Parotid Infection Guide: Symptoms & Treatment
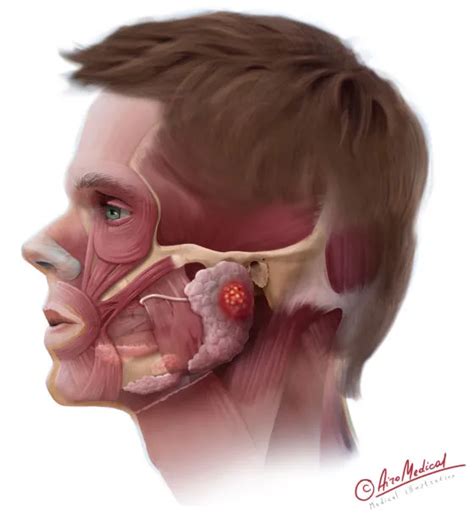
The parotid gland, one of the major salivary glands, plays a crucial role in the production of saliva, which aids in digestion and helps maintain oral health. However, like any other part of the body, the parotid gland can be susceptible to infections, leading to a condition known as parotitis. Parotitis can cause significant discomfort and, if left untreated, may lead to more serious complications. Understanding the symptoms and treatment options for parotid infections is essential for prompt and effective management.
Causes of Parotid Infection
Parotid infections, or parotitis, can be caused by a variety of factors including bacterial, viral, or fungal pathogens. The most common cause of acute parotitis is bacterial infection, often due to Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus. Viral infections, such as mumps, can also lead to parotitis, although vaccination has significantly reduced the incidence of mumps-related parotitis in many regions. Certain conditions, like dehydration, poor oral health, or blockage of the salivary ducts, can increase the risk of developing a parotid infection.
Symptoms of Parotid Infection
Recognizing the symptoms of a parotid infection is crucial for seeking timely medical attention. Common symptoms include:
- Swelling and Pain: The parotid gland becomes swollen and painful, which can be tender to the touch. The swelling may extend to the face and neck.
- Redness and Warmth: The area over the infected gland may appear red and feel warm due to inflammation.
- Fever: A low-grade fever can accompany the infection, especially if it’s bacterial.
- Discharge: In some cases, especially with bacterial infections, there may be a foul-tasting discharge from the duct of the parotid gland into the mouth.
- Difficulty Opening the Mouth: Swelling and pain can make it hard to open the mouth wide or chew.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: The lymph nodes in the neck may become swollen in response to the infection.
Diagnosis of Parotid Infection
Diagnosing a parotid infection involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and sometimes imaging tests or laboratory analyses. A healthcare provider will typically perform a thorough examination of the head and neck, checking for signs of swelling, redness, and tenderness. Imaging tests like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI might be ordered to assess the extent of the infection or to rule out other conditions, such as a tumor. Laboratory tests, including blood work or culture of any discharge, can help identify the causative agent and guide treatment.
Treatment of Parotid Infection
Treatment for parotid infections depends on the underlying cause and can range from supportive care for viral infections to antibiotics for bacterial infections. The primary goal is to manage symptoms, treat the infection, and prevent complications.
- Supportive Care: For viral infections, treatment is mainly supportive and includes measures to reduce symptoms such as pain and discomfort. This may involve applying warm compresses to the affected area, staying hydrated, and using over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Antibiotics: For bacterial infections, antibiotics are prescribed. It’s crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics as directed by the healthcare provider to ensure the infection is fully cleared.
- Surgical Intervention: In rare cases, especially where an abscess (a collection of pus) has formed, surgical drainage may be necessary to treat the infection.
Prevention of Parotid Infection
Preventing parotid infections involves maintaining good oral health, staying hydrated, and managing conditions that may increase the risk of infection. Regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene practices, and a balanced diet can help prevent blockages in the salivary ducts and reduce the risk of infection. Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption can also contribute to overall health and reduce the risk of various infections, including those affecting the salivary glands.
Complications of Untreated Parotid Infection
Untreated parotid infections can lead to several complications, including the formation of an abscess, which may require surgical drainage, and the spread of infection to other parts of the body. In severe cases, the infection can lead to sepsis, a life-threatening condition. Therefore, it’s vital to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
Early recognition and treatment of parotid infections can significantly improve outcomes. If you're experiencing symptoms of a parotid infection, such as swelling, pain, or difficulty opening your mouth, don't hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common causes of parotid infections?
+The most common causes include bacterial infections, often due to Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus, and viral infections, such as mumps. Other factors like dehydration, poor oral health, or blockage of the salivary ducts can also increase the risk.
How are parotid infections diagnosed?
+Diagnosis involves a physical examination, review of medical history, and sometimes imaging tests or laboratory analyses to identify the causative agent and assess the extent of the infection.
What is the treatment for a parotid infection?
+Treatment depends on the cause and can include supportive care for viral infections, antibiotics for bacterial infections, and in some cases, surgical intervention to drain an abscess.
How can I prevent parotid infections?
+Prevention involves maintaining good oral health through regular dental check-ups and proper hygiene practices, staying hydrated, and managing conditions that may increase the risk of infection.
What are the potential complications of untreated parotid infections?
+Untreated parotid infections can lead to complications such as abscess formation requiring surgical drainage and the spread of infection to other parts of the body, potentially leading to sepsis.
In conclusion, parotid infections, while potentially painful and disruptive, can be effectively managed with appropriate treatment and care. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for parotid infections empowers individuals to seek timely medical intervention and prevent complications. By prioritizing good oral health and overall wellness, individuals can reduce their risk of developing parotid infections and maintain the health of their salivary glands.