Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health, as it directly impacts the body’s ability to function properly. Blood sugar, or glucose, is the primary energy source for the cells in the body. It is obtained from the food we eat, specifically from carbohydrates, and is regulated by insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. Understanding what constitutes normal blood sugar levels and how they are regulated can help in managing conditions like diabetes and preventing complications associated with abnormal blood sugar levels.
The Role of Insulin and Glucagon
Insulin and glucagon are two hormones that play a key role in regulating blood sugar levels. Insulin lowers blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose by cells, whereas glucagon raises blood sugar levels by stimulating the liver to release stored glucose (glycogen) into the bloodstream. This delicate balance between insulin and glucagon ensures that the body’s cells receive the energy they need without the blood becoming too concentrated with glucose, which can be harmful.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels
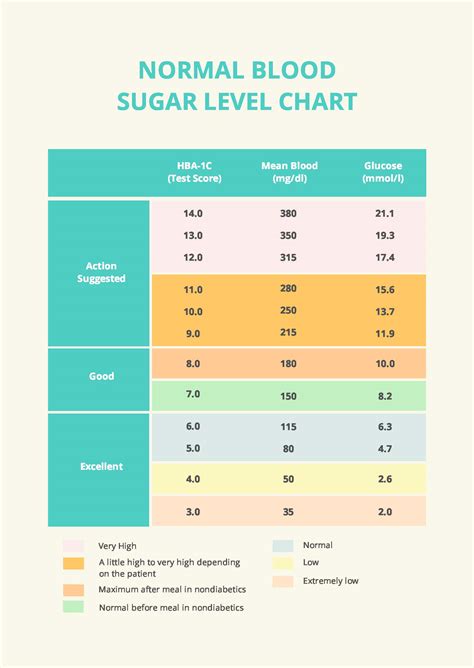
Normal blood sugar levels vary throughout the day, depending on when you last ate and what you consumed. Here are the general guidelines for normal blood sugar levels:
- Fasting Blood Sugar: Less than 100 mg/dL. This is your blood sugar level after an overnight fast, before eating anything in the morning.
- After Eating (Postprandial): Less than 140 mg/dL. This level should be checked 2 hours after eating to see how your body is managing the glucose from your meal.
- Before Meals: 70 to 130 mg/dL. Checking your blood sugar before meals helps ensure that it is within a healthy range.
Factors Affecting Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence blood sugar levels, including:
- Diet: Eating foods high in simple sugars or refined carbohydrates can cause spikes in blood sugar. Foods with a low glycemic index, on the other hand, can help maintain more stable blood sugar levels.
- Physical Activity: Regular physical activity can help lower blood sugar levels by increasing the body’s sensitivity to insulin.
- Medications: Certain drugs can affect blood sugar levels. For example, steroids can increase blood sugar, while some psychiatric medications can lower it.
- Stress: Stress can raise blood sugar levels by stimulating the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which in turn increase glucose release from energy stores.
Complications of Abnormal Blood Sugar Levels
Abnormally high or low blood sugar levels can lead to serious health complications:
- Hyperglycemia (High Blood Sugar): Prolonged high blood sugar levels can lead to diabetes and its complications, such as heart disease, kidney failure, and nerve damage.
- Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar): Severe low blood sugar can cause confusion, loss of consciousness, and even death if not promptly treated.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
For individuals with diabetes or those at risk, managing blood sugar levels involves a combination of lifestyle changes and, if necessary, medication:
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet that is low in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium can help manage blood sugar levels.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps the body use insulin more efficiently, lowering blood sugar levels.
- Monitoring: Regularly checking blood sugar levels helps in understanding how different factors affect your levels and in making informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication.
- Medication: For those with diabetes, medications like metformin or insulin therapy may be prescribed to help control blood sugar levels.
Strategies for Preventing Abnormal Blood Sugar Levels
Prevention is key when it comes to maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. Here are some strategies:
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water can help keep blood sugar levels stable.
- Choose Whole Foods:Whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats provide sustained energy and fiber, which can help regulate blood sugar.
- Limit Added Sugars: Foods with added sugars can cause significant spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity not only helps manage blood sugar levels but also improves overall health.
What is the normal range for blood sugar levels after eating?
+After eating, normal blood sugar levels should be less than 140 mg/dL. However, this can vary depending on the individual and the type of food consumed. It's best to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
How can diet affect blood sugar levels?
+Diet plays a significant role in managing blood sugar levels. Foods with a low glycemic index, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, can help keep blood sugar levels stable. On the other hand, foods high in simple sugars and refined carbohydrates can cause spikes in blood sugar.
What are the complications of having high blood sugar levels?
+Prolonged high blood sugar levels can lead to serious health complications, including heart disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision problems. It's crucial to manage blood sugar levels through a combination of diet, exercise, and, if necessary, medication.
Understanding and maintaining normal blood sugar levels is a crucial aspect of health management. By being informed about the factors that influence blood sugar and taking proactive steps towards a healthy lifestyle, individuals can prevent complications and improve their overall well-being. Regular monitoring, balanced diets, and physical activity are key elements in managing blood sugar levels, and seeking advice from healthcare professionals can provide personalized guidance tailored to individual needs.



