Jaw Lymph Node Swelling
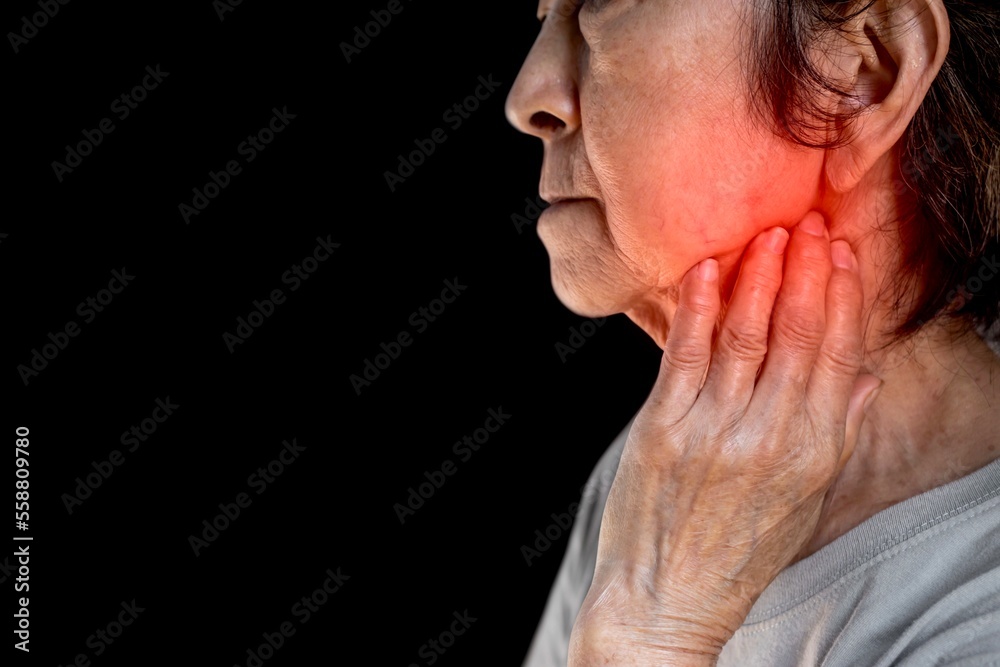
Swelling in the jaw lymph nodes can be a concerning symptom for many individuals, prompting a series of questions about its causes, implications, and potential treatments. Lymph nodes, small, bean-shaped structures that are part of the body’s lymphatic system, play a crucial role in filtering lymph fluid, trapping pathogens, and housing immune cells called lymphocytes. The jaw area, being rich in lymphatic tissue, can exhibit swelling due to a variety of reasons, ranging from benign, self-limiting conditions to more serious, potentially life-threatening diseases.
Understanding Jaw Lymph Node Swelling
To approach jaw lymph node swelling, it’s essential to understand the basic function of lymph nodes and how they respond to infection or inflammation. When the body detects foreign substances or pathogens, the lymph nodes in the affected area can become enlarged as they produce more immune cells to fight off the invader. This swelling is a natural response and can be accompanied by other symptoms such as pain, redness, and warmth in the area.
Causes of Jaw Lymph Node Swelling
The causes of jaw lymph node swelling are diverse, reflecting the wide range of infectious, inflammatory, and neoplastic conditions that can affect the head and neck region. Some of the common causes include:
- Infections: Dental infections, such as abscesses or periodontal disease, are common causes of jaw lymph node swelling. Viral infections like the common cold, flu, or mononucleosis can also lead to lymphadenopathy (enlargement of the lymph nodes).
- Allergic Reactions: Allergic reactions to substances like pollen, dust mites, or certain foods can cause lymph nodes to swell.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus, can lead to swollen lymph nodes.
- Cancer: Both lymphomas (cancers of the lymphatic system) and other types of cancer that metastasize to the lymph nodes can cause swelling in the jaw area.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
Diagnosing the cause of jaw lymph node swelling involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
- Clinical History and Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will typically start by taking a detailed history of the patient’s symptoms, including the duration of swelling, associated symptoms, and any recent infections or exposures. A physical examination will focus on assessing the size, tenderness, and mobility of the lymph nodes, as well as examining for any other signs of infection or disease in the head and neck region.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests can help identify signs of infection, inflammation, or autoimmune diseases. In some cases, a biopsy of the lymph node may be necessary to examine for cancer cells.
- Imaging Studies: Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI may be used to evaluate the size and characteristics of the lymph nodes and to look for any signs of infection or tumor in the surrounding tissues.
Treatment Approaches
The treatment of jaw lymph node swelling is highly dependent on the underlying cause.
- Infections: Antibiotics are prescribed for bacterial infections, while antiviral medications may be used for certain viral infections. Supportive care, such as pain management and rest, is also important.
- Allergic Reactions: Avoiding the allergen and using antihistamines or corticosteroids can help alleviate symptoms.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Treatment typically involves immunosuppressive drugs to reduce the immune system’s attack on the body’s own tissues.
- Cancer: Treatment may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these, depending on the type and stage of cancer.
Prevention and Self-Care
While not all causes of jaw lymph node swelling can be prevented, maintaining good oral hygiene, practicing safe sex, avoiding close contact with individuals who have infectious diseases, and getting vaccinated against certain viruses can reduce the risk of some infectious causes. Additionally, a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and not smoking, can help support the immune system.
Conclusion
Jaw lymph node swelling is a symptom that warrants medical evaluation to determine its underlying cause. By understanding the potential causes, recognizing the importance of a thorough diagnosis, and following appropriate treatment plans, individuals can address this symptom effectively and improve their overall health. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider if symptoms persist or worsen over time, as timely intervention can significantly impact outcomes, especially in cases of serious underlying conditions.
FAQ Section
What are the common symptoms associated with jaw lymph node swelling?
+Common symptoms include pain or tenderness in the jaw, swelling in the face or neck, fever, and general feeling of illness. In some cases, there may be difficulty swallowing or breathing if the swelling is significant.
How is the cause of jaw lymph node swelling diagnosed?
+Diagnosis involves a combination of clinical history, physical examination, laboratory tests such as blood work, and imaging studies like ultrasound or CT scans. In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to rule out cancer.
Can jaw lymph node swelling be a sign of cancer?
+What are the treatment options for jaw lymph node swelling?
+Treatment options vary depending on the cause and can include antibiotics for infections, antihistamines or corticosteroids for allergic reactions, immunosuppressive drugs for autoimmune diseases, and surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy for cancer.



