Muscle Strain Abdominal
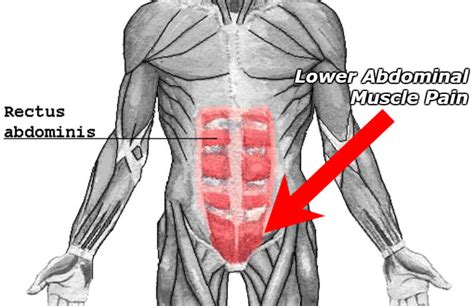
Muscle strain in the abdominal region is a common injury that can occur due to various reasons, including overuse, sudden contraction, or direct blows to the area. The abdominal muscles, which include the rectus abdominis, obliques, and transversus abdominis, play a crucial role in maintaining posture, supporting the spine, and facilitating movement. When these muscles are strained, it can lead to significant discomfort, pain, and limited mobility.
Understanding Abdominal Muscle Strain
Abdominal muscle strain typically occurs when the muscle fibers are stretched or torn, leading to inflammation and pain. This can happen due to various activities, such as heavy lifting, sudden twists, or repetitive movements. The severity of the strain can vary, ranging from mild to severe, and can be classified into three grades:
- Grade 1: Mild strain with minimal pain and limited mobility
- Grade 2: Moderate strain with noticeable pain and reduced mobility
- Grade 3: Severe strain with significant pain and substantial loss of mobility
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of abdominal muscle strain, including:
- Overuse: Engaging in repetitive activities, such as crunches or leg raises, without adequate rest and recovery
- Sudden contraction: Suddenly contracting the abdominal muscles, such as during a cough or sneeze
- Direct blows: Receiving a direct impact to the abdominal area, such as during contact sports
- Poor posture: Maintaining poor posture, which can put strain on the abdominal muscles
- Weak core: Having a weak core, which can increase the risk of muscle strain
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of abdominal muscle strain can vary depending on the severity and location of the injury. Common symptoms include:
- Pain: Aching or sharp pain in the abdominal region, which can worsen with movement or coughing
- Tenderness: Tenderness to the touch, which can be localized to a specific area
- Swelling: Swelling or bruising in the affected area
- Limited mobility: Reduced range of motion or difficulty performing daily activities
Diagnosing abdominal muscle strain typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and possibly imaging tests, such as an MRI or ultrasound.
Treatment and Management
Treatment for abdominal muscle strain depends on the severity of the injury and may involve a combination of the following:
- Rest: Avoiding activities that aggravate the condition and allowing the muscle to rest
- Ice: Applying ice to the affected area to reduce pain and inflammation
- Compression: Using compression bandages or wraps to support the muscle
- Elevation: Elevating the affected area to reduce swelling
- Pain management: Using over-the-counter pain medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, to manage pain and inflammation
- Physical therapy: Engaging in gentle exercises and stretches to promote healing and strengthen the muscle
Prevention and Recovery
Preventing abdominal muscle strain involves maintaining a strong core, engaging in regular exercise, and avoiding activities that can cause strain. To recover from abdominal muscle strain, it’s essential to:
- Gradually return to activity: Gradually returning to normal activities and exercises to avoid re-injury
- Strengthen the core: Engaging in exercises that strengthen the core muscles, such as planks and bridges
- Improve flexibility: Incorporating stretching exercises to improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension
- Maintain good posture: Maintaining good posture to reduce strain on the abdominal muscles
What are the most common causes of abdominal muscle strain?
+The most common causes of abdominal muscle strain include overuse, sudden contraction, direct blows, poor posture, and weak core muscles.
How long does it take to recover from abdominal muscle strain?
+Recovery time for abdominal muscle strain can vary depending on the severity of the injury, but typically ranges from a few days to several weeks.
Can abdominal muscle strain be prevented?
+Yes, abdominal muscle strain can be prevented by maintaining a strong core, engaging in regular exercise, and avoiding activities that can cause strain.
In conclusion, abdominal muscle strain is a common injury that can be caused by various factors, including overuse, sudden contraction, and direct blows. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help individuals prevent and manage this condition. By engaging in regular exercise, maintaining good posture, and strengthening the core muscles, individuals can reduce their risk of developing abdominal muscle strain and promote overall abdominal health.



