Pantoprazole Is Used For
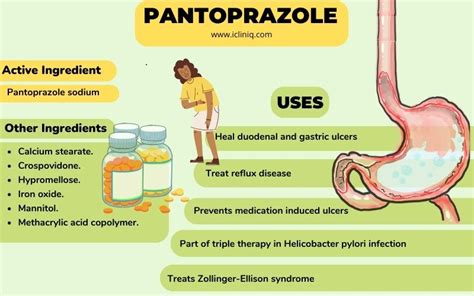
Pantoprazole is a type of medication known as a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) that is used to reduce the amount of acid produced in the stomach. It works by blocking the action of the proton pumps in the stomach lining, which are responsible for producing stomach acid. By decreasing the amount of acid in the stomach, pantoprazole can help to relieve symptoms and prevent complications associated with a range of conditions.
One of the primary uses of pantoprazole is to treat a condition known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), which occurs when stomach acid flows back up into the esophagus, causing symptoms such as heartburn, chest pain, and difficulty swallowing. Pantoprazole can help to reduce the frequency and severity of these symptoms, allowing individuals to eat and drink without discomfort.
Pantoprazole is also used to treat other conditions, including:
- Peptic ulcer disease: Pantoprazole can help to heal and prevent the recurrence of peptic ulcers, which are open sores that develop in the lining of the stomach or duodenum (the first part of the small intestine).
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome: This is a rare condition in which the stomach produces excessive amounts of acid, leading to severe ulceration and other complications. Pantoprazole can help to reduce acid production and alleviate symptoms.
- Stress ulcer prophylaxis: In critically ill patients, pantoprazole can be used to prevent stress ulcers, which are ulcers that develop in response to severe physical stress, such as that caused by trauma, burns, or surgery.
- Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) eradication: Pantoprazole can be used in combination with antibiotics to treat H. pylori infections, which are a common cause of peptic ulcers and other gastrointestinal disorders.
In addition to these uses, pantoprazole may also be prescribed for other conditions, such as functional dyspepsia, which is a term used to describe persistent or recurring upper abdominal symptoms, such as bloating, discomfort, and early satiety, that are not explained by other conditions.
Pantoprazole is generally well-tolerated, but like all medications, it can cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects include:
- Headache
- Diarrhea
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Dizziness
If you experience any of these side effects, it’s essential to discuss them with your doctor, as they may be able to adjust your dosage or recommend alternative treatments.
How to Take Pantoprazole
- Take pantoprazole exactly as directed by your doctor or pharmacist.
- Swallow the tablets whole with a glass of water, without crushing or chewing them.
- Take pantoprazole at the same time each day, preferably in the morning.
- Do not take pantoprazole with other medications that may interact with it, unless advised to do so by your doctor.
In conclusion, pantoprazole is a valuable medication for reducing stomach acid and alleviating symptoms associated with a range of gastrointestinal disorders. While it can be effective, it’s crucial to use pantoprazole under the guidance of a healthcare professional and to follow their instructions carefully to minimize the risk of side effects and ensure optimal treatment outcomes.
What is the typical dosage of pantoprazole for GERD?
+The typical dosage of pantoprazole for GERD is 40 mg once daily, taken in the morning.
Can pantoprazole be used for long-term treatment?
+Yes, pantoprazole can be used for long-term treatment of conditions such as GERD and peptic ulcer disease, but it should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Are there any potential interactions between pantoprazole and other medications?
+Yes, pantoprazole can interact with other medications, such as warfarin and clopidogrel, so it’s essential to inform your doctor or pharmacist about all medications you are taking before starting pantoprazole.



