Normal Blood Sugar For Diabetic

Maintaining normal blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes. Diabetes, a chronic health condition, affects how your body turns food into energy, and it’s characterized by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or effectively use the insulin it produces (Type 2 diabetes). Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. When you have diabetes, managing blood glucose levels is key to preventing long-term complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, and nerve damage.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
Before diving into what constitutes normal blood sugar levels for diabetics, it’s essential to understand how blood sugar levels are measured and what the numbers mean. Blood glucose levels are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). The targets for blood sugar control can vary depending on the individual, their age, and other health conditions they may have, but general guidelines are as follows:
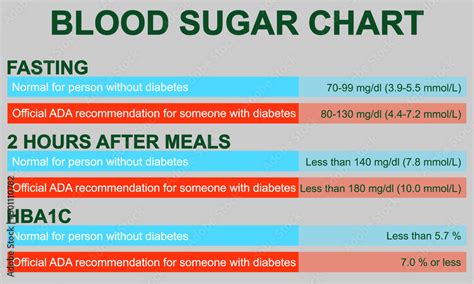
Fasting blood sugar: This test measures blood glucose after an overnight fast (not eating for at least 8 hours). For people without diabetes, normal fasting blood sugar levels are typically between 70 and 99 mg/dL. For those with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association suggests the following targets:
- For adults, a fasting blood sugar level of less than 130 mg/dL before meals and less than 180 mg/dL after meals.
- However, these targets may be adjusted based on individual factors, and some people might aim for levels between 80 and 130 mg/dL before meals and less than 180 mg/dL after meals.
After meals (postprandial): For individuals with diabetes, it’s recommended to keep blood sugar levels below 180 mg/dL 1 to 2 hours after the start of a meal.
HbA1c: This is a blood test that provides information about a person’s average levels of blood glucose over the past 3 months. For people with diabetes, an HbA1c level of less than 7% is generally considered a good target, though this can vary.
Achieving Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining blood sugar levels within a target range is crucial for managing diabetes effectively and preventing long-term complications. Here are several strategies to help achieve and maintain normal blood sugar levels:
Medication Adherence: If you’re prescribed diabetes medications, including insulin, metformin, or others, it’s crucial to take them exactly as directed by your healthcare provider.
Diet: Following a well-balanced diet that’s low in added sugars, salt, and unhealthy fats can help manage blood sugar levels. The American Diabetes Association recommends a variety of whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Physical Activity: Regular physical activity not only helps lower blood sugar levels but also improves insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week.
Monitoring Blood Sugar: Regular blood glucose monitoring can help you understand how different factors (like food, exercise, and medication) affect your blood sugar levels. This information can be used to make informed decisions about your diabetes care.
Stress Management: High levels of stress can increase cortisol levels, which can raise blood sugar levels. Engaging in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can be beneficial.
Sleep and Recovery: Getting enough quality sleep and allowing time for recovery after exercise are important. Poor sleep quality and insufficient sleep can disrupt hormones that regulate hunger and fullness, leading to overeating and weight gain, which can worsen insulin resistance.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes involves more than just keeping blood sugar levels in check; it’s about adopting a holistic approach to health that includes diet, exercise, stress management, and adhering to medication regimens. By understanding what normal blood sugar levels are and working towards maintaining them, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing complications and improve their quality of life. Always consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best targets and strategies for your specific situation.
FAQ Section
What is a normal blood sugar level for someone with diabetes?
+For individuals with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends the following blood sugar targets: less than 130 mg/dL before meals and less than 180 mg/dL after meals. However, these targets can vary based on individual factors.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of blood glucose monitoring depends on the type of diabetes you have, your treatment plan, and how well your blood sugar levels are controlled. Your healthcare provider can give you a personalized schedule.
Can diet and exercise alone control blood sugar levels?
+For some people with type 2 diabetes, particularly those who have been recently diagnosed, losing weight, eating a healthy diet, and engaging in regular physical activity can help manage blood sugar levels. However, many people will also need medication or insulin therapy to achieve their target blood sugar levels.
What happens if my blood sugar levels remain high?
+High blood sugar levels over time can lead to serious health problems, including heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems. It’s crucial to work with your healthcare team to bring your levels under control.
How can I prevent low blood sugar levels?
+Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) can be prevented by eating regular meals, avoiding skipping meals, not over-exercising without adjusting your food or medication, and monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly. Always carry a fast-acting source of glucose with you, like glucose tablets or juice, in case of an emergency.



