Parotid Gland Infection: Causes & Cures
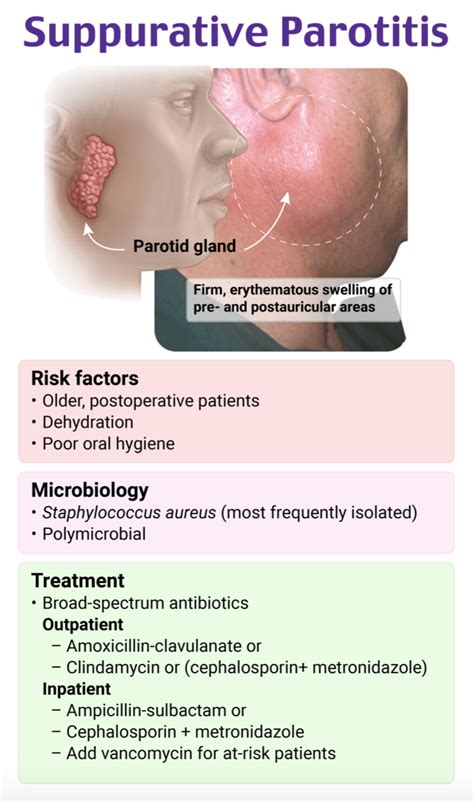
The parotid gland, one of the major salivary glands located on either side of the face, plays a crucial role in the production of saliva, which is essential for digestion, oral health, and the overall balance of the oral microbiome. However, this vital gland can sometimes become infected, leading to a condition known as parotid gland infection, or parotitis. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of parotid gland infections is essential for managing this condition effectively.
Causes of Parotid Gland Infection
Parotid gland infections can arise from various sources, including bacterial, viral, and, less commonly, fungal organisms. The most common cause of acute parotitis is bacterial infection, with Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus being prominent pathogens. These bacteria can enter the gland through the ductal system, which connects the gland to the mouth, or via the bloodstream from other infected sites in the body.
Viral infections, such as mumps, also known as epidemic parotitis, used to be a leading cause of parotid gland infection, especially in children. However, the introduction of the mumps vaccine has significantly reduced the incidence of this condition. Other viral infections and certain autoimmune conditions can also lead to parotid gland inflammation and infection.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase an individual’s risk of developing a parotid gland infection. These include:
- Dehydration: Reduced saliva production can increase the concentration of bacteria in the mouth, leading to infection.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Failure to maintain good oral hygiene practices can lead to an accumulation of bacteria in the mouth, which can then infect the parotid gland.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of essential nutrients can impair the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as Sjögren’s syndrome, can affect the salivary glands and increase the risk of infection.
- Surgery or Trauma: Any surgical procedure or trauma to the face or neck can increase the risk of parotid gland infection.
Symptoms of Parotid Gland Infection
The symptoms of a parotid gland infection can vary depending on the severity of the infection and the causative agent. Common symptoms include:
- Pain and Swelling: The parotid gland area becomes painful and swollen, which can be tender to the touch.
- Redness and Warmth: The skin over the affected gland may appear red and feel warm due to inflammation.
- Fever: The body may respond to the infection with a fever.
- Difficulty Opening the Mouth: In severe cases, the swelling and pain can make it difficult to open the mouth wide.
- Pus or Discharge: In cases of bacterial infection, there may be pus or discharge from the duct of the parotid gland into the mouth.
Treatment and Management
The treatment of parotid gland infection depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the symptoms. Here are some common approaches:
- Antibiotics: For bacterial infections, antibiotics are prescribed to eliminate the bacteria causing the infection.
- Pain Management: Medications such as pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs can help manage pain and reduce swelling.
- Hydration: Encouraging fluid intake to help keep the mouth moist and promote saliva production.
- Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the affected area can help relieve pain and encourage drainage.
- Rest and Recovery: Allowing the body time to rest and recover, especially in cases of viral infections, where the body’s immune response is crucial for fighting off the virus.
Prevention
Preventing parotid gland infections involves maintaining good oral hygiene, staying hydrated, and managing any underlying medical conditions effectively. Regular dental check-ups can help identify any issues early on, and vaccination against diseases like mumps can prevent viral parotitis.
Advanced Therapeutic Options
In cases where the infection is severe or does not respond to conventional treatments, advanced therapeutic options may be considered. These can include:
- Surgical Drainage: In cases of abscess formation, surgical drainage may be necessary to remove the accumulated pus.
- Antiviral Medications: For viral parotitis, antiviral medications may be prescribed, although their effectiveness can vary depending on the virus.
Conclusion
Parotid gland infections, while potentially serious, can often be managed effectively with appropriate treatment and self-care measures. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking medical attention when necessary are crucial steps in preventing complications and ensuring a full recovery. As with any health condition, prevention through good hygiene practices, a balanced diet, and maintaining overall health is key to reducing the risk of parotid gland infections.
What are the most common symptoms of a parotid gland infection?
+The most common symptoms include pain and swelling in the area of the parotid gland, redness and warmth of the skin, fever, difficulty opening the mouth, and in some cases, pus or discharge from the duct of the parotid gland into the mouth.
How can parotid gland infections be prevented?
+Prevention involves maintaining good oral hygiene, staying hydrated, managing underlying medical conditions effectively, and getting vaccinated against diseases like mumps to prevent viral parotitis.
What is the treatment for a parotid gland infection?
+Treatment depends on the cause and severity of the infection but can include antibiotics for bacterial infections, pain management, hydration, warm compresses, and in severe cases, surgical drainage or antiviral medications.