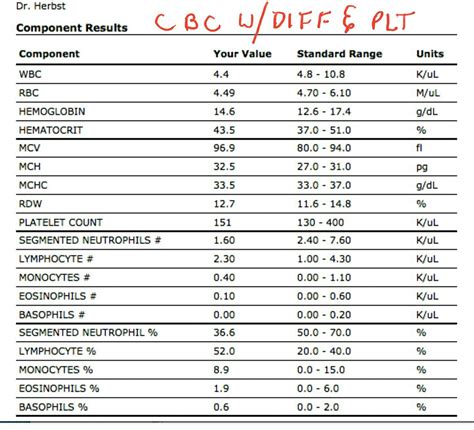
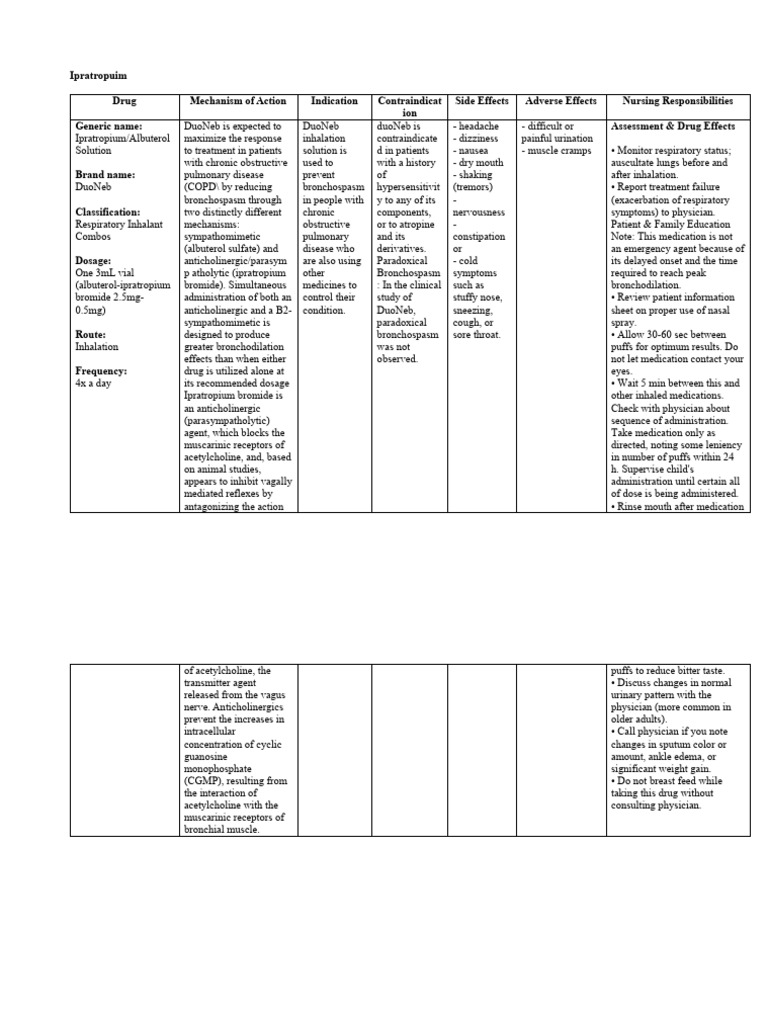
Kaiser Guide: Comprehensive Care Options

In the realm of healthcare, the term “comprehensive care” refers to a holistic approach that encompasses the physical, emotional, and social aspects of a patient’s well-being. This concept is at the core of the Kaiser model, a renowned healthcare system that has been at the forefront of providing high-quality, patient-centered care for decades. At its essence, comprehensive care is about treating the whole person, not just the disease or condition, and it is this principle that guides the delivery of healthcare services within the Kaiser framework.
What is Comprehensive Care?
Comprehensive care is a healthcare approach that integrates a wide range of medical and social services to address the complex needs of patients. It emphasizes prevention, early intervention, and the management of chronic conditions, aiming to improve health outcomes, enhance the quality of life, and reduce healthcare costs in the long run. This approach requires a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals working together, sharing information, and coordinating their efforts to provide seamless, high-quality care.
