Medical Abbreviation Esbl
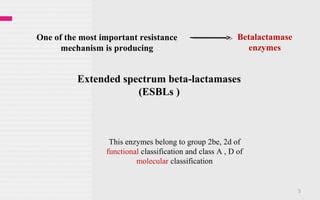
ESBL stands for Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase, which refers to a type of enzyme produced by certain bacteria that makes them resistant to a wide range of beta-lactam antibiotics. These antibiotics include penicillins, cephalosporins, and carbapenems, which are commonly used to treat bacterial infections.
Bacteria that produce ESBL enzymes are often referred to as ESBL-producing organisms or ESBL-positive bacteria. These bacteria are typically gram-negative, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Klebsiella pneumoniae, and can cause a variety of infections, including urinary tract infections, pneumonia, and bloodstream infections.
The presence of ESBL-producing bacteria is a significant concern in healthcare settings, as these bacteria can spread rapidly and cause severe infections that are difficult to treat. ESBL-producing bacteria are often resistant to multiple antibiotics, making treatment challenging.
The medical community uses various abbreviations related to ESBL, including:
- ESBLi: ESBL inhibitor
- ESBL-p: ESBL-producing
- ESBL-PE: ESBL-positive Enterobacteriaceae
- CRE: Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae, which can also produce ESBL enzymes
In clinical practice, healthcare professionals use ESBL-related abbreviations to communicate effectively and efficiently about patient care and treatment options. For example, a patient’s medical record might include notes such as “ESBL-positive E. coli” or “ treating with ESBL-active antibiotics.”
To combat the spread of ESBL-producing bacteria, healthcare facilities implement infection control measures, such as:
- Hand hygiene
- Contact precautions
- Environmental cleaning and disinfection
- Antibiotic stewardship programs
By understanding the significance of ESBL and its related abbreviations, healthcare professionals can provide better patient care and help prevent the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
In addition to ESBL, other medical abbreviations related to antibiotic resistance include:
- MRSA: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- VRE: Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus
- MDR: Multidrug-resistant
These abbreviations highlight the growing concern of antibiotic resistance and the need for effective infection control measures and antibiotic stewardship programs.
FAQ Section
What does ESBL stand for in medical terminology?
+ESBL stands for Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase, which refers to a type of enzyme produced by certain bacteria that makes them resistant to a wide range of beta-lactam antibiotics.
What types of bacteria produce ESBL enzymes?
+Bacteria that produce ESBL enzymes are typically gram-negative, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Why is ESBL a concern in healthcare settings?
+The presence of ESBL-producing bacteria is a significant concern in healthcare settings, as these bacteria can spread rapidly and cause severe infections that are difficult to treat.
How can healthcare professionals prevent the spread of ESBL-producing bacteria?
+Healthcare professionals can prevent the spread of ESBL-producing bacteria by implementing infection control measures, such as hand hygiene, contact precautions, environmental cleaning and disinfection, and antibiotic stewardship programs.
By understanding the ESBL abbreviation and its significance in medical terminology, healthcare professionals can provide better patient care and help prevent the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.



