluticasone) and a long-acting beta-agonist (salmeterol).
- Tiotropium-olodaterol: This combination inhaler contains an anticholinergic (tiotropium) and a long-acting beta-agonist (olodaterol).
Using Inhalers Effectively
To get the most out of an inhaler, it’s essential to use it correctly. Here are some tips for using an inhaler effectively:
- Read the instructions: Before using an inhaler, read the instructions carefully to make sure you understand how to use it correctly.
- Use the inhaler at the same time every day: Using an inhaler at the same time every day can help to establish a routine and improve adherence to treatment.
- Breathe out completely: Before inhaling the medication, breathe out completely to empty the lungs.
- Inhale slowly and deeply: Inhale the medication slowly and deeply, holding the breath for 10 seconds before exhaling.
- Rinse the mouth: After using an inhaler, rinse the mouth with water to help prevent thrush (a fungal infection).
It's essential to work with a healthcare provider to find the right inhaler and medication for COPD. They can help to determine the best course of treatment and provide guidance on how to use the inhaler effectively.
Managing Side Effects
While inhalers can be effective in managing COPD symptoms, they can also cause side effects. Common side effects of inhalers include:
- Thrush: A fungal infection that can cause white patches on the tongue and inside the mouth.
- Coughing: Some inhalers can cause coughing, especially when first starting treatment.
- Dry mouth: Some inhalers can cause dry mouth, which can increase the risk of tooth decay and other oral health problems.
To manage side effects, it’s essential to:
- Rinse the mouth: After using an inhaler, rinse the mouth with water to help prevent thrush.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help to prevent dry mouth and reduce the risk of oral health problems.
- Talk to a healthcare provider: If side effects are severe or persistent, talk to a healthcare provider about adjusting the treatment plan.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using an Inhaler
- Read the instructions carefully before using the inhaler.
- Remove the cap and shake the inhaler well.
- Breathe out completely to empty the lungs.
- Put the mouthpiece in the mouth and inhale slowly and deeply.
- Hold the breath for 10 seconds before exhaling.
- Rinse the mouth with water to help prevent thrush.
Conclusion
Inhalers are a common treatment for COPD, and they can be effective in managing symptoms and improving quality of life. By understanding the different types of inhalers and medications available, individuals with COPD can work with their healthcare provider to find the best course of treatment. Remember to use the inhaler correctly, manage side effects, and stay hydrated to get the most out of treatment.
What is the best type of inhaler for COPD?
+The best type of inhaler for COPD depends on the individual’s needs and preferences. A healthcare provider can help determine the best course of treatment and recommend the most suitable inhaler.
How often should I use my inhaler?
+The frequency of inhaler use depends on the medication and the individual’s treatment plan. It’s essential to follow the instructions provided by the healthcare provider and use the inhaler as directed.
Can I use my inhaler with other medications?
+It’s essential to talk to a healthcare provider before using an inhaler with other medications. Some medications can interact with each other, and a healthcare provider can help determine the best course of treatment.