The medication metformin has been a cornerstone in the treatment of type 2 diabetes for decades, thanks to its ability to lower blood glucose levels by decreasing glucose production in the liver and increasing insulin sensitivity. However, its uses extend far beyond the management of diabetes, and it has garnered significant attention in recent years for its potential benefits in weight loss, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) treatment, and even as a potential anti-aging agent.
Introduction to Metformin
Metformin belongs to the biguanide class of medications and is currently the most commonly prescribed oral antidiabetic drug in the world. Its mechanism of action is multifaceted, involving the inhibition of hepatic glucose production, enhancement of insulin sensitivity, and possibly even a mild increase in insulin secretion. These effects contribute to its efficacy in managing hyperglycemia in diabetic patients.
Metformin for Weight Loss
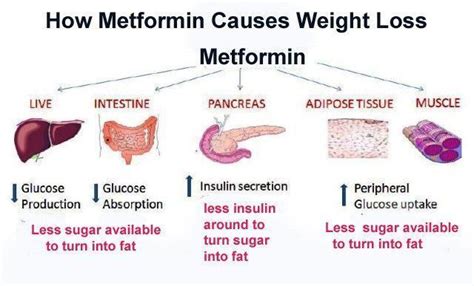
One of the notable side effects of metformin is weight loss, which has sparked interest in its potential as a treatment for obesity. Studies have shown that metformin can lead to a modest reduction in body weight, primarily through its effects on reducing appetite and food intake, as well as possibly altering the gut microbiome to favor weight loss. This makes metformin an attractive option for individuals with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes who are also struggling with their weight.
Mechanisms Behind Weight Loss
The exact mechanisms by which metformin induces weight loss are not entirely understood but are thought to involve several pathways: - Decreased Hunger: Metformin may decrease levels of ghrelin, the “hunger hormone,” leading to reduced appetite. - Increased Insulin Sensitivity: By improving the body’s response to insulin, metformin can help reduce the amount of glucose in the bloodstream, which in turn can reduce fat storage. - Modulation of the Gut Microbiome: There is emerging evidence that metformin can alter the composition of the gut microbiome in a way that promotes weight loss.
Metformin and PCOS
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder causing enlarged ovaries with small cysts on the outer edges. One of the common issues associated with PCOS is insulin resistance, which can lead to high blood sugar levels and contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. Metformin has been used off-label for the treatment of PCOS due to its ability to improve insulin sensitivity, which can help regulate menstrual cycles, improve ovulation, and reduce androgen levels (such as testosterone), thus alleviating some of the symptoms of PCOS.
Benefits for PCOS Patients
- Regulation of Menstrual Cycles: By improving insulin sensitivity, metformin can help regulate menstrual cycles in women with PCOS, which can improve fertility.
- Enhanced Fertility: Through its effects on ovulation, metformin can increase the chances of pregnancy in women with PCOS.
- Reduction of Androgen Levels: Lowering androgen levels can reduce the severity of acne and hirsutism, common symptoms of PCOS.
Metformin as an Anti-Aging Agent
There is a growing body of research suggesting that metformin may have anti-aging properties. The drug has been shown to extend the lifespan of various organisms, from worms to mice, by activating cellular pathways that promote longevity, such as AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). AMPK plays a key role in energy balance within the cell and has been implicated in the regulation of aging and age-related diseases.
Potential Anti-Aging Mechanisms
- Activation of AMPK: Metformin’s activation of AMPK has been linked to increased longevity and reduced incidence of age-related diseases.
- Mitochondrial Function: Improvement in mitochondrial function could delay the onset of aging and age-related diseases.
- Reduced Oxidative Stress: By decreasing oxidative stress, metformin may protect against cellular damage that contributes to aging.
Safety and Side Effects
While metformin is generally well-tolerated, it is not without side effects. Common adverse effects include gastrointestinal disturbances such as diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal bloating. A rare but serious side effect is lactic acidosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of lactic acid in the blood, which can be fatal if not treated promptly. It’s crucial for patients to adhere to the prescribed dosage and to monitor their kidney function, as metformin is contraindicated in patients with severe kidney disease.
Conclusion
Metformin’s utility extends far beyond its traditional role in diabetes management. Its effects on weight loss, its benefits for PCOS patients, and its potential as an anti-aging agent make it a versatile medication with a wide range of applications. As research continues to unravel the complex mechanisms behind metformin’s effects, its use is likely to expand, offering new hope for the treatment of various metabolic and age-related disorders.
What are the primary uses of metformin beyond diabetes treatment?
+Metformin is used for weight loss, particularly in individuals with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes, and for the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) due to its ability to improve insulin sensitivity. There is also emerging evidence suggesting its potential as an anti-aging agent.
How does metformin promote weight loss?
+Metformin promotes weight loss by reducing appetite, possibly altering the gut microbiome to favor weight loss, and improving insulin sensitivity, which helps reduce fat storage.
What are the potential anti-aging mechanisms of metformin?
+Metformin’s potential anti-aging effects are thought to be mediated through the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), improvement in mitochondrial function, and reduction in oxidative stress.