Mri Of Head
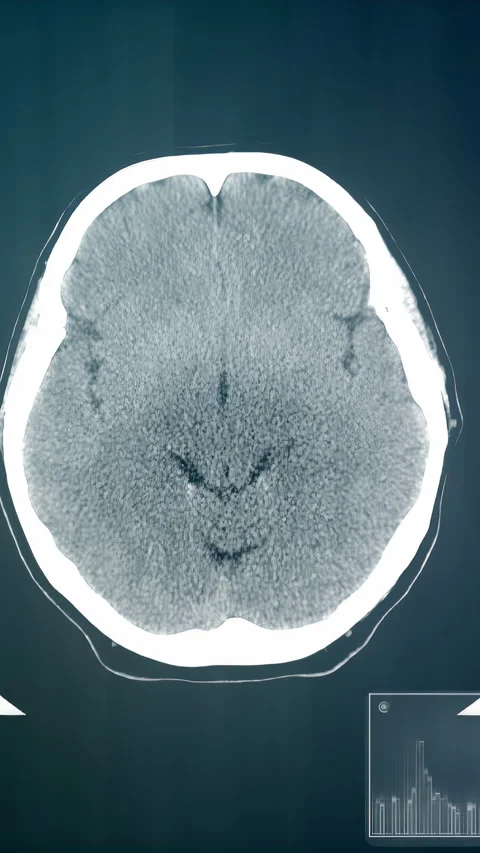
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of the head is a sophisticated diagnostic tool that has revolutionized the field of neurology and neuroscience. This non-invasive imaging technique provides detailed, high-resolution images of the brain and its surrounding structures, allowing healthcare professionals to diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions affecting the head and brain.
How MRI of the Head Works
MRI uses a combination of strong magnetic fields, radio waves, and computer technology to generate images of the brain and its surrounding tissues. During an MRI scan, the patient lies on a table that slides into a large, cylindrical machine. The machine contains a strong magnet that aligns the hydrogen atoms in the body, and radio waves are used to disturb these atoms, producing signals that are picked up by the machine’s sensors. These signals are then used to create detailed images of the brain and its structures.
Types of MRI Scans
There are several types of MRI scans that can be used to image the head, including:
- T1-weighted MRI: This type of scan is useful for visualizing the brain’s anatomy and is often used to diagnose conditions such as tumors, cysts, and vascular malformations.
- T2-weighted MRI: This type of scan is useful for visualizing the brain’s water content and is often used to diagnose conditions such as edema, inflammation, and infection.
- Diffusion-weighted MRI: This type of scan is useful for visualizing the brain’s white matter tracts and is often used to diagnose conditions such as stroke and multiple sclerosis.
- Functional MRI (fMRI): This type of scan is useful for visualizing the brain’s functional activity and is often used to diagnose conditions such as brain tumors, epilepsy, and psychiatric disorders.
Uses of MRI of the Head
MRI of the head is used to diagnose and monitor a wide range of conditions, including:
- Brain tumors: MRI is used to diagnose and monitor brain tumors, including benign and malignant tumors.
- Stroke and cerebrovascular disease: MRI is used to diagnose and monitor stroke and cerebrovascular disease, including ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke.
- Multiple sclerosis: MRI is used to diagnose and monitor multiple sclerosis, a chronic and often disabling disease that affects the central nervous system.
- Epilepsy: MRI is used to diagnose and monitor epilepsy, a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures.
- Head trauma: MRI is used to diagnose and monitor head trauma, including concussions and traumatic brain injury.
- Infection and inflammation: MRI is used to diagnose and monitor infections and inflammation of the brain and its surrounding tissues, including meningitis and encephalitis.
Benefits of MRI of the Head
MRI of the head has several benefits, including:
- High-resolution images: MRI provides high-resolution images of the brain and its surrounding tissues, allowing healthcare professionals to diagnose and monitor conditions with greater accuracy.
- Non-invasive: MRI is a non-invasive procedure, meaning that it does not require surgery or the insertion of instruments into the body.
- No radiation: MRI does not use ionizing radiation, making it a safer alternative to other imaging modalities such as CT scans.
- Functional information: MRI can provide functional information about the brain, including information about blood flow, metabolism, and neural activity.
Risks and Limitations of MRI of the Head
While MRI of the head is a safe and effective diagnostic tool, there are some risks and limitations to consider:
- Claustrophobia: Some patients may experience claustrophobia or anxiety during an MRI scan, which can be managed with sedation or other relaxation techniques.
- Metal objects: MRI is not suitable for patients with certain metal objects in their body, such as pacemakers or artificial joints.
- Contrast agents: Some patients may be allergic to contrast agents used in MRI scans, which can cause adverse reactions.
- Cost: MRI scans can be expensive, and some insurance plans may not cover the cost of the procedure.
Expert insight: MRI of the head is a powerful diagnostic tool that can provide valuable information about the brain and its surrounding tissues. However, it is essential to carefully evaluate the risks and limitations of the procedure and to discuss any concerns with a healthcare professional.
What is the difference between a CT scan and an MRI scan of the head?
+A CT scan uses ionizing radiation to produce images of the brain and its surrounding tissues, while an MRI scan uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves. MRI scans are generally considered safer and more effective for diagnosing conditions affecting the brain and its surrounding tissues.
Can I have an MRI scan if I have a pacemaker or artificial joint?
+No, MRI scans are not suitable for patients with certain metal objects in their body, such as pacemakers or artificial joints. However, some newer MRI machines may be compatible with certain types of metal implants, so it is essential to discuss any concerns with a healthcare professional.
How long does an MRI scan of the head take?
+The length of an MRI scan of the head can vary depending on the type of scan and the individual patient's needs. Typically, an MRI scan can take anywhere from 15 to 90 minutes to complete.
In conclusion, MRI of the head is a powerful diagnostic tool that can provide valuable information about the brain and its surrounding tissues. While there are some risks and limitations to consider, MRI scans are generally considered safe and effective for diagnosing and monitoring a wide range of conditions affecting the head and brain.