Normal Blood Sugar Levels Chart
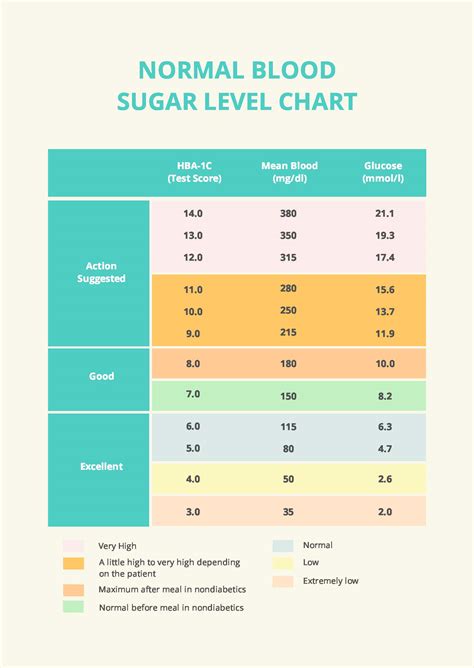
Understanding normal blood sugar levels is crucial for maintaining good health, whether you’re managing diabetes or simply aiming to keep your glucose levels in check. Blood sugar levels, also known as blood glucose levels, are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). The following chart provides a general guideline for normal blood sugar levels at different times of the day and in response to various conditions.
Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
- Normal: Less than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L)
- Prediabetes: 100 mg/dL to 125 mg/dL (5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L)
- Diabetes: 126 mg/dL or higher (7 mmol/L or higher)
After Eating (Postprandial)
- Normal: Less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) two hours after eating
- Prediabetes: 140 mg/dL to 199 mg/dL (7.8 to 11 mmol/L) two hours after eating
- Diabetes: 200 mg/dL or higher (11.1 mmol/L or higher) two hours after eating
Before Meals
- Normal: 70 mg/dL to 130 mg/dL (3.9 to 7.2 mmol/L)
- Target for Diabetes Management: Less than 130 mg/dL (7.2 mmol/L) for many people, but this can vary
At Bedtime
- Normal: 100 mg/dL to 140 mg/dL (5.6 to 7.8 mmol/L)
- For People with Diabetes: Often around 100 mg/dL to 140 mg/dL (5.6 to 7.8 mmol/L), but can vary based on treatment plans and individual health goals
During Pregnancy
- Normal Fasting: Less than 92 mg/dL (5.1 mmol/L)
- Normal One Hour After Eating: Less than 180 mg/dL (10 mmol/L)
- Normal Two Hours After Eating: Less than 153 mg/dL (8.5 mmol/L)
- Gestational Diabetes: These levels are slightly higher and can vary by individual and specific health guidelines.
Additional Considerations
- Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c): This test measures average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months.
- Normal: Less than 5.7%
- Prediabetes: 5.7% to 6.4%
- Diabetes: 6.5% or higher
It’s essential to remember that these are general guidelines. Your healthcare provider might have slightly different targets based on your age, other health conditions, the duration of your diabetes, your lifestyle, and your personal preferences. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice on managing your blood sugar levels.
Maintaining Normal Blood Sugar Levels
To keep your blood sugar levels within the normal range, consider the following strategies: - Diet: Focus on a diet rich in whole foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit your intake of sugary drinks and foods high in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium. - Exercise: Regular physical activity can help lower your blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week. You should also incorporate strength-training activities, high-intensity interval training, and other physical activities into your routine. - Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can improve your body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. If you’re overweight, losing even a small amount of weight can make a significant difference. - Stress Management: Stress can affect your blood sugar levels. Engage in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. - Medication and Monitoring: If you have diabetes, work closely with your healthcare provider to manage your condition. This may include taking medications as prescribed, monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly, and making lifestyle adjustments based on the data you collect.
By combining these strategies and understanding what normal blood sugar levels are, you can effectively manage your glucose levels and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes and prediabetes.



