Normal Value Of Pt Inr
The Prothrombin Time (PT) and International Normalized Ratio (INR) are crucial blood tests used to assess the blood clotting process, particularly in patients taking anticoagulant medications like warfarin. These tests measure how long it takes for blood to clot and compare it to a normal sample.
What is the normal value of PT/INR?
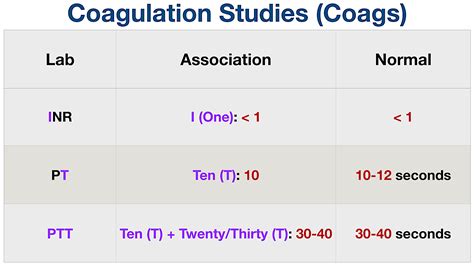
For individuals not taking anticoagulant medications, the normal range for Prothrombin Time (PT) is typically around 11-14 seconds, but this can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the specific test used. The International Normalized Ratio (INR) is a calculation based on the PT and is used to standardize the results across different laboratories. For people not on anticoagulant therapy, the normal INR range is usually between 0.9 and 1.1.
Understanding PT/INR Results:
PT (Prothrombin Time) Results:
- Normal: 11-14 seconds
- Prolonged (indicating a higher risk of bleeding): >14 seconds
- Shortened (indicating a higher risk of clotting): <11 seconds
INR (International Normalized Ratio) Results:
- Normal (for individuals not on anticoagulation therapy): 0.9-1.1
- Therapeutic range (for individuals on warfarin, varies depending on the condition being treated):
- For atrial fibrillation, deep vein thrombosis, or pulmonary embolism, the target INR range is usually between 2.0 and 3.0.
- For mechanical heart valves, the target INR range may be slightly higher, typically between 2.5 and 3.5.
Importance of Monitoring PT/INR:
For patients on warfarin or similar anticoagulants, regular monitoring of PT/INR is essential to ensure that the blood is within the therapeutic range. If the INR is too high, the patient is at an increased risk of bleeding. Conversely, if the INR is too low, the patient may not be adequately protected against clot formation. Adjustments to the anticoagulant dose are made based on the INR results to maintain the patient within the target therapeutic range.
Variability and Factors Influencing PT/INR:
Several factors can influence PT/INR results, including diet (notably vitamin K intake, which can counteract the effects of warfarin), other medications, alcohol consumption, and certain medical conditions. It’s crucial for individuals on anticoagulant therapy to maintain a consistent diet and lifestyle and to inform their healthcare provider about any changes or additions to their medication regimen.
Conclusion:
The normal value of PT/INR is a critical benchmark for assessing blood clotting status, especially in the management of anticoagulation therapy. Understanding the significance of these tests and the factors that can influence their results is essential for effective management and to minimize the risk of thrombotic or bleeding complications.