Core Principles of Comprehensive Care
Several key principles underpin the concept of comprehensive care: - Patient-Centeredness: Care is tailored to the individual needs and preferences of the patient, ensuring that their values and wishes are respected and incorporated into the care plan. - Coordination: This involves the smooth transition of patients between different healthcare settings and providers, ensuring continuity of care. - Comprehensiveness: A wide range of services is offered, including preventive care, diagnosis, treatment, and management of chronic conditions, as well as palliative care. - Accessibility: Patients have easy access to the care they need, when they need it, with minimal barriers to seeking medical help. - Continuity: Care is provided over time, allowing for the development of a trusting relationship between the patient and their healthcare team.
The Kaiser Model
The Kaiser Permanente model is a prime example of a healthcare system that embodies the principles of comprehensive care. Founded in the 1940s, Kaiser Permanente is a non-profit healthcare organization that integrates healthcare delivery, financing, and insurance functions. This integration enables the organization to focus on preventive care, manage chronic conditions more effectively, and reduce costs by avoiding unnecessary tests and treatments.
Key Features of the Kaiser Model
- Integrated Delivery System: Kaiser Permanente operates its own hospitals, clinics, and medical offices, employing its own physicians and other healthcare professionals. This vertical integration allows for better coordination of care.
- Preventive Medicine: A strong emphasis is placed on preventive care, including health screenings, vaccinations, and health education, aiming to prevent illnesses rather than just treating them.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): The use of EHRs facilitates the sharing of patient information among healthcare providers, enhancing care coordination and reducing errors.
- Patient Engagement: Programs are in place to empower patients to take an active role in their health care, including self-management support for chronic conditions and online access to medical records and communication with healthcare providers.
Achievements and Benefits
The Kaiser model has been associated with several benefits, including improved health outcomes, higher patient satisfaction, and more efficient use of healthcare resources. Studies have shown that patients within the Kaiser system tend to have better control of chronic conditions, such as diabetes and hypertension, and are less likely to be hospitalized for preventable conditions. Moreover, the focus on preventive care and early intervention helps in reducing healthcare costs over time.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its successes, the Kaiser model, like any healthcare system, faces challenges. These include adapting to changing population health needs, managing the increasing complexity of healthcare, and addressing healthcare disparities. The future of comprehensive care within the Kaiser framework will involve further leveraging technology, such as telehealth and advanced data analytics, to enhance patient engagement, improve care coordination, and personalize healthcare services.
Implementing Comprehensive Care: Lessons Learned
Implementing comprehensive care requires a systematic approach that includes: - Assessing Patient Needs: Understanding the comprehensive needs of patients, including their medical, social, and emotional requirements. - Building a Multidisciplinary Team: Assembling a team of healthcare professionals with diverse skills and expertise to address the range of patient needs. - Fostering Communication: Encouraging open communication among healthcare providers, patients, and families to ensure that care is well-coordinated and responsive to patient preferences. - Embracing Technology: Utilizing digital health technologies to support care coordination, patient engagement, and the management of chronic conditions.
Conclusion
Comprehensive care, as exemplified by the Kaiser model, represents a gold standard in healthcare delivery, focusing on the holistic needs of patients and aiming to achieve better health outcomes at lower costs. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, the principles of comprehensive care will remain fundamental, guiding healthcare systems towards a more patient-centered, efficient, and effective approach to caring for individuals and communities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the core principle of comprehensive care in the Kaiser model?
+The core principle of comprehensive care is treating the whole person, not just the disease, by integrating physical, emotional, and social aspects of care. This approach ensures that patients receive well-coordinated, high-quality care that addresses their comprehensive needs.
How does the Kaiser model achieve better health outcomes and higher patient satisfaction?
+The Kaiser model achieves better health outcomes and higher patient satisfaction through its integrated delivery system, emphasis on preventive care, use of electronic health records, and initiatives to engage patients in their healthcare. These elements work together to ensure care is well-coordinated, responsive to patient needs, and focused on prevention and early intervention.
What are some future directions for the Kaiser model in terms of comprehensive care?
+Future directions for the Kaiser model include further leveraging technology such as telehealth and advanced data analytics to enhance patient engagement, improve care coordination, and personalize healthcare services. There will also be a focus on adapting to changing population health needs, managing healthcare complexity, and addressing disparities in healthcare outcomes.