Nerve Conduction Test

The human body is a complex network of interconnected systems, and one of the most fascinating aspects of its functioning is the way nerves transmit signals. Nerve conduction tests are a crucial diagnostic tool used to assess the health and functioning of the nervous system. In this article, we will delve into the world of nerve conduction tests, exploring what they are, how they work, and what they can reveal about our nervous system.
To understand the importance of nerve conduction tests, let’s first consider how nerves operate. Nerves are like electrical cables, transmitting signals between different parts of the body. These signals are vital for controlling various bodily functions, such as movement, sensation, and cognition. However, when nerves are damaged or diseased, these signals can be disrupted, leading to a range of symptoms, including numbness, weakness, and pain.
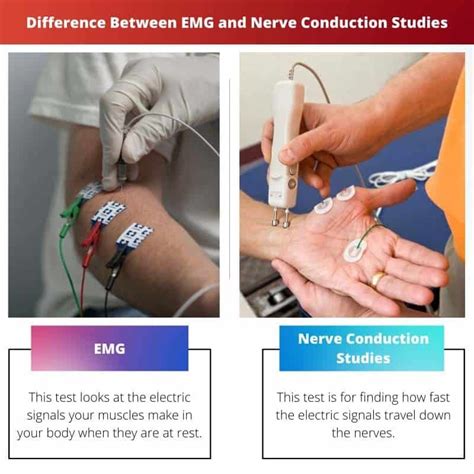
A nerve conduction test is a non-invasive procedure that measures the speed and strength of electrical signals as they travel through a nerve. The test involves placing electrodes on the skin, which emit small electrical impulses that stimulate the nerve. The resulting signals are then detected by other electrodes and recorded for analysis. By assessing the speed and strength of these signals, healthcare professionals can determine whether a nerve is functioning normally or if it’s being compromised by damage or disease.
One of the key benefits of nerve conduction tests is their ability to diagnose a range of neurological conditions. For example, they can help identify peripheral neuropathy, a condition characterized by damage to the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. This condition can cause symptoms such as numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hands and feet. Nerve conduction tests can also aid in the diagnosis of conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome, which affects the median nerve in the wrist, and Guillain-Barré syndrome, an autoimmune disorder that can cause muscle weakness and paralysis.
The process of undergoing a nerve conduction test is relatively straightforward. The test typically begins with the patient lying on an examination table or sitting in a chair. The healthcare professional will then clean and prepare the skin where the electrodes will be placed. The electrodes are usually attached to the skin using a gentle adhesive, and the patient may feel a mild tingling sensation as the electrical impulses are delivered.
Step-by-Step Guide to Nerve Conduction Tests
- Patient preparation: The patient lies on an examination table or sits in a chair, and the skin is cleaned and prepared for electrode placement.
- Electrode placement: Electrodes are attached to the skin using a gentle adhesive.
- Stimulation: The nerves are stimulated using small electrical impulses, which may cause a mild tingling sensation.
- Signal detection: The resulting signals are detected by other electrodes and recorded for analysis.
While nerve conduction tests are a valuable diagnostic tool, they do have some limitations. For example, they may not be able to detect certain types of nerve damage, such as small fiber neuropathy, which can cause symptoms like burning pain and numbness. Additionally, the test may be influenced by various factors, such as temperature, which can affect the speed of nerve conduction.
Pros and Cons of Nerve Conduction Tests
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Non-invasive and relatively painless | May not detect certain types of nerve damage |
| Can aid in the diagnosis of a range of neurological conditions | Results may be influenced by various factors, such as temperature |
| Can be used in conjunction with other diagnostic tools for comprehensive understanding | May require specialized equipment and training to perform |
In conclusion, nerve conduction tests are a powerful diagnostic tool that can provide valuable insights into the functioning of the nervous system. By measuring the speed and strength of electrical signals as they travel through nerves, healthcare professionals can diagnose a range of neurological conditions and develop effective treatment plans. While the test has its limitations, it remains an essential component of neurological diagnosis and treatment.
What is the purpose of a nerve conduction test?
+A nerve conduction test is used to assess the health and functioning of the nervous system by measuring the speed and strength of electrical signals as they travel through nerves.
How is a nerve conduction test performed?
+The test involves placing electrodes on the skin, which emit small electrical impulses that stimulate the nerve. The resulting signals are then detected by other electrodes and recorded for analysis.
What are the benefits of nerve conduction tests?
+Nerve conduction tests can aid in the diagnosis of a range of neurological conditions, including peripheral neuropathy, carpal tunnel syndrome, and Guillain-Barré syndrome. They are also non-invasive and relatively painless.


