Musculoskeletal Chest Pain
Musculoskeletal chest pain is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide, often causing significant distress and disrupting daily life. This type of chest pain originates from the muscles, bones, and soft tissues surrounding the chest cavity, rather than from the heart or lungs. Despite its prevalence, musculoskeletal chest pain remains poorly understood, and its diagnosis can be challenging due to its similarity in presentation to other, more serious conditions.
Historically, the understanding of musculoskeletal chest pain has evolved significantly. In the past, it was often dismissed as a psychosomatic disorder, with patients being told that their symptoms were “all in their head.” However, as our knowledge of anatomy, physiology, and pain mechanisms has improved, so too has our appreciation for the complexity of musculoskeletal chest pain. Today, we recognize that this condition can result from a variety of factors, including muscle strain, poor posture, trauma, and repetitive motion injuries.
One of the primary challenges in diagnosing musculoskeletal chest pain is distinguishing it from other conditions that present with similar symptoms. For instance, chest pain can be a symptom of myocardial infarction (heart attack), pulmonary embolism, or pneumonia, all of which are medical emergencies. Therefore, a thorough medical evaluation is essential to rule out these potentially life-threatening conditions. This evaluation typically includes a detailed medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as electrocardiograms (ECGs), chest X-rays, and blood tests.
The management of musculoskeletal chest pain is multifaceted and may involve a combination of pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions. Pain relief medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or acetaminophen can be effective in reducing pain and inflammation. Additionally, physical therapy plays a crucial role in addressing underlying musculoskeletal issues, such as muscle imbalances or poor posture, through targeted exercises and stretches.
| Intervention | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Therapy | Customized exercises to improve posture, strengthen muscles, and enhance flexibility. |
| Medications | NSAIDs or acetaminophen for pain relief and reduction of inflammation. |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Changes in daily activities to avoid exacerbating factors, such as improving ergonomics at work or home. |
Lifestyle modifications are also essential in managing musculoskeletal chest pain. This includes making changes to daily activities to avoid exacerbating factors, such as improving ergonomics at work or home, taking regular breaks to stretch and move, and maintaining a healthy weight to reduce strain on the musculoskeletal system.
In some cases, musculoskeletal chest pain can be chronic, lasting for weeks, months, or even years. Chronic pain management often requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving not only medical treatments but also psychological support and alternative therapies such as acupuncture or massage. The goal of chronic pain management is to improve the patient’s quality of life by reducing pain, enhancing function, and promoting overall well-being.
Managing Chronic Musculoskeletal Chest Pain: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Consult with a healthcare provider to rule out other conditions and develop a personalized treatment plan.
- Engage in physical therapy to address musculoskeletal imbalances and improve posture.
- Utilize pain management medications as directed by a healthcare provider.
- Implement lifestyle changes to reduce strain on the musculoskeletal system.
- Consider alternative therapies such as acupuncture or massage for pain relief.
The future of managing musculoskeletal chest pain looks promising, with ongoing research into new treatments and therapies. For instance, advancements in physical therapy techniques, the development of new pain management medications, and a greater understanding of the role of mindfulness and cognitive-behavioral therapy in chronic pain management are expected to improve outcomes for patients.
In conclusion, musculoskeletal chest pain is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive and multifaceted approach to management. By understanding its causes, recognizing its presentation, and utilizing a combination of medical, physical, and lifestyle interventions, patients and healthcare providers can work together to alleviate symptoms, improve function, and enhance quality of life.
What are the common causes of musculoskeletal chest pain?
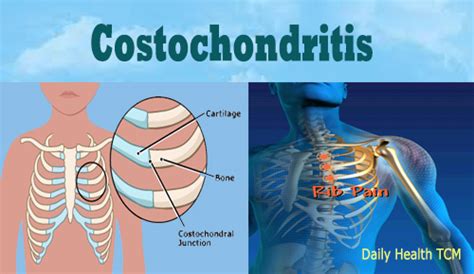
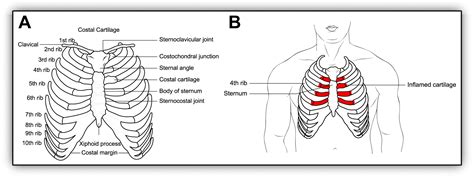
+Musculoskeletal chest pain can result from a variety of factors, including muscle strain, poor posture, trauma, and repetitive motion injuries. Additionally, conditions such as costochondritis (inflammation of the cartilage that connects the ribs to the breastbone) and Tietze’s syndrome (inflammation of the cartilages and surrounding tissues) can also cause musculoskeletal chest pain.
How is musculoskeletal chest pain diagnosed?
+Diagnosis involves a thorough medical evaluation, including a detailed medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as electrocardiograms (ECGs), chest X-rays, and blood tests to rule out other conditions. A healthcare provider may also perform specific maneuvers or movements to assess musculoskeletal structures.
What are the treatment options for musculoskeletal chest pain?
+Treatment options include pain relief medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. In some cases, alternative therapies such as acupuncture or massage may be recommended. The goal of treatment is to alleviate symptoms, improve function, and enhance quality of life.