Maintaining normal blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health, as it directly impacts the body’s ability to function properly. Blood sugar, or glucose, is the primary source of energy for the cells in the body. When we eat, our body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. The pancreas, an organ located behind the stomach, releases two main hormones that help regulate blood sugar levels: insulin and glucagon.
Insulin, often referred to as the “key” that unlocks cells to allow glucose to enter, is produced by the beta cells of the pancreas. When blood glucose levels rise after a meal, insulin is released to facilitate the entry of glucose into the cells, thereby lowering blood glucose levels. On the other hand, glucagon, produced by the alpha cells of the pancreas, raises blood glucose levels by stimulating the liver to release stored glucose (glycogen) into the bloodstream. This process is vital when we haven’t eaten for a while, as it ensures that our brain and other tissues receive the glucose they need to function properly.
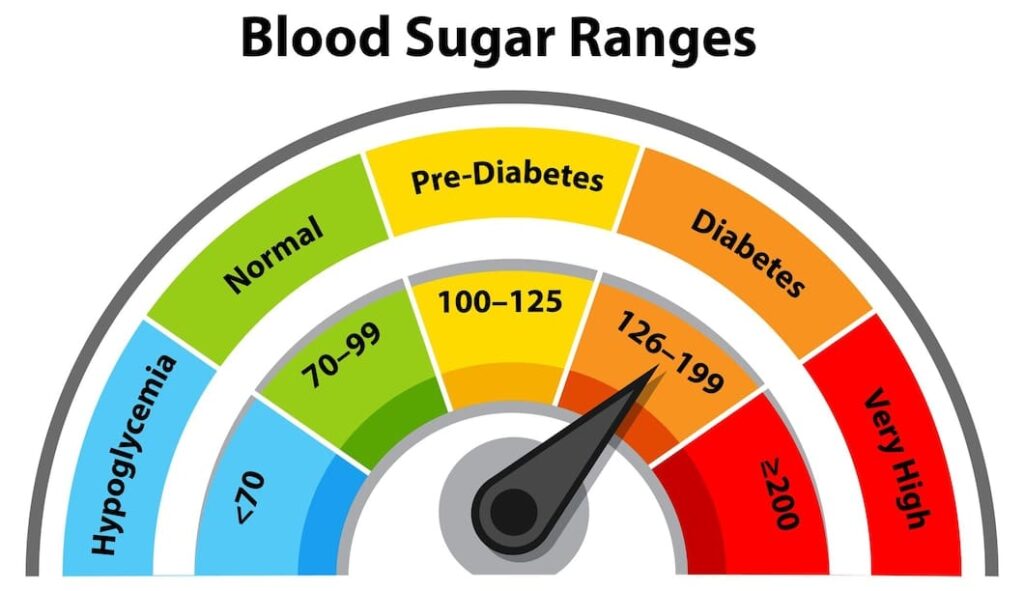
Normal blood sugar levels vary throughout the day, depending on when we last ate and the composition of our meals. Here’s a general guideline for what are considered normal blood sugar levels:
- Fasting Blood Sugar: This is the level of glucose in the blood after an overnight fast (not having eaten for at least 8 hours). Normal levels are typically between 70 and 99 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter).
- Postprandial Blood Sugar (After Eating): This level can vary more significantly, but ideally, it should be less than 140 mg/dL two hours after eating. However, the American Diabetes Association suggests that for people with diabetes, the target should be to keep their 2-hour postprandial glucose levels below 180 mg/dL to reduce the risk of complications.
- Random Blood Sugar: This test, performed at any time of day regardless of when the person last ate, should ideally show levels below 200 mg/dL to avoid indicating a problem with glucose regulation.
Maintaining these levels within the normal range is essential to prevent both short-term and long-term complications associated with abnormal blood sugar levels. Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) can lead to symptoms such as shakiness, dizziness, sweating, hunger, headaches, and even confusion or loss of consciousness in severe cases. On the other hand, hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) over time can lead to more severe complications, including damage to blood vessels, which can increase the risk of heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and other conditions.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
For individuals looking to manage their blood sugar levels, whether due to a predisposition towards diabetes, a diagnosis of prediabetes, or managing existing diabetes, several strategies can be employed:
Dietary Modifications: Eating a balanced diet that is rich in whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help manage blood sugar spikes. Foods with a low glycemic index are particularly beneficial as they release glucose more slowly and steadily.
Physical Activity: Regular exercise helps improve the body’s sensitivity to insulin, meaning glucose can enter the cells more efficiently. This doesn’t necessarily require intense workouts; even walking or light exercises can make a significant difference.
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of developing insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin, leading to elevated blood glucose levels.
Monitoring and Medication: For individuals with diabetes, regularly monitoring blood glucose levels and adhering to a prescribed medication regimen can help keep levels within the target range.
Stress Reduction: Stress can affect blood sugar levels, and engaging in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help manage this aspect.
Understanding and maintaining normal blood sugar levels is a critical aspect of health and wellness. By adopting healthy lifestyle choices and being proactive about monitoring and managing blood glucose, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of developing complications associated with abnormal blood sugar levels.
The Role of Technology in Blood Sugar Management
Technology has advanced significantly in recent years, offering a variety of tools that can aid in the management of blood sugar levels. From continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems that track glucose levels throughout the day to mobile apps that help track carbohydrate intake and physical activity, these tools can provide valuable insights and help make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication.
Implementing a Personalized Diabetes Management Plan
- Consult with a healthcare provider to discuss goals and create a tailored plan.
- Start monitoring blood glucose levels regularly to understand how different factors (food, exercise, stress) affect levels.
- Gradually introduce dietary changes, focusing on whole foods and balanced meals.
- Incorporate physical activity into the daily routine, aiming for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise per day.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
- Utilize technology, such as mobile apps or CGM systems, to help track and manage levels more effectively.
Conclusion
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels is a multifaceted process that involves dietary adjustments, regular physical activity, weight management, and for some, medication. By embracing a holistic approach to health and leveraging the support of healthcare professionals and technology, individuals can effectively manage their blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of diabetes and its associated complications.
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar?
+Symptoms can include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, cuts or wounds that are slow to heal, and tingling or numbness in the hands and feet.
How can I lower my blood sugar quickly?
+Drinking water, engaging in light physical activity, and taking medication as prescribed by a healthcare provider can help lower blood sugar levels. However, it’s crucial to do so under the guidance of a healthcare professional to avoid causing hypoglycemia.
What foods can help lower blood sugar?
+Foods with a low glycemic index, such as whole grains, non-starchy vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can help manage blood sugar levels. Specific foods like leafy greens, citrus fruits, and berries are also beneficial.