Normal Blood Sugar: Know Your Ideal Levels
Understanding and maintaining normal blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is an essential source of energy for the cells in the body. However, when blood sugar levels become too high or too low, it can lead to various health complications.
What are Normal Blood Sugar Levels?
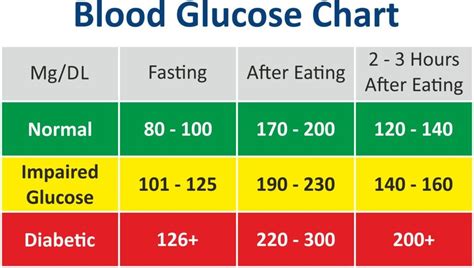
Normal blood sugar levels vary throughout the day, depending on factors such as the time of day, the type and amount of food consumed, and the individual’s physical activity level. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) provides the following guidelines for normal blood sugar levels:
- Fasting blood sugar: 70-99 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter)
- After eating (postprandial): Less than 140 mg/dL
- Before meals (preprandial): 70-130 mg/dL
It’s essential to note that these are general guidelines, and normal blood sugar levels may vary slightly from person to person.
The Impact of Blood Sugar on the Body
Blood sugar plays a vital role in the body’s functioning. When blood sugar levels are within the normal range, the body can function properly, and the cells can receive the energy they need. However, when blood sugar levels become too high or too low, it can lead to various health complications, such as:
- Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar): Can cause damage to the blood vessels, nerves, and organs, increasing the risk of heart disease, kidney disease, and other complications.
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar): Can cause symptoms such as shakiness, dizziness, and confusion, and if left untreated, can lead to seizures, coma, and even death.
Factors That Affect Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can affect blood sugar levels, including:
- Diet: The type and amount of carbohydrates, protein, and fat consumed can impact blood sugar levels.
- Physical activity: Regular exercise can help lower blood sugar levels, while a sedentary lifestyle can increase them.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids and certain psychiatric medications, can raise blood sugar levels.
- Stress: Stress can cause the body to release hormones that raise blood sugar levels.
- Sleep: Poor sleep quality and duration can affect blood sugar control.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels requires a combination of healthy lifestyle habits, including:
- Eating a balanced diet: Focusing on whole, unprocessed foods, such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water and limiting sugary drinks.
- Engaging in regular physical activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week.
- Getting enough sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night.
- Managing stress: Engage in stress-reducing activities, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
For individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition, monitoring blood sugar levels is crucial. This can be done using a glucose meter, which measures the amount of glucose in the blood. It’s essential to work with a healthcare provider to determine the best monitoring schedule and to set target blood sugar levels.
Conclusion
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels is essential for overall health. By understanding the factors that affect blood sugar levels and implementing healthy lifestyle habits, individuals can reduce their risk of developing complications associated with high or low blood sugar. If you have concerns about your blood sugar levels or are at risk of developing diabetes, consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar?
+The symptoms of high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) may include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds. If left untreated, high blood sugar can lead to more severe complications, such as diabetic ketoacidosis or hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome.
How can I lower my blood sugar levels quickly?
+If you have high blood sugar, it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance. However, some general tips to lower blood sugar levels quickly include drinking water, taking a short walk, or engaging in some light physical activity. It's also crucial to monitor your blood sugar levels and adjust your medication or insulin dosages as directed by your healthcare provider.
What are the risks of low blood sugar?
+Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) can be a life-threatening condition if left untreated. The risks of low blood sugar include confusion, seizures, loss of consciousness, and even death. It's essential to recognize the symptoms of low blood sugar, such as shakiness, dizziness, and confusion, and to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of these symptoms.
In conclusion, maintaining normal blood sugar levels requires a combination of healthy lifestyle habits, regular monitoring, and personalized guidance from a healthcare provider. By understanding the factors that affect blood sugar levels and taking proactive steps to manage them, individuals can reduce their risk of developing complications associated with high or low blood sugar.