Opcon A Eye Drops
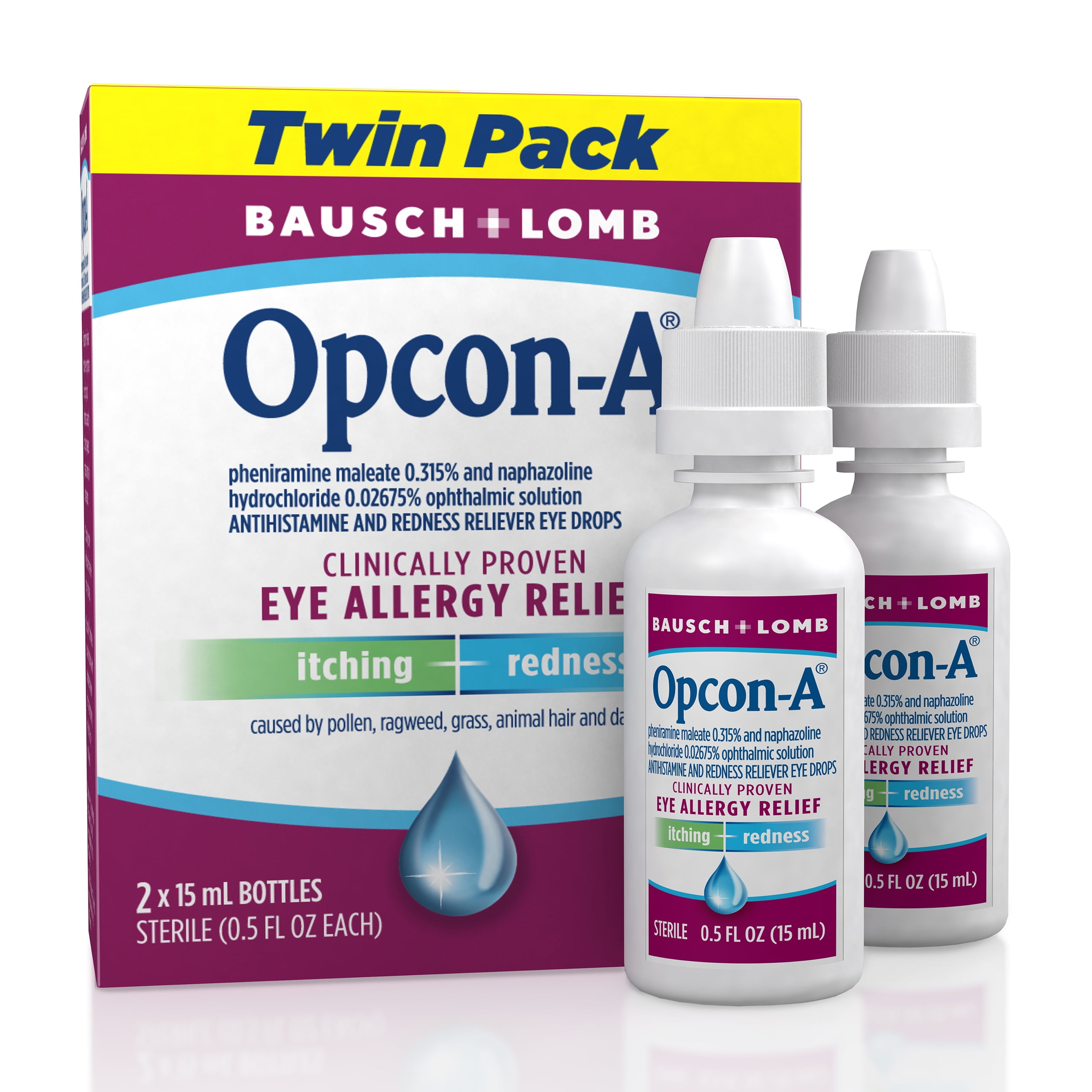
The realm of ophthalmic medications is vast and complex, with various formulations designed to address a wide range of eye-related issues. Among these, Opcon A Eye Drops stand out as a notable product, utilized for their antihistamine and vasoconstrictor properties. To understand the role and applications of Opcon A Eye Drops, it’s essential to delve into their composition, mechanism of action, and the conditions they are intended to treat.
Composition and Mechanism of Action
Opcon A Eye Drops primarily contain two active ingredients: naphazoline (a vasoconstrictor) and pheniramine (an antihistamine). Naphazoline works by constricting blood vessels in the conjunctiva, which helps reduce redness and swelling. Pheniramine, on the other hand, is effective in alleviating symptoms associated with allergic reactions, such as itching, redness, and tearing, by blocking the action of histamine—a chemical released by the body during an allergic response.
Uses and Applications
These eye drops are commonly recommended for the relief of symptoms associated with allergic conjunctivitis, which can include redness, itching, and excessive tearing. Allergic conjunctivitis occurs when the body’s immune system overreacts to foreign substances like pollen, dust mites, or pet dander, leading to the release of histamine and other chemical mediators, which in turn cause the symptoms. By combining an antihistamine with a vasoconstrictor, Opcon A Eye Drops address both the allergic response and the subsequent inflammation.
Administration and Precautions
When using Opcon A Eye Drops, it’s crucial to follow the instructions provided by a healthcare professional or those included with the packaging. Generally, this involves instilling one or two drops into the affected eye(s) up to four times a day. However, the frequency and duration of use should be guided by medical advice, as prolonged use of vasoconstrictors can lead to rebound congestion—a condition where the blood vessels become dependent on the medication to remain constricted, leading to increased redness when the medication wears off.
Furthermore, individuals with certain medical conditions, such as glaucoma, or those taking specific medications (like MAOIs), should exercise caution when using these drops. It’s also important to note that Opcon A Eye Drops are for external use only and should not be ingested.
Side Effects and Interactions
While generally considered safe when used as directed, Opcon A Eye Drops can cause side effects, including blurred vision, sensitivity to light, and dryness of the eye. In rare cases, more severe reactions can occur, such as increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and in susceptible individuals, these medications may exacerbate conditions like glaucoma due to their vasoconstrictive effects.
Interactions with other medications are also possible, particularly with those that have sympathomimetic properties (which mimic the effects of the sympathetic nervous system), as combining these can lead to increased blood pressure and other cardiovascular effects.
Comparison with Other Treatments
In the context of managing allergic conjunctivitis, there are several treatment options available, ranging from oral antihistamines to topical corticosteroids, depending on the severity and persistence of symptoms. Opcon A Eye Drops are often preferred for their rapid onset of action and localized effects, which minimize systemic side effects compared to oral medications. However, for chronic conditions or more severe allergic responses, other treatments may be necessary, underscoring the importance of a healthcare provider’s assessment in determining the best course of treatment.
Future Trends and Developments
The landscape of ophthalmic treatments is continually evolving, with advancements in drug delivery systems, novel antihistamines with reduced side effects, and a growing understanding of the complex interplay between allergic responses and the ocular surface. Future developments are likely to focus on improving the safety profile of current medications while enhancing their efficacy, possibly through more targeted therapeutic approaches that address the underlying mechanisms of allergic conjunctivitis without the need for vasoconstrictors.
Conclusion
Opcon A Eye Drops represent a valuable option in the management of allergic conjunctivitis, offering relief from symptoms through their combined antihistamine and vasoconstrictor effects. However, their use should be guided by medical advice to ensure safety and efficacy. As the field of ophthalmology continues to advance, the development of new treatments and the refinement of existing ones promise improved outcomes for individuals suffering from allergic eye conditions.
Key Points about Opcon A Eye Drops:
- Contain naphazoline and pheniramine to address allergic conjunctivitis symptoms.
- Provide relief from redness, itching, and tearing.
- Should be used under medical guidance due to potential side effects and interactions.
- Part of a broader spectrum of treatments for allergic eye conditions, each with its own benefits and drawbacks.
What are Opcon A Eye Drops used for?
+Opcon A Eye Drops are used for the relief of symptoms associated with allergic conjunctivitis, including redness, itching, and excessive tearing.
How often can I use Opcon A Eye Drops?
+The frequency of use should be guided by a healthcare professional, but generally, it is recommended to use one or two drops up to four times a day.
Can I use Opcon A Eye Drops with other medications?
+It's essential to consult with a healthcare provider before using Opcon A Eye Drops with other medications, as interactions are possible, particularly with sympathomimetic drugs.
As the discussion around Opcon A Eye Drops illustrates, the effective management of allergic conjunctivitis and other eye conditions requires a comprehensive understanding of available treatments, their applications, and potential limitations. By exploring the intricacies of these medications and staying informed about advancements in the field, individuals can make more informed decisions about their eye care, working in tandem with healthcare professionals to achieve the best possible outcomes